Pure Mathematics
Vol.07 No.04(2017), Article ID:21401,9
pages
10.12677/PM.2017.74040
Classical and Nonclassical Symmetry Classification of a Composite Type Equation
Yuexing Bai, Bilige Sudao*
College of Sciences, Inner Mongolia University of Technology, Hohhot Inner Mongolia

Received: Jun. 25th, 2017; accepted: Jul. 9th, 2017; published: Jul. 19th, 2017

ABSTRACT
In this paper, the classifications of classical and nonclassical symmetries to a composite type equation are determined. Firstly, the classification of classical symmetries to the composite equation is determined based on the differential characteristic set algorithm. Secondly, the classification of nonclassical symmetries for the composite equation is determined. First step, adding invariant surface condition and the original equation composed a new system of partial differential equations (PDEs), and the determining equations (DTEs) of symmetry to PDEs are determined by using the symbolic computation software Mathematica. Second step, the nonclassical symmetries are classified by calculating DTEs, so we can obtain the specific form of F(u) which is the parameter of the composite equation. Third step, the invariant solutions and exact solutions of the corresponding nonclassical symmetry are determined. The invariant solutions and exact solutions cannot be obtained by classical symmetry, so enrich the exact solutions of the composite equation.
Keywords:Classical Symmetry, Nonclassical Symmetry, Symmetry Classification, Differential Characteristic Set Algorithm, The Composite Equation
一类复合方程的古典和非古典对称分类
白月星,苏道毕力格*
内蒙古工业大学理学院,内蒙古 呼和浩特

收稿日期:2017年6月25日;录用日期:2017年7月9日;发布日期:2017年7月19日

摘 要
本文确定了一类复合方程的古典对称分类和非古典对称分类。首先,基于微分特征列集算法确定了复合方程的古典对称分类。其次,确定了复合方程的非古典对称的分类。第一步,添加不变曲面条件与原方程组成一个新的偏微分方程组(PDEs),利用符号计算软件Mathematica确定上面PDEs的对称对应的确定方程组(DTEs);第二步,根据所得的DTEs进行非古典对称分类,得到复合方程中参数F(u)的具体形式。第三步,确定了非古典对称所对应的不变解以及精确解。所得的不变解和精确解无法利用古典对称得到,所以丰富了复合方程的精确解。
关键词 :古典对称,非古典对称,对称分类,微分特征列集算法,复合方程

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
Lie对称是一个较为普适性的方法 [1] [2] ,且偏微分方程组(PDEs)对称已有了广泛的应用 [1] [2] [3] 。为了更好的运用对称方法,人们扩充古典对称概念,提出了各种广义对称概念,如非古典对称 [4] 、势对称 [5] 、近似对称 [6] 、条件对称 [7] 等。这些广义对称得到了广泛的应用,并且理论正在蓬勃发展。其中非古典对称的计算与古典对称不同之处是添加一个不变曲面条件,再计算确定方程组;并且非古典对称的确定方程组(DTEs)是非线性PDEs,所以非古典对称的确定仍然是目前具有挑战性的问题。然而通过获得非线性PDEs的非古典对称,扩充方程的古典对称依然是目前研究的热门课题。目前国内外研究者对非古典对称进行了一些研究,推动了其发展 [8] - [13] 。
本文将确定一类复合方程的古典对称分类和非古典对称分类。考虑下面的一类复合方程
 (1)
(1)
其中 为常数。在该方程中函数
为常数。在该方程中函数 取不同表达式时,得到一些重要的偏微分方程,如:当
取不同表达式时,得到一些重要的偏微分方程,如:当
时,方程(1)变为Burgers方程 [14] ;当 时,方程(1)变为BBM-Burgers方程
时,方程(1)变为BBM-Burgers方程 [15] 和RLW-Burgers方程
[15] 和RLW-Burgers方程 的特殊情况
的特殊情况 [16] 。所以对该方程对称分类的研究具有很重要的物理意义。
[16] 。所以对该方程对称分类的研究具有很重要的物理意义。
2. 复合方程的古典和非古典对称分类
在线性变换
 (2)
(2)
的作用下方程(1)变成
 (3)
(3)
其中 ,
,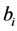 是任意常数,并且
是任意常数,并且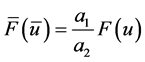 ,即方程(1)在变换(2)下形式不变。所以称(2)为方程(1)的等价变换。因此在对称分类的计算中可以应用
,即方程(1)在变换(2)下形式不变。所以称(2)为方程(1)的等价变换。因此在对称分类的计算中可以应用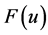 的伸缩群和关于
的伸缩群和关于 的平移群,
的平移群,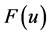 表示成其典则坐标。
表示成其典则坐标。
2.1. 古典对称分类
设方程(1)的对称对应的无穷小生成元为
 (4)
(4)
根据Lie算法,我们得到X的确定方程组 ,其中
,其中
 (5)
(5)
2.1.1. 主对称
当 为任意函数时,确定方程组变为
为任意函数时,确定方程组变为
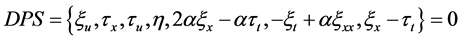 (6)
(6)
解上面的方程组,很容易得到
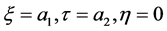 (7)
(7)
其中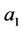 ,
,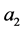 为任意常数,所以主对称为
为任意常数,所以主对称为
 (8)
(8)
2.1.2. 扩充对称
根据确定含参数PDEs的完全对称分类微分特征列集算法 [17] ,得到分类方程为

