Advances in Clinical Medicine
Vol.
13
No.
11
(
2023
), Article ID:
75491
,
4
pages
10.12677/ACM.2023.13112505
鼻腔上颌窦嗜酸性乳头状瘤1例并文献复习
李杨1,王亚婷2*
1济宁医学院临床医学院,山东 济宁
2济宁市第一人民医院耳鼻咽喉科,山东 济宁
收稿日期:2023年10月16日;录用日期:2023年11月10日;发布日期:2023年11月17日

摘要
目的:探讨鼻嗜酸性乳头状瘤临床及病理学特点,提高对该疾病的认识。方法:回顾性分析1例罕见的鼻嗜酸性乳头状瘤患者的临床及病理学特点并进行文献复习。结果:该病在影像学表现无特异性,术中完整切除肿物,随访1年未见复发。结论:鼻嗜酸性细胞乳头状瘤是一种罕见的鼻黏膜良性肿瘤,易误诊,具有潜在恶变可能,彻底的手术治疗及术后随访至关重要。
关键词
鼻腔,鼻窦,乳头状瘤,病例报告

One Case of Oncocytic Schneiderian Papilloma of the Maxillary Sinus and Literature Review
Yang Li1, Yating Wang2*
1School of Clinical Medicine, Jining Medical University, Jining Shandong
2Department of Otolaryngology, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining Shandong
Received: Oct. 16th, 2023; accepted: Nov. 10th, 2023; published: Nov. 17th, 2023

ABSTRACT
Objective: To explore the clinical and pathological characteristics of oncocytic schneiderian papilloma and improve understanding of the disease. Methods: Retrospective analysis of the clinical and pathological characteristics of a rare case of oncocytic schneiderian papilloma in one patient and literature review. Results: The disease has no specific imaging features. The tumor was completely removed during surgery and no recurrence was observed during a one-year follow-up. Conclusion: Oncocytic schneiderian papilloma is a rare benign tumor of the nasal mucosa that is easily misdiagnosed and has potential malignant transformation. Thorough surgical treatment and postoperative follow-up are crucial.
Keywords:Nasal Cavity, Sinus, Papilloma, Case Report

Copyright © 2023 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 病例报告
患者男,60岁,因左涕中带血1月余于2022年2月20日来我院就诊治疗。患者1年前无明显诱因出现左鼻涕中带血,偶有鼻痒,喷嚏。专科检查:双鼻腔黏膜慢性充血,双下鼻甲肿大,鼻中隔左偏。副鼻窦CT示副鼻窦炎症,左侧息肉待排,右侧上颌窦囊肿可能(见图1)。鼻内镜示左鼻肿物(息肉?)、鼻炎(见图2)。2022-02-21在全身麻醉下行鼻内窥镜下左侧上颌窦、筛窦开放 + 左侧鼻腔鼻窦肿物切除 + 鼻中隔成形术。术中见左侧中鼻道内见分叶状新生物,来源于左侧上颌窦,开放并扩大左侧上颌窦口,开放左侧前后组筛窦,见筛窦粘膜水肿息肉样变,切除左侧鼻腔及上颌窦内肿物,见左侧上颌窦肿物根蒂位于上颌窦内侧壁,根蒂处骨质增生,予以刮除增生处骨质表面粘膜,生理盐水冲洗术腔,见左上颌窦内无肿物残留。术后病理示:(左鼻腔鼻窦病变组织)嗜酸性乳头状瘤(见图3)。
2. 讨论
起源于鼻黏膜上皮的Schneiderian膜的乳头瘤,也称为施奈德乳头状瘤,属良性肿瘤。1971年,Hyams 等 [1] 将其分型为内翻性、真菌样和柱状细胞型。Barnes等 [2] 根据柱状细胞乳头状瘤的颗粒状嗜酸性细胞质特点,将其称为嗜酸性乳头状瘤。

