International Journal of Fluid Dynamics
Vol.05 No.01(2017), Article ID:19955,7
pages
10.12677/IJFD.2017.51003
A Four-Order Difference Type Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Poisson Equation
Bo Yan1, Jianchao Wang1, Guangwu Yan2
1College of Civil Engineering, Jilin Jianzhu University, Changchun Jilin
2College of Mathematics, Jilin University, Changchun Jilin

Received: Mar. 3rd, 2017; accepted: Mar. 20th, 2017; published: Mar. 23rd, 2017

ABSTRACT
A four-order difference type lattice Boltzmann model is employed to investigate the Poisson equation in this paper. By using the steady lattice Boltzmann equation and the multi-spatial scale expansion, the Poisson equation with four-order accuracy is obtained. Examples show that the numerical results agree well with exact solutions.
Keywords:Finite Difference Method, Lattice Boltzmann Model, Poisson Equation
一种用于Poisson方程的四阶差分型格子Boltzmann模型
闫铂1,王建朝1,闫广武2
1吉林建筑大学土木工程学院,吉林 长春
2吉林大学数学学院,吉林 长春
收稿日期:2017年3月3日;录用日期:2017年3月20日;发布日期:2017年3月23日

摘 要
本文给出了用于求解Poisson方程的四阶差分型格子Boltzmann模型,应用定常的格子Boltzmann方程和空间多尺度展开,得到了截断误差是四阶精度的Poisson方程。数值例子表明,该模型在精度上较相应的二阶模型有所提高。
关键词 :有限差分法,格子Boltzmann模型,Poisson方程

