Applied Physics
Vol.
10
No.
05
(
2020
), Article ID:
35439
,
5
pages
10.12677/APP.2020.105035
The Eigen-Charge Distribution of Plasmon in Two Dimensional Rectangular Atomic Clusters
Hongjie Xue*, Jiahao Li, Yangjie Wang, Facheng Jin, Limin Wei, Xiaomei Wang
School of Science, Xi’an Aeronautical University, Xi’an Shannxi

Received: Apr. 16th, 2020; accepted: Apr. 30th, 2020; published: May 7th, 2020

ABSTRACT
In this paper, we present a new method to find the plasmon in two dimensional rectangular atomic clusters. Using this method, we can overcome the disadvantage that the results are easily affected by the external field when we are looking for plasmon modes. In addition, the eigen-charge distributions of the plasmon is also provided, which can provide inspiration for plasmons excitation.
Keywords:Plasmons, Eigen-Charge, The Free-Electron Gas Mode

二维矩形原子团簇中等离激元的本征电荷分布
薛红杰*,李嘉豪,王杨杰,金发成,魏丽敏,王小梅
西安航空学院,理学院,陕西 西安

收稿日期:2020年4月16日;录用日期:2020年4月30日;发布日期:2020年5月7日

摘 要
本文提供了在矩形原子团簇中查找等离激元的新方法。利用此方法可以克服目前在寻找等离激元模式时,结果易受外场影响的缺点。此外,本文还提供了等离激元的本征电荷分布。通过分析本征电荷分布,可以为等离激元的激发方案提供启示。
关键词 :等离激元,本征电荷,自由电子气体模型

Copyright © 2020 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
表面等离激元是局域在材料界面纳米尺度内的多电子激发,其有很强的局域场增强特点,能够突破衍射极限,能通过改变其尺形状、周围环境、激发条件等对其共振频率进行调制。表面等离激元目前已被广泛的应用于纳米激光器 [1] [2]、纳米光刻 [3] [4]、光学天线 [5]、生物探测和传感技术 [6] 等领域。
目前,在原子团簇中,等离激元的研究主要是借助系统对外界的各种响应(如:偶极响应、四极响应、能量吸收谱)来查找原子团簇可维持的等离激元模式 [7] [8] [9] [10]。然而,这种方法有一个明显的不足之处,这就是所得结果会受到外加电场的影响,例如:在原子团簇中,等离激元的激发会受到外加电场及方向的影响,一些等离激元会因没有被激发而不能被发现。这个时候,通过新的合适的方法来计算等离激元是很有必要的。
本文中,我们在自由电子气体模型下,基于线性响应理论,推导了等离激元振荡的本征方程,并通过本征方程和电荷分布研究了系统可维持的等离激元模式。这个方法的优点是理论上可以找出系统的所有等离激元模式。
2. 等离激元的本征方程
在自由电子气体模型下,二维矩形原子团簇(见图1所示)中电子的本征函数和本征能量可以分别写成
Figure 1. Two dimensional rectangular atomic cluster model
图1. 二维矩形原子团簇模型
(1)
(2)
这里a代表虚拟晶格常数, 和 分别代表矩形原子团簇的长度和宽度, 是电子的质量, 是普朗特常数, ,。
根据线性响应理论,外界扰动在系统内所产生的电荷密度可以表示成:
(3)
其中, 是费米分布函数, 是系统未受到扰动时电子的本征波函数, 是系统未受到扰动时电子的本征能量。 是系统受到的扰动电势,其可以看做是由外加电势 和诱导电势 两部分组成,即
(4)
将电荷密度的表达式(3)代入电荷密度和电势之间的关系式
(5)
可以得到:
(6)
这里, 。(6)式两边同乘以 并对整个原子团簇空间积分,则有
(7)
令
(8)
则(7)式可简写为:
(9)
设外加电势 为零,则 ,可以得到诱导电势 的本征方程:
(10)
等离激元的频率可通过令上式中的系数行列式为零而确定,即:
(11)
3. 等离激元的本征频率查找
在实际计算中,由于电子存在散射,虚部 (见8式)是不可能为零的,因为 表示电子在振荡过程中不会受到阻尼,等离激元的寿命为无限大,这在实际中是不可能出现的。所以我们要取一个不为零的 ,以表示电子在振荡过程中有阻尼存在及等离激元寿命的有限性。这样,本征函数 一般情况下都会是个复函数。在求等离激元的过程中既要保证本征函数的实部 为零,又要保证本征函数的虚部 。正因如此, 会在等离激元频率处显示一个有限峰,等离激元的频率可以借此峰来寻找(如图2所示,这里 。
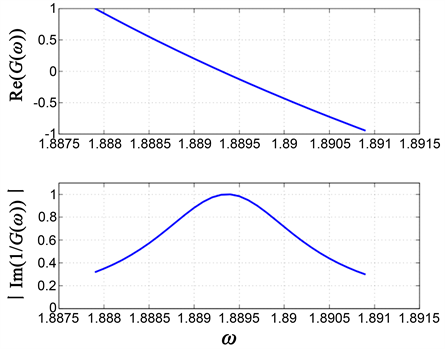
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of searching for plasmon mode
图2. 等离激元模式查找示意图
4. 等离激元的本征电荷分布
当等离激元的本征频率被获得后,利用(3)式可获得等离激元的本征电荷分布。在图3中,我们展示了原子团簇( )中一些等离激元模式的本征电荷分布。在图3中, 是以 为单位, 是, 是金的晶格常数, 代表电子的质量, 。

