Dynamical Systems and Control
Vol.06 No.04(2017), Article ID:22082,6
pages
10.12677/DSC.2017.64020
Quasi-Synchronization of Discrete-Time Networks with Parameter Mismatches under Impulsive Control
*通讯作者。
Jiamin Li, Honghua Bin, Zhenkun Huang*
School of Science, Jimei University, Xiamen Fujian

Received: Aug. 15th, 2017; accepted: Sep. 8th, 2017; published: Sep. 18th, 2017

ABSTRACT
This paper deals with quasi-synchronization problem of neural networks for a class of discrete-time networks with parameter mismatches under impulsive control. By using the direct Lyapunov method, the synchronization criteria for the discrete neural networks with parameter mismatches are obtained at the first time.
Keywords:Quasi-Synchronization, Discrete-Time Networks, Parameter Mismatches, Impulsive Control
具有不匹配参数的脉冲离散网络准同步
李嘉敏,宾红华,黄振坤*
集美大学理学院,福建 厦门

收稿日期:2017年8月15日;录用日期:2017年9月8日;发布日期:2017年9月18日

摘 要
本文研究了一类具有不匹配参数的离散神经网络在脉冲控制下的准同步问题。通过运用直接Lyapunov函数方法,文章首次给出了含不匹配参数的离散神经网络准同步条件。
关键词 :准同步,离散神经网络,参数不匹配,脉冲控制