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
Poisson方程在流体力学中有着广泛的应用。例如,在具势流动的势函数求解和涡流系统的流函数求解等问题中,Poisson方程的求解直接影响流体力学量的精度。最近研究表明,格子Boltzmann方法(LBM)可成功应用于求解反应扩散方程 [1] 、交叉扩散方程 [2] 、Ginzburg-Landau方程 [3] 、波动方程 [4] 、Poisson方程 [5] [6] 等。本文提出了一种用于Poisson方程的有限差分格子Boltzmann模型(FDLBM)。与以前的LBM模型不同 [7] [8] [9] [10] ,本文所构造的模型没有粒子速度,在迭代中只有粒子从一个位置到相邻位置的位移。与其它调用矩阵公式和带有预处理的LBM不同,我们将有限差分格式引入到标准LBM方程中。数值结果表明,该模型与解析解吻合的很好。
2. 格子Boltzmann模型
2.1. 迭代方程
考虑一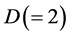 维空间,将其离散成网格,网格中心与相邻的
维空间,将其离散成网格,网格中心与相邻的 个格点通过格线相连。每个格点的粒子可以分为
个格点通过格线相连。每个格点的粒子可以分为 个部分,每一部分的状态只与本身和相邻粒子有关。定义从
个部分,每一部分的状态只与本身和相邻粒子有关。定义从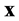 位置到同一位置的位移为
位置到同一位置的位移为 ,从
,从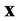 位置到其他相邻格点的位移为
位置到其他相邻格点的位移为
 . (1)
. (1)
其中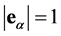 ,
,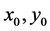 分别为x,y方向的单位矢量。
分别为x,y方向的单位矢量。
由于二维Poisson方程独立于时间,所以把LBM方程改写为
 , (2)
, (2)
其中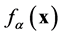 为
为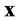 位置粒子的分布函数,
位置粒子的分布函数,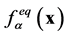 为同一位置的平衡态分布函数,
为同一位置的平衡态分布函数,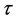 为松弛因子,
为松弛因子, 为空间步长的量级,
为空间步长的量级, 为
为 方向的单位矢量。
方向的单位矢量。
定义宏观量
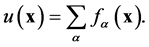 (3)
(3)
此外,局部平衡态分布函数 满足守恒条件
满足守恒条件
 (4)
(4)
认为模型中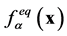 为迭代后的最终状态,而不是过渡状态。迭代过程从宏观量
为迭代后的最终状态,而不是过渡状态。迭代过程从宏观量 的任意分布开始到最终平衡状态结束,即Poisson方程的解。所以方程(2)写为
的任意分布开始到最终平衡状态结束,即Poisson方程的解。所以方程(2)写为
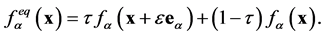 (5)
(5)
在方程(5)中,由于不含时间,所以迭代的表述与标准LBM方程不同。宏观量只用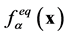 ,即
,即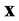 位置及其相邻位置的分布值计算。因为方程中没有
位置及其相邻位置的分布值计算。因为方程中没有 项用来迭代,所以不需要流动过程。
项用来迭代,所以不需要流动过程。
将方程(5)中的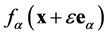 写成五点差分格式,其精度为二阶精度。令
写成五点差分格式,其精度为二阶精度。令 结点坐标为
结点坐标为 ,四个相邻结点坐标依次为
,四个相邻结点坐标依次为 ,
,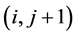 ,
, ,
,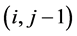 。带入五结点差分公式,得到二阶精度Poisson方程的FDLBM模型
。带入五结点差分公式,得到二阶精度Poisson方程的FDLBM模型
 (6)
(6)
其中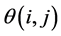 定义为
定义为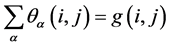 。
。
特别地,二阶精度Laplace方程的FDLBM模型表示为
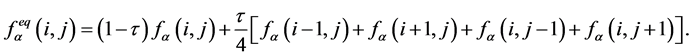 (7)
(7)
四阶精度的差分格式与九个结点有关,带入方程(5),得出四阶精度Poisson方程的FDLBM模型
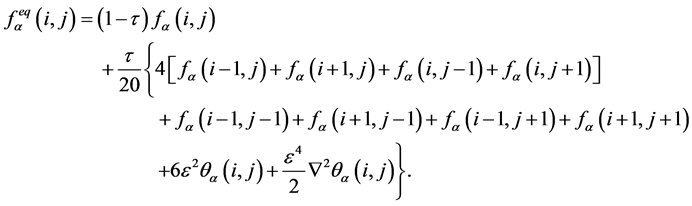 (8)
(8)
相应地,对于Laplace方程,(8)式可表示为
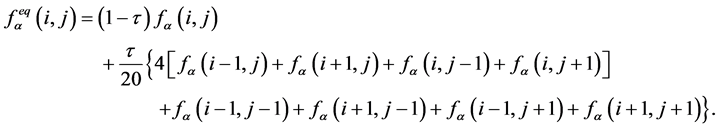 (9)
(9)
2.2. 精度分析
将(6)式两端对 求和,得出关于
求和,得出关于 的方程
的方程
 , (10)
, (10)
其中,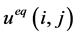 表示
表示 的结果,
的结果,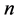 为迭代步数。在
为迭代步数。在 点附近进行Taylor展开,有
点附近进行Taylor展开,有
 . (11)
. (11)
当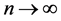 时,
时, 等价于
等价于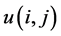 。那么,
。那么,
 . (12)
. (12)
同样地,(8)式两端对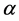 求和,得出关于
求和,得出关于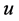 的方程
的方程
 (13)
(13)
在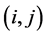 点附近进行Taylor展开,得
点附近进行Taylor展开,得
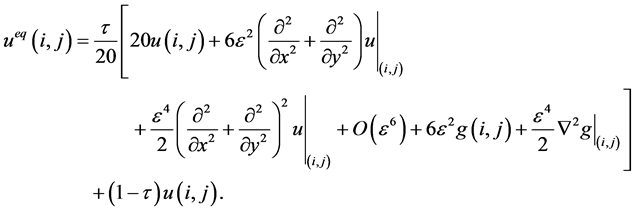 (14)
(14)
因为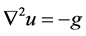 ,所以
,所以
 . (15)
. (15)
即
 . (16)
. (16)
方程(12)和(16)分别为二阶和四阶精度的修正Poisson方程。
3. 数值算例
下面应用本文所提出的FDLBM模型求解Laplace方程和Poisson方程。
例1:考虑一个二维Laplace方程
 . (17)
. (17)
其Dirichlet边界条件为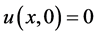 ,
,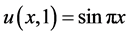 ,
, ,
, 。方程的解析解为
。方程的解析解为
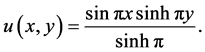 (18)
(18)
本文使用了二阶和四阶模型计算例1。其模拟结果与解析解的比较如图1所示。其它参数为:格子数 ,
,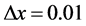 ,
, 。计算域内宏观量
。计算域内宏观量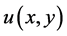 的初值为0,边界条件为上述的Dirichlet边界条件。在模拟过程中,边界上函数的分布等于平衡态分布,由宏观量
的初值为0,边界条件为上述的Dirichlet边界条件。在模拟过程中,边界上函数的分布等于平衡态分布,由宏观量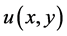 给出。把
给出。把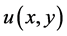 的新旧值之差设置为结束迭代的条件,当最大差值小于
的新旧值之差设置为结束迭代的条件,当最大差值小于 时,迭代结束。然后,
时,迭代结束。然后,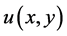 的值即为Laplace方程的数值模拟结果。图1(a)和图1(b)分别给出了
的值即为Laplace方程的数值模拟结果。图1(a)和图1(b)分别给出了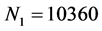 和
和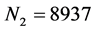 时的模拟结果,其中
时的模拟结果,其中 和
和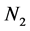 分别为五结点和九结点FDLBM模型的迭代步数;图1(c)为解析解。从图中可以看出数值模拟结果与解析解有很好的一致性。
分别为五结点和九结点FDLBM模型的迭代步数;图1(c)为解析解。从图中可以看出数值模拟结果与解析解有很好的一致性。
为了进一步比较,图2给出了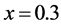 处的解析解和数值解曲线以及两个FDLBM模型的绝对误差曲
处的解析解和数值解曲线以及两个FDLBM模型的绝对误差曲