由此得到下面的古典对称分类结果,见表1。
其中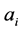 是任意常数。
是任意常数。
2.2. 非古典对称分类
假设方程(1)的非古典对称对应的无穷小生成元为(4)的形式。方程(1)对应的不变曲面条件为
 (9)
(9)
在文中分别讨论 与
与 两种情况。
两种情况。
当 时,不失一般性,设
时,不失一般性,设 ,根据非古典对称的理论得到确定方程组
,根据非古典对称的理论得到确定方程组
 (10)
(10)
当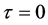 时,不失一般性,设
时,不失一般性,设 ,根据非古典对称的理论得到确定方程组
,根据非古典对称的理论得到确定方程组
Table 1. Classical symmetry classification of composite Equation (1)
表1. 复合方程(1)的古典对称分类
 . (11)
. (11)
2.2.1. 的情况
的情况
情形I:当 为任意函数时,确定方程组(10)变为
为任意函数时,确定方程组(10)变为
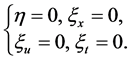 (12)
(12)
容易得到 ,
, ,其中
,其中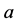 为任意常数。与该复合方程的古典对称对比知这种情况不具有非古典对称。
为任意常数。与该复合方程的古典对称对比知这种情况不具有非古典对称。
情形II:当 为具体函数时,为了确定函数
为具体函数时,为了确定函数 ,首先从(10)式的第四个方程得到
,首先从(10)式的第四个方程得到 ,将其代入(10)式,化简得到
,将其代入(10)式,化简得到
 (13)
(13)
在(13)中,我们要考虑在 的情况。
的情况。
(II.1) 当 ,
,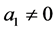 时,化简(13)得
时,化简(13)得
 (14)
(14)
由(14)的最后一个式子解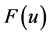 有
有 ,因
,因 是只关于
是只关于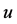 的函数,故其中不含有关于
的函数,故其中不含有关于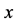 ,
, 的函数,因此
的函数,因此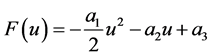 ,其中
,其中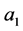 ,
,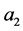 ,
, 为任意常数。通过计算得
为任意常数。通过计算得
 (15)
(15)
(1) 取 ,
, ,
, ,原复合方程变为Burgers方程 [14] ,由表1知该情况具有非古典对称。
,原复合方程变为Burgers方程 [14] ,由表1知该情况具有非古典对称。
(2) 取 ,
, ,
, ,原复合方程变为BBM-Burgers方程
,原复合方程变为BBM-Burgers方程 [15] ,由表1知该情况具有非古典对称。
[15] ,由表1知该情况具有非古典对称。
(3) 取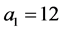 ,
, ,
,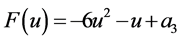 ,原复合方程变为RLW-Burgers方程
,原复合方程变为RLW-Burgers方程 [16] ,由表1知该情况具有非古典对称。
[16] ,由表1知该情况具有非古典对称。
(II.2) 当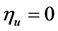 ,
, 时,化简(14)得
时,化简(14)得
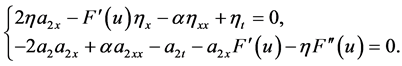 (16)
(16)
(II.2.1) 若 ,由(16)中的第一式得
,由(16)中的第一式得 ,因
,因 是
是 的函数,知
的函数,知 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, 。令
。令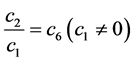 ,由(16)中的第二式得
,由(16)中的第二式得 ,
, 。其中
。其中 ,
, ,
,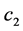 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, 是任意常数,且
是任意常数,且 ,最后我们得到
,最后我们得到
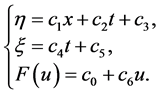 (17)
(17)
通过表1知该情况没有非古典对称。
(II.2.2) 若 ,化简(14)得到
,化简(14)得到
 (18)
(18)
通过计算,得该情形没有非古典对称。
(II.3) ,根据(10)的化简知必须满足条件
,根据(10)的化简知必须满足条件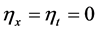 ,化简(10)得到
,化简(10)得到
 (19)
(19)
由(19)的第一个式子知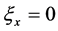 ,由(19)的最后式子知
,由(19)的最后式子知 ,故(19)化简为
,故(19)化简为
 (20)
(20)
(II.3.1) 若 ,设
,设 ,
, ,化简(20)得到
,化简(20)得到
 ,
,
其中 ,
, ,
, ,
,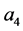 ,
, ,
, 是任意常数。通过计算得
是任意常数。通过计算得
 (21)
(21)
当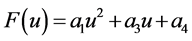 对应的古典对称的无穷小生成元为
对应的古典对称的无穷小生成元为
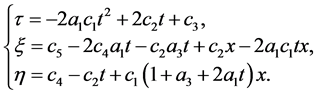 (22)
(22)
通过比较知该情况具有非古典对称。
(II.3.2) 若 ,计算得
,计算得 ,
, ,化简(20)有
,化简(20)有