Figure 3. The eigen-charge distribution of plasmon
图3. 等离激元本征电荷分布
5. 小结
本文主要做了如下工作:1) 推导了矩形原子团簇中等离激元的本征方程;2) 给出了利用本征方程获得等离激元频率的方法,利用这种方法,在理论上可以找到系统所有的等离激元模式;3) 利用本征电荷分布形象地展示了等离激元。后续工作,将利用获得的等离激元模式,绘制等离激元的色散图,并将其与经典的色散图进行对比。
基金项目
国家自然基金理论物理专项(11847146,11947080),陕西省科技厅项目(2018JQ1091),西安航空学院大创项目(DCX2019039)。
文章引用
薛红杰,李嘉豪,王杨杰,金发成,魏丽敏,王小梅. 二维矩形原子团簇中等离激元的本征电荷分布
The Eigen-Charge Distribution of Plasmon in Two Dimensional Rectangular Atomic Clusters[J]. 应用物理, 2020, 10(05): 276-280. https://doi.org/10.12677/APP.2020.105035
参考文献
- 1. Berini, P. and De Leon, I. (2012) Surface Plasmon-Polariton Amplifiers and Lasers. Nature Photonics, 6, 16. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.285
- 2. Bergman, D.J. and Stockman, M.I. (2003) Surface Plasmon Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation: Quantum Generation of Coherent Surface Plasmons in Nanosystems. Physical Review Letters, 90, Article ID: 027402. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.027402
- 3. Srituravanich, W., Fang, N., Sun, C., Luo, Q. and Zhang, X. (2004) Plasmonic Nanolithography. Nano Letters, 4, 1085-1088. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl049573q
- 4. Fang, N., Lee, H., Sun, C. and Zhang, X. (2005) Sub-Diffraction-Limited Optical Imaging with a Silver Superlens. Science, 308, 534-537. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1108759
- 5. Giannini, V., Fernández-Domínguez, A.I., Heck, S.C. and Maier, S.A. (2011) Plasmonic Nanoantennas: Fundamentals and Their Use in Controlling the Radiative Properties of Nanoemitters. Chemical Reviews, 111, 3888-3912. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1002672
- 6. Anker, J.N., Hall, W.P., Lyandres, O., Shah, N.C., Zhao, J. and Van Duyne, R.P. (2008) Biosensing with Plasmonic Nanosensors. Nature Materials, 7, 442-453. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814287005_0032
- 7. 尹海峰, 毛力. 一维原子链局域等离激元的非线性激发[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(8): 321-327.
- 8. De Abajo, F.G. (2010) Optical Excitations in Electron Microscopy. Reviews of Modern Physics, 82, 209. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.82.209
- 9. Wu, R.L., Yu, Y., Xue, H.J., Hu, H.F. and Liu, Q.H. (2014) Dipole and Quadrupole Plasmon in Confined Quasi-One-Dimensional Electron Gas Systems. Physics Letters A, 378, 2995-3000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2014.08.013
- 10. Xue, H.J., Hao, D.P, Zhang, M. and Wang, X.M. (2017) Plasmon Excitations in the Dimers Formed by Atom Chains. Physica E, 86, 292-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2016.10.030
NOTES
*通讯作者。