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 1. Comparison between the numerical results and the exact solution of Laplace equation: (a) 5-bit FDLBM model; (b) 9-bit FDLBM model; (c) Exact solution
图1. Laplace方程的数值解与解析解的比较:(a) 五结点FDLBM模型;(b) 九结点FDLBM模型;(c) 解析解

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 2. (a) Comparison between numerical results and analytical solution at x = 0.3; (b) The absolute errors of the two FDLBM models for Laplace equation at x = 0.3
图2. (a) Laplace方程数值解和解析解在x = 0.3处的比较;(b) Laplace方程两个FDLBM模型数值解在x = 0.3的绝对误差曲线
线。绝对误差 ,其中
,其中 为数值解,
为数值解, 为解析解。从图2(a)中可以看出,FDLBM模型与解析解吻合的很好;图2(b)表明,九结点模型比五结点模型误差小,两个模型的误差都是可接受的。此外,表1给出了不同位置的解析解和数值解以及绝对误差。从表中可以看出,FDLBM模型的误差是令人满意的。
为解析解。从图2(a)中可以看出,FDLBM模型与解析解吻合的很好;图2(b)表明,九结点模型比五结点模型误差小,两个模型的误差都是可接受的。此外,表1给出了不同位置的解析解和数值解以及绝对误差。从表中可以看出,FDLBM模型的误差是令人满意的。
例2:考虑下列齐次Helmholtz方程 [5] [11]
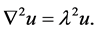 (19)
(19)
计算域为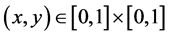 。边界条件与解析解相同,即
。边界条件与解析解相同,即
 ,
,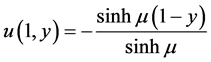 ;
;
 ,
, 。
。
在本文中,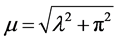 ,
,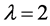 。该方程的解析解为
。该方程的解析解为
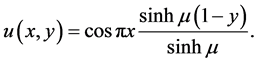 (20)
(20)
图3(a)、图3(b)和图3(c)分别给出了五结点模型、九结点模型和解析解的计算结果,其中五结点模型和九结点模型的迭代步数分别为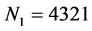 和
和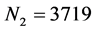 。除边界外,迭代的初值条件为
。除边界外,迭代的初值条件为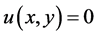 。程序终止的条件与例1相同。从图中可以发现,FDLBM模型的模拟结果与解析解吻合的很好。
。程序终止的条件与例1相同。从图中可以发现,FDLBM模型的模拟结果与解析解吻合的很好。
此外,图4和表2给出了FDLBM模型的计算结果与解析解的比较。格子数为 ,松弛因子
,松弛因子 。可以看出,两个模型的绝对误差都小于
。可以看出,两个模型的绝对误差都小于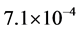 ,FDLBM模拟结果与解析解有较好的一致性。图4和表2表明,我们的模型可以用来模拟Poisson方程。
,FDLBM模拟结果与解析解有较好的一致性。图4和表2表明,我们的模型可以用来模拟Poisson方程。
在两个数值例子中,松弛因子 都等于0.99。在模拟过程中,我们发现
都等于0.99。在模拟过程中,我们发现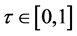 ;并且随着
;并且随着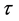 的增大,数值结果更精确。
的增大,数值结果更精确。
Table 1. The comparison between exact solution and LBM results and the absolute errors of the two models at x = 0.3 for Laplace equation
表1. Laplace方程x = 0.3处的解析解和LBM结果的比较以及两个模型的绝对误差