通过计算得
 (23)
(23)
其中 ,
,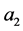 ,
, ,
, ,
,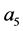 ,
, 是任意常数。当
是任意常数。当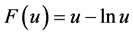 ,即取
,即取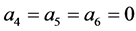 ,
, 对应的古典对称的无穷小生成元为
对应的古典对称的无穷小生成元为
 (24)
(24)
其中 ,
, ,
,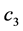 是任意常数。通过比较知该情况没有非古典对称。
是任意常数。通过比较知该情况没有非古典对称。
从上面的分析,我们得到了方程(1)的非古典对称分类,具体结果列表如表2。
其中 ,
, 是任意常数。
是任意常数。
2.2.2. 的情况
的情况
同样,我们通过求解方程(11),得到了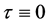 情况的方程(1)的非古典对称分类,具体结果列表如表3。
情况的方程(1)的非古典对称分类,具体结果列表如表3。
3. 不变解
3.1. 非古典对称对应的不变解
下面计算方程(1)的非古典对称对应的不变解。
(1) 当 ,
,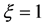 ,
,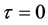 ,
, 时,复合方程变为
时,复合方程变为
Table 2. Nonclassical symmetry classification of composite Equation (1)
表2. 复合方程(1)的非古典对称分类
Table 3. Nonclassical symmetry classification, of composite Equation (1)
表3. 复合方程(1)的非古典对称分类 ,
, 
 , (25)
, (25)
并且 的特征方程为
的特征方程为
 . (26)
. (26)
由特征方程(26)得到不变量 ,并且由
,并且由 ,得
,得 ,将其代入方程(25),解得
,将其代入方程(25),解得 ,即可得到方程(25)的不变解
,即可得到方程(25)的不变解 。
。
(2) 当 ,
, ,
, ,
, 时,复合方程变为
时,复合方程变为
 , (27)
, (27)
并且 的特征方程为
的特征方程为
 (28)
(28)
由特征方程(28)得到不变量 ,并且由
,并且由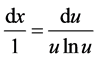 ,得
,得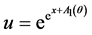 ,将其代入方程(27),解得
,将其代入方程(27),解得
 ,即可得到方程(27)的不变解
,即可得到方程(27)的不变解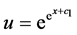 。
。
(3) 当 ,
,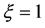 ,
,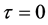 ,
, 时,复合方程变为
时,复合方程变为
 (29)
(29)
并且对称 的特征方程为
的特征方程为
 (30)
(30)
由特征方程(30)得到不变量 ,并且由
,并且由 ,得
,得 ,将其代入方程(29),解得
,将其代入方程(29),解得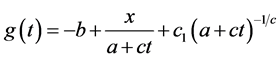 ,故可得到方程(29)的不变解
,故可得到方程(29)的不变解 。
。
注:由于篇幅所限,在本文中省略了其它 形式的方程的不变解。
形式的方程的不变解。
3.2. 精确解
1、下面首先确定当 时,古典对称
时,古典对称 对应的Lie变换群,
对应的Lie变换群,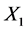
对应的初值问题为
 (31)
(31)
通过求解(31),得到对应的单参数Lie变换群如下:
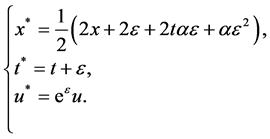 (32)
(32)
我们将Lie变换群(32)作用于该情况的不变解 ,得到下面的新解
,得到下面的新解
 .
.
2、下面首先确定当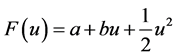 时,古典对称
时,古典对称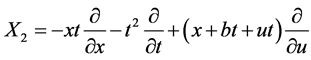 对应的Lie变换群为:
对应的Lie变换群为:
 (33)
(33)
将Lie变换群(33)作用于该情况的不变解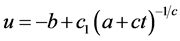 ,得到
,得到
 .
.
以上得到的精确解都是对应方程的新解,而且这些解是不能通过古典对称来得到的,因为篇幅有限,其它情况在本文中不进行讨论。
4. 本文结论
本文通过应用古典对称和非古典对称理论,借助于微分特征列集算法和Mathematica软件,对一类复合方程进行了古典对称和非古典对称分类。最后我们确定了非古典对称所对应的不变解以及精确解,所得的不变解和精确解无法利用古典对称得到。本文的优点是在分类过程中发现了8种允许非古典对称的函数 得到的结果丰富了该方程的对称和精确解。
得到的结果丰富了该方程的对称和精确解。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(11661060, 11571008)。
文章引用
白月星,苏道毕力格. 一类复合方程的古典和非古典对称分类
Classical and Nonclassical Symmetry Classification of a Composite Type Equation[J]. 理论数学, 2017, 07(04): 301-309. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/PM.2017.74040