Figure 1. CT of oncocytic schneiderian papilloma of the maxillary sinu
图1. 鼻腔上颌窦嗜酸性乳头状瘤的CT
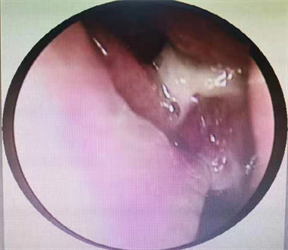
Figure 2. Nasal endoscope of oncocytic schneiderian papilloma of the maxillary sinu
图2. 鼻腔嗜酸性细胞乳头状瘤鼻内镜
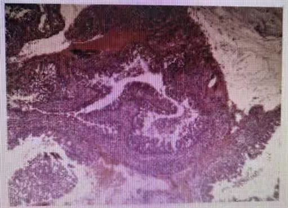
Figure 3. Pathology of oncocytic schneiderian papilloma of the maxillary sinu
图3. 鼻腔上颌窦嗜酸性细胞乳头状瘤组织病理学
根据WHO (1991年)上呼吸道肿瘤分类方法 [3] 分为3种组织病理类型:外生型或蕈状乳头状瘤(exophytic or fungiform papilloma, EP);内翻型乳头状瘤(inverted papilloma, IP);嗜酸性细胞乳头状瘤(oncocytic schneiderian papilloma, OSP)。其中以OSP最为少见 [4] ,约占3%~5%,国内报道少见。
1938年Ringertz等 [5] 首次报道了SP的特殊临床表现,即具有潜在的复发和癌变倾向。具有多次手术史及病史较长的IP患者易发生恶性转化。鼻乳头状瘤的发病机制目前尚不明确,Robinson、Roh等推测IP与与黏膜炎症反应有关 [6] [7] 。鼻息肉病和IP的频繁共同发生 [8] 。研究表明IP中有显着的炎性细胞浸润,特别是在低级别IP中。此外,鼻息肉病和IP的共同原发部位是中鼻道。多数文献报道认为人乳头瘤病毒HPV (human papilloma virus)感染与鼻乳头状瘤的发生密切相关。一般认为IP及EP与HPV6及HPV11感染有关,但目前研究未发现OSP与HPV感染有明显相关性。OSP发病年龄多在50岁以上,年轻患者少见,无明显性别差异 [9] 。
OSP多为单侧发病,临床表现与其他鼻腔鼻窦乳头状瘤无明显差异,与其发病部位及肿物大小有关,多为单侧鼻塞,流涕,偶有涕中带血,嗅觉改变及头痛等,但好发部位有所差别,IP好发于鼻腔的外侧壁、上颌窦、筛窦,较少发生于额窦、蝶窦及鼻中隔,OSP好发于鼻腔外侧壁、上颌窦及筛窦,根据过往文献报道,其中上颌窦最为多见 [10] 。也有报道发病于鼻咽部的OSP,推测是:(1) 鼻窦OSP直接延伸至咽鼓管所致;(2) 胚胎发育过程中,外胚层衍生的Schneiderian膜发生异位迁移,成为鼓室和咽鼓管部的OSP [11] 。
鼻窦CT及MRI检查可显示病变范围,观察有无骨质破坏,提示病变性质,为手术治疗提供切除依据,但OSP的影像学表现与其他鼻乳头状瘤相比无特异性,故本病的确诊依靠病理学诊断,组织学表现为复层柱状上皮形成的乳头状结构,胞质内有大量的嗜酸性颗粒,上皮内可见微脓肿,其中充满黏液和中性粒细胞 [12] 。
手术治疗为OSP首选的治疗方法。随诊鼻内镜技术的成熟,鼻内镜手术治疗以其安全、微创等优点,常作为首选手术方式。基于影像学检查及术中探查结果,应将病变肿物及其周围水肿充血的粘膜一并彻底清除,从而降低复发及恶变的风险。
OSP与IP一样,尽管组织学上为良性肿瘤,但都存在复发性、组织破坏性及恶变性可能,病灶可侵犯邻近组织,甚至扩散至眼眶及颅内,有报道称OSP的复发率及恶变率较IP更高 [13] ,常见的癌变类型为鳞状细胞癌,此外还有粘液表皮样癌,鼻腔鼻窦未分化癌 [14] 。因此术中要完全切除肿物,尽量降低其复发及恶变几率,对术中怀疑恶变的可以行术中冰冻,对于合并癌性病变的患者,建议术后联合放疗治疗。术后注意定期随访,本例患者鼻内镜下完全切除肿物,已复查随访一年,无复发及转移。
文章引用
李 杨,王亚婷. 鼻腔上颌窦嗜酸性乳头状瘤1例并文献复习
One Case of Oncocytic Schneiderian Papilloma of the Maxillary Sinus and Literature Review[J]. 临床医学进展, 2023, 13(11): 17864-17867. https://doi.org/10.12677/ACM.2023.13112505
参考文献
- 1. Hyams, V.J. (1971) Papillomas of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses. A Clinicopathological Study of 315 Cases. Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology, 80, 192-206. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348947108000205
- 2. Barnes, L. and Bedetti, C. (1984) Oncocytic Schneiderian Pap-illoma: A Reappraisal of Cylindrical Cell Papilloma of the Sinonasal Tract. Human Pathology, 15, 344-351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0046-8177(84)80033-7