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 3. Comparison between the numerical results and the exact solution of Poisson equation: (a) 5-bit FDLBM model; (b) 9-bit FDLBM model; (c) Exact solution
图3. Poisson方程的数值解与解析解的比较:(a) 五结点FDLBM模型;(b) 九结点FDLBM模型;(c) 解析解

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 4. (a) Comparison between numerical results and analytical solution at x = 0.3; (b) The absolute errors of the two FDLBM models for Laplace equation at x = 0.3
图4. (a) Laplace方程数值解和解析解在x = 0.3处的比较;(b) Laplace方程两个FDLBM模型数值解在x = 0.3的绝对误差曲线
Table 2. The comparison between exact solution and LBM results and the absolute errors of the two models at x = 0.3 for Poisson equation
表2. Poisson方程x = 0.3处的解析解和LBM结果的比较以及两个模型的绝对误差
4. 结论
与以前的格子Boltzmann模型相比,本文提出的模型优势是可以直接模拟定常问题,不需要采用时间相关法。由于采用不含时间的格子Boltzmann方程,使得算法清晰,程序代码简单。
我们发现,松弛因子被限定在 区间内,这是由于迭代过程是松弛迭代,而不是超松弛迭代。与经典格子Boltzmann模型不同,本算法松弛因子在
区间内,这是由于迭代过程是松弛迭代,而不是超松弛迭代。与经典格子Boltzmann模型不同,本算法松弛因子在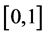 区间是稳定的,而在
区间是稳定的,而在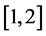 区间不稳定。随着
区间不稳定。随着 的增大,收敛被加速,数值结果变得精确。
的增大,收敛被加速,数值结果变得精确。
从计算结果中发现,九结点模型比五结点模型误差小,这是因为九结点模型包含了更多相邻结点的信息,使得九结点模型是四阶精度而五结点模型是二阶精度。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金No. 51406067, No. 11272133;吉林省教育厅科研项目(吉教科合字[2016]第141号)。
文章引用
闫铂,王建朝,闫广武. 一种用于Poisson方程的四阶差分型格子Boltzmann模型
A Four-Order Difference Type Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Poisson Equation[J]. 流体动力学, 2017, 05(01): 22-28. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/IJFD.2017.51003
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Chen, S.Y., Dawson, S.P., Doolen, G.D., Janecky, D.R. and Lawniczak, A. (1995) Lattice Methods and Their Applications to Reacting Systems. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 19, 617-646. https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-1354(94)00072-7
- 2. Zhang, J.Y. and Yan, G.W. (2015) Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Pattern Formation under Cross-Diffusion. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 69, 157-169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2014.11.016
- 3. Zhang, J.Y. and Yan, G.W. (2014) Three Dimensional Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Complex Ginzburg-Landau Equation. Journal of Scientific Computing, 60, 660-683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-013-9811-z
- 4. Yan, G.W. (2000) A Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Waves. Journal of Computational Physics, 161, 61-69. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.2000.6486
- 5. Chai, Z.H. and Shi, B.C. (2008) A Novel Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Poisson Equation. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 32, 2050-2058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2007.06.033
- 6. 王博宇, 闫广武. 用于求解Poisson方程的格子Boltzmann模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版), 2015, 53(3): 407-413.
- 7. Xu, A.G. (2004) Finite-Difference Lattice-Boltzmann Methods for Binary Fluids. Physical Review E, 71, Article ID: 066706. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.71.066706
- 8. Guo, Z.L. and Zhao, T.S. (2005) Finite-Difference-Based Lattice Boltzmann Model for Dense Binary Mixtures. Physical Review E, 71, Article ID: 026701. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.71.026701
- 9. Cao, N.Z., Chen, S.Y., Jin, S. and Daniel, M. (1997) Physical Symmetry and Lattice Symmetry in the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Physical Review E, 55, R21-R24. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.55.r21
- 10. Peng, G.W., Xi, H.W. and Comer, D. (1999) Finite Volume Scheme for the Lattice Boltzmann Method on Unstructured Meshes. Physical Review E, 59, 4675-4682. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.59.4675
- 11. Averbuch, A., Vozovoi, L. and Israeli, M. (1997) On a Fast Direct Elliptic Solver by a Modified Fourier Method. Numerical Algorithms, 15, 287-313. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019106223154