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
近年来,网络间的同步问题受到了诸多领域学者的关注。同步作为网络之间的一个重要特征,在很多方面都有着重要的应用,如文献 [1] - [6] 。不同于其他类型的同步,准同步是由于系统之间参数不匹配而形成的一种特殊同步,其所有的系统误差会同步到一个小邻域的范围中,而非同步到零 [4] [5] [6] 。
在过去的几十年当中,离散网络在诸多领域都有广泛应用,如图像处理,时间序列分析,二次优化问题和系统识别。因此,离散情形下的神经网络一直是很热点的研究领域之一 [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] ,其中的同步现象更是引起了极大关注。但是如果网络自身不能实现状态同步,就需要采用一定的控制策略来达到同步,与连续时间的控制方法相比较,脉冲控制作为一种经典的控制方法,其结构简单,控制成本低,得到了众多研究者的青睐。 [10] 则首次采用脉冲控制方法研究了含有时滞影响的离散系统同步。文献 [7] 研究了离散情形下具有变时滞和随机扰动的驱动-响应网络同步问题。
受上述文献启发,由参数不匹配导致的离散网络脉冲准同步问题尚未被研究,因此本文的目的就在于探讨离散时间情形下采用脉冲控制策略使网络达到准同步的充分条件。通过应用直接Lyapunov函数方法和矩阵正交分解理论,本文得到了一个使离散网络达到准同步的误差域。文章其余结构如下,第二部分介绍了所研究的模型以及一些预备知识,第三部分给出了主要结果,第四部分作简要总结。
2. 预备知识及模型简介
在本文中,考虑 个节点的离散耦合神经网络模型,
个节点的离散耦合神经网络模型,
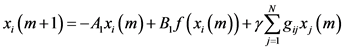 ,
, (1)
(1)
其中 ,
,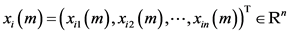 表示第
表示第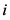 个节点的状态向量,
个节点的状态向量,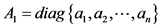 ,
,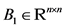 ,
,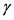 表示耦合强度
表示耦合强度
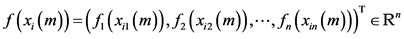 ;
;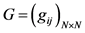 是外部耦合矩阵,若第
是外部耦合矩阵,若第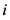 个节点和
个节点和
第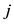 个节点有连接,则
个节点有连接,则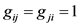 ,否则,
,否则,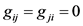 ,对角线元素
,对角线元素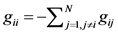 。离散网络(1)的初值条件为
。离散网络(1)的初值条件为 。
。
与离散网络(1)含有不匹配参数的孤立点系统为
 , (2)
, (2)
其中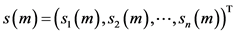 ,初值条件为
,初值条件为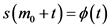 。假设存在一个正常数
。假设存在一个正常数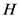 使得
使得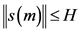 ,即
,即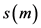 以
以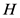 为界;
为界;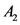 是一个对角矩阵,
是一个对角矩阵,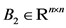 。
。
为使系统(1)和(2)达到同步,设计脉冲控制器如下
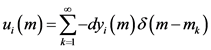 , (3)
, (3)
其中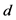 是脉冲控制增益,
是脉冲控制增益,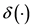 是狄拉克函数。脉冲序列
是狄拉克函数。脉冲序列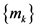 满足
满足 和
和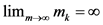 。
。
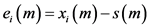 表示第
表示第 个节点的误差状态向量,误差系统可表示为
个节点的误差状态向量,误差系统可表示为
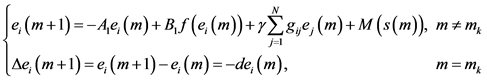 (4)
(4)
其中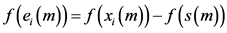 ,
, 。
。
引理1 [12] Kronecker 积有如下性质:
(1) ;
;
(2) 。
。
引理2 [11] 对于实数阵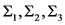 ,存在
,存在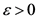 和矩阵
和矩阵 ,使得
,使得
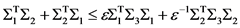 。
。
假设1 函数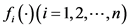 满足:存在常数
满足:存在常数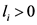 ,使得
,使得
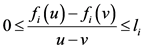 ,
,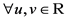 ,
, 。
。
3. 主要结果
在本节中,我们将给出使(1)和(2)达到准同步的充分条件。
定理1 在假设1条件下,存在常数 ,
,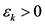 使得
使得
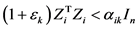 ,
,
其中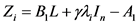 且
且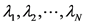 是矩阵
是矩阵 的特征值,
的特征值, 。则误差系统(4)可收
。则误差系统(4)可收
敛到集合 ,其中
,其中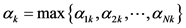 ,
,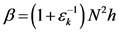 ,
,
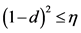 ,
,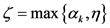 。因此,神经网络(1)和(2)可在误差区域
。因此,神经网络(1)和(2)可在误差区域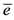 内达到准同步。
内达到准同步。
证明 令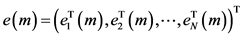 ,则误差系统(4)可改写为
,则误差系统(4)可改写为
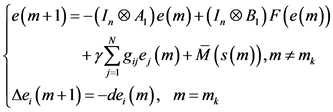 (5)
(5)
其中
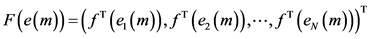 ,
,
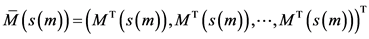 。
。
根据矩阵分解理论,存在正交矩阵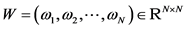 使得
使得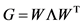 ,其中
,其中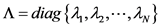 ,
,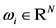 。令
。令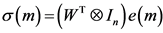 ,则
,则 ,
,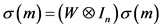 。由(5),对于
。由(5),对于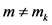 ,
,
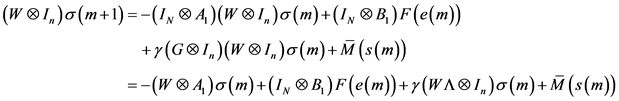
两边同乘以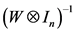
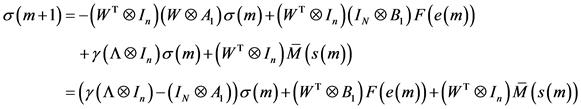 。
。
由假设(1)的条件可得
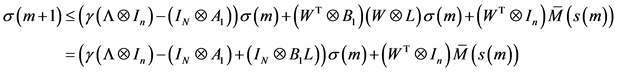 , (6)
, (6)
因此,
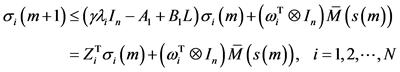 。 (7)
。 (7)
考虑Lyapunov函数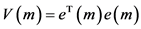 ,
,
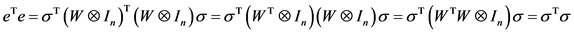 。
。
对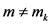 ,
,
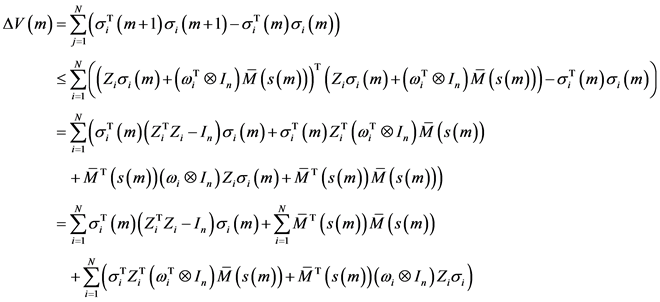
根据引理2可知,
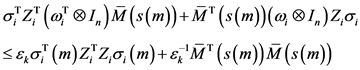 。
。
因此,
 ,
,
故
 . (8)
. (8)
当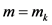 ,我们可以得到
,我们可以得到
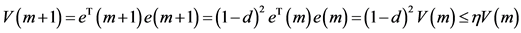 ,