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Bluman, G.W. and Kumei, S. (1989) Symmetries and Differential Equations. Spring-Verlag, New York Berlin.
- 2. Olver, P.J. (1993) Applications of Lie Groups to Differential Equations. 2nd Edition, Spring-Verlag, New York.
- 3. Bluman, G.W. and Cole, J.D. (2010) The General Similarity Solutions of the Heat Equations. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 66, 181-199.
- 4. Bluman, G.W. and Cole, J.D. (1969) The General Similarity Solution of the Heat Equation. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 18, 1025-1042.
- 5. Huang, Q., Qu, C.Z. and Zhdanov, R. (2011) Group-Theoretical Framework for Potential Symmetries of Evolution Equations. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 52, 023514. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3554692
- 6. 吴琼, 李德生. 在广义条件对称下的一类非线性扩散方程的精确解[J]. 理论数学, 2013, 3(5): 289-294.
- 7. 惠小健. 扩散方程的条件对称及其精确解[D]: [硕士学位论文]. 西安: 西北大学, 2007.
- 8. 特木尔朝鲁, 额尔敦布和, 夏铁成, 等. 具源项的波动方程的非古典对称[J]. 数学年刊A辑(中文版), 2012, 33(2): 193-204.
- 9. Yun, Y. and Temuer, C. (2015) Classical and Nonclassical Symmetry Classifications of Nonlinear Wave Equation with Dissipation. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 36, 365-378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-1910-6
- 10. Wan, W.T., Chen, Y., Wan, W.T., et al. (2009) A Note on Non-Classical Symmetries of a Class of Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations and Compatibility. Communications in Theoretical Physics, 52, 398.
- 11. Xin, X.P., Liu, Y.T. and Liu, X.Q. (2016) Nonlocal Symmetries, Exact Solutions and Conservation Laws of the Coupled Hirota Equations. Applied Mathematics Letters, 55, 63-71.
- 12. Arrigo, D.J., Ekrut, D.A., Fliss, J.R., et al. (2010) Non-Classical Symmetries of a Class of Burgers’ Systems. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 371, 813-820.
- 13. Zhang, Z. and Chen, Y. (2010) Classical and Nonclassical Symmetries Analysis for Initial Value Problems. Physics Letters A, 374, 1117-1120.
- 14. Estevez, P.G. and Gordoa, P.R. (1994) Nonclassical Symmetries and the Singular Manifold Method: The Burgers Equation. Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, 99, 562-566. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01016139
- 15. 苏道毕力格, 特木尔朝鲁. 用吴方法计算BBM-Burgers方程的势对称及其不变解[J]. 内蒙古大学学报自然科学版, 2006, 37(4): 366-373.
- 16. 鲍春玲, 苏道毕力格, 韩雁清. RLW-Burgers方程的势对称及其精确解[J]. 应用数学进展, 2016, 5(1): 112-120.
- 17. 特木尔朝鲁, 白玉山. 基于吴方法的确定和分类(偏)微分方程古典和非古典对称新算法理论[J]. 中国科学: 数学, 2010, 4: 331-348.