- 3. Shanmugaratnam, K. and Sobin, L.H. (1993) The World Health Organization Histological Classification of Tumours of the Upper Respiratory Tract and Ear. A Commentary on the Second Edition. Cancer, 71, 2689-2697. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19930415)71:8<2689::AID-CNCR2820710843>3.0.CO;2-H
- 4. Liu, C.Y., Tsai, T.L., Hsu, C.Y., et al. (2004) Oncocytic Schneiderian Papilloma. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association, 67, 255-257.
- 5. Ringertz, N. (1938) Pathology of Malignant Tumors Arising in the Nasal and Paranasal Cavities and Maxilla. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 27, 31-42.
- 6. Robinson, S., Tan, L.W., James, C., Karakousis, A. and Wormald, P.J. (2006) Do Nasal Polyps and Inverted Papilloma Have Similar Disorders in Cell Cycle Regulation. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy, 25, A195-A196.
- 7. Roh, H.J., Procop, G.W., Batra, P.S., Citardi, M.J. and Lanza, D.C. (2004) Inflammation and the Pathogenesis of Inverted Papilloma. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy, 18, 65-74. https://doi.org/10.1177/194589240401800201
- 8. Orlandi, R.R., Rubin, A., Terrell, J.E., Anzai, Y., Bugdaj, M. and Lanza, D.C. (2002) Sinus Inflammation Associated with Contralateral Inverted Papilloma. American Journal of Rhi-nology & Allergy, 16, 91-95. https://doi.org/10.1177/194589240201600204
- 9. Olusina, D., Nzegwu, M. and Okoroafor, I. (2008) Oncocytic Schneiderian Papilloma Occurring in a Young Nigerian Male: A Case Report. Annals of African Medicine, 7, 91-93. https://doi.org/10.4103/1596-3519.55672
- 10. Vorasubin, N., Vira, D., Suh, J.D., et al. (2012) Schneiderian Pap-illomas: Comparative Review of Exophytic, Oncocytic, and Inverted Types. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy, 27, 287-292. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2013.27.3904
- 11. 王琴, 李勇, 何文斌, 等. 鼻咽部嗜酸性细胞乳头状瘤1例[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2023, 30(1): 62-63. https://doi.org/10.16066/j.1672-7002.2023.01.016
- 12. 刘红刚, 高岩. 头颈部肿瘤病理学和遗传学(WHO肿瘤分类) [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006.
- 13. Chrysovergis, A., Paschalidis, J., Michaels, L., et al. (2011) Naso-pharyngeal Cylindrical Cell Papilloma. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, 125, 86-88. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215110002094
- 14. Terada, T. (2012) Malignant Transformation of Exophytic Schneiderian papilloma of the Nasal Cavity. Pathology International, 62, 199-203. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1827.2012.02795.x
NOTES
*通讯作者。