,
故对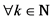 ,有
,有
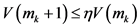 。 (9)
。 (9)
令 ,则
,则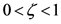 。由(8)~(9)可得
。由(8)~(9)可得
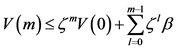 , (10)
, (10)
则
 。(11)
。(11)
当 ,
,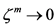 ,
,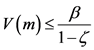 ,即
,即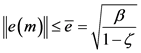 。因此,误差系统(4)可指数型收敛到
。因此,误差系统(4)可指数型收敛到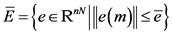 ,即离散网络(1)和(2)最终可在误差域
,即离散网络(1)和(2)最终可在误差域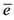 内达到准同步。
内达到准同步。
注释2本文的主要贡献有以下几点:(1)文献 [13] 中,准同步条件由线性矩阵不等式(LMI)形式给出。而本文在Kronecker积性质和矩阵分解理论方法的基础上,得到了形式更为简洁的准同步标准。(2)在过去的几十年中,人们对于具有不匹配参数的离散系统进行了广泛的研究,并且得到了很多重要且有意义的结论,如 [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] 。但大多数的文献研究了连续时间的情形,极少数人关注到了离散情形。本文则采用脉冲控制方法研究了具有参数不匹配的离散网络同步。
注释3当系统(1)和(2)中的参数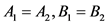 时,则
时,则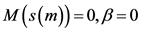 ,此时
,此时 ,(1)和(2)即可达到完全同步。
,(1)和(2)即可达到完全同步。
4. 结论
本文基于Lyapunov理论研究了在脉冲控制下具有不匹配参数的离散神经网络同步条件。文章首次应用脉冲控制方法讨论了参数不匹配的离散网络准同步问题,得到了同步误差区域。
致 谢
本文得到国家自然科学基金(批准号:61573005,11361010)的资助,在此表示感谢。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(61573005,11361010)。
文章引用
李嘉敏,宾红华,黄振坤. 具有不匹配参数的脉冲离散网络准同步
Quasi-Synchronization of Discrete-Time Networks with Parameter Mismatches under Impulsive Control[J]. 动力系统与控制, 2017, 06(04): 158-163. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/DSC.2017.64020
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Yang, X., Cao, J. and Yang, Z. (2009) Synchronization of Coupled Reaction-Diffusion Neural Networks with time-Varying Delays via Pinning-Impulsive Controller. SIAM Journal on Control & Optimization, 51, 3486-3510. https://doi.org/10.1137/120897341
- 2. Du, H., Shi, P. and Lv, N. (2013) Function Projective Synchronization in Complex Dynamical Networks with Time Delay via Hybrid Feedback Control. Nonlinear Analysis Real World Appli-cations, 14, 1182-1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2012.09.009
- 3. Zhang, Q., Chen, J. and Wan, L. (2013) Impulsive Generalized Function Synchronization of Complex Dynamical Networks. Physics Letters A, 377, 2754-2760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2013.08.014
- 4. Zhang, W., Huang, J. and Wei, P. (2011) Weak Synchroniza-tion of Chaotic Neural Networks with Parameter Mismatch via Periodically Intermittent Control. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 35, 612-620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2010.07.009
- 5. Yuan, K. and Cao, J. (2008) Synchronization of Master-Slave Systems with Mixed Time Delays and Mismatched Parameters. Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control Conference, 540-543. https://doi.org/10.1109/CHICC.2008.4605704
- 6. Huang, T., Li. C. and Liao, X. (2007) Synchroniza-tion of a Class of Coupled Chaotic Delayed Systems with Parameter Mismatch. American Institute of Physics, 17, 033121. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2776668
- 7. Liang, J., Wang, Z. and Liu, X. (2008) Exponential Synchroniza-tion of Stochastic Delayed Discrete-Time Complex Networks. Nonlinear Dynamics, 53, 153-165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-007-9303-5
- 8. Liu, B., Liu, T. and Dou, C. (2014) Stability of Discrete-Time Delayed Impulsive Linear Systems with Application to Multitracking. International Journal of Control, 87, 911-924. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207179.2013.861930
- 9. Liu, B. and Marquez. H (2007) Razumikhin-Type Stability Theorems for Discrete Delay Systems. Automatica, 43, 1219-1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2006.12.032
- 10. Zhang, Y., Sun, J. and Feng, G. (2009) Impulsive Control of Discrete Systems with Time Delay. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 54, 830-834. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2008.2010968
- 11. Boyd, S., Ghaoui, L., Feron, E. and Balakrishnan, V. (1994) Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory. SIAM, Philadephia.
- 12. Langville, A. and Stewart, W. (2004) The Kronecker Product and Stochastic Automata Networks. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 167, 429-447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2003.10.010
- 13. Tang, Z., Park, J. and Feng, W. (2017) Impulsive Effects on Quasi-Synchronization of Neural Networks with Parameter Mismatches and Time-Varying Delay. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 99, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2651024