Operations Research and Fuzziology
Vol.
10
No.
02
(
2020
), Article ID:
34989
,
7
pages
10.12677/ORF.2020.102012
Stability of Fractional Order Chen Chaos Based on Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Model
Yuting Li
Xi’an Aeronautical University , Xi’an Shaanxi

Received: Mar. 24th, 2020; accepted: Apr. 6th, 2020; published: Apr. 13th, 2020

ABSTRACT
The control problem of fractional order Chen chaos system based on fractional order Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model is studied. The Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model for fractional order Chen chaos systems is given, and a parallel distributed compensate fuzzy controller is designed to asymptotically stabilize the model. Then effectiveness of the approach is tested on fractional order Chen chaos system with .
Keywords:Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Model, Fractional Order Chen Chaos System, PDC (Parallel Distributed Compensating)

基于分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型的分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制
李玉婷
西安航空学院,陕西 西安

收稿日期:2020年3月24日;录用日期:2020年4月6日;发布日期:2020年4月13日

摘 要
本文研究了基于Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型的分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制问题。对分数阶Chen混沌系统建立了相应的Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型,基于分布补偿原理对分数阶Chen系统进行控制,对阶数 的Chen混沌系统进行了仿真,验证了分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统对分数阶Chen混沌系统控制的有效性。
关键词 :Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型,分数阶Chen系统,并行分布补偿原理(PDC)

Copyright © 2020 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
混沌是指对初值具有极端敏感性的确定性动力系统的随机行为。1963年,Lorenz [1] 发现了被称为“蝴蝶效应”的Lorenz混沌系统,之后就有许多新的混沌系统被不断的发现。1999年陈关荣教授发现了与Lorenz混沌系统相关但不拓扑等价且更复杂的Chen混沌系统 [2] [3] 后,有许多关于Chen混沌系统的研究结论 [4] [5] [6] [7] 产生了。同时分数阶混沌系统的相关动力学性质、控制及同步等问题也得到了广泛的关注并取得各种成果。如:文献 [8] 研究了一种新的分数阶超混沌系统的动力学行为、电路实现、混沌控制及同步问题;分数阶Chua系统的混沌与同步问题在文献 [9] 中进行了探讨;文献 [10] 讨论了具有输入饱和的分数阶混沌系统的同步问题;文献 [11] 分析了分数阶Chen混沌系统的局部分叉理论。
日本学者Takagi和Sugeno在1985年提出了Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统 [12] [13],其本质是将非线性的动力学系统通过一系列局部线性系统来描述,线性系统之间通过非线性的隶属度函数来连接。目前利用Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型来研究非线性混沌系统的控制与同步等问题目前已经成为研究混沌模型的主要方法之一。如:文献 [14] 研究了基于Takagi-Sugeno模型的非PDC观测器的跟踪控制器在混沌控制中的应用;文献 [15] 讨论了降阶模糊控制器对Lorenz-Stenflo系统的控制和同步问题;文献 [16] 考虑了输入未知的Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统在混沌同步中的应用问题;目前这些讨论主要是基于整数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统对混沌系统的研究。本文基于分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统理论建立了分数阶Chen混沌系统的Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型,讨论了分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制问题。
2. 分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统
2.1. Caputo型分数阶导数
在分数阶微积分理论整个发展的历史过程中,许多学者和研究人员从不同的角度给出了分数阶微积分的定义。比较常用的有Grünwald-Letnikov (G-L)型定义,Riemann-Liouville (R-L)型定义和Caputo型定义,本文使用Caputo型分数阶微积分的概念。
定义1 [17]:Caputo 型分数阶微分的定义为
(1)
其中 是gamma函数, 。为了讨论方便,本文中用 表示 算子。
2.2. 分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统
Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型自产生之日起就是处理非线性系统问题的有效方法之一。混沌系统是一类典型的非线性系统,本文利用分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型来研究非线性分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制问题。首先我们介绍分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统。
考虑如下形式的分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统:
Rule i: If is and … is ;
Then
其中, ,r是模糊推理规则的数目, 是模糊集合, 是前件变量,可以是状态、输入或输出变量。 是状态变量, 是输入变量, 是分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统的阶数。 和 是系统的已知系数矩阵,则全局分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统模型可以表示为如下形式:
(2)
其中, ,,, 是 在模糊集合 中的隶属度函数,且满足:
下面介绍分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊闭环系统渐进稳定的结论。
引理1 [18]:如果存在一个对称正定矩阵Q,矩阵 ( ),使得下面的LMIs成立
, (3)
, (4)
则分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊闭环系统(2)是渐进稳定的。
3. 分数阶Chen混沌系统
3.1. 分数阶Chen混沌系统
下面给出分数阶Chen混沌自治系统的模型描述,其中 为混沌系统的状态变量,a、b和c表示混沌系统的参数, 表示分数阶阶数且满足 :
(5)
其中, ,, 时,取 时,初值 时相应的分数阶Chen系统的状态轨迹如图1所示。
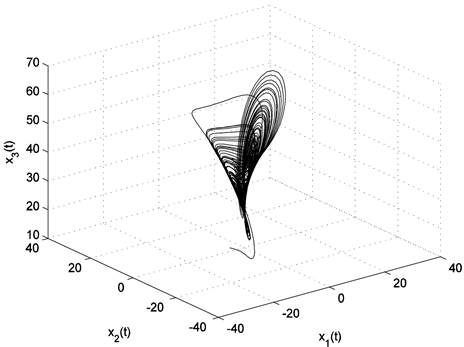
Figure 1. Chaotic behaviors of the fractional order Chen system
图1. 分数阶Chen混沌系统的仿真曲线
3.2. 分数阶Chen混沌系统的Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型
本节给出分数阶Chen混沌自治系统的分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型。取 ,,根据混沌系统的有界性可知此假设是合理的。选择 作为模糊规则的前件变量,分数阶Chen混沌系统可以表示成如下形式的分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型:
Rule 1: If is , then ;
Rule 2: If is , then .
其中 ,
,
对应隶属度函数为:
分数阶Chen混沌系统的全局分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型可表示为:
(6)
且
3.3. 基于分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统的分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制
本节考虑基于分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型的分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制问题,即讨论分数阶混沌系统的镇定问题。假设对分数阶Chen混沌系统施加控制输入如下:
(7)
根据对分数阶Chen混沌系统的建模过程可得,对系统施加控制后其分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型为:
Rule 1: If is , then ;
Rule 2: If is , then .
其中, 。
利用PDC设计模糊控制器,考虑以下模糊控制规则:
Rule 1: If is , then ;
Rule 2: If is , then .
则系统的模糊控制器总输出为:
(8)
将上面给出的控制律带入,则相应的分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊闭环系统可表述为:
(9)
根据引理1,如果存在一个对称正定矩阵Q,矩阵 及 ,使得下面的LMIs成立,则分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊闭环系统是渐进稳定的,其中状态反馈增益矩阵 ( )。
(10)
由前面的讨论可知,当存在对称正定矩阵Q,矩阵 及 ,使得以上线性矩阵不等式成立时,分数阶Chen混沌系统是可镇定的。将参数 ,,,并选 带入 、 ,应用Matlab求解上述的线性矩阵不等式,可以得到如下的可行解:
又由于状态反馈增益矩阵 ( ),可得
根据并行分布补偿原理知,
将反馈增益带入,计算出系统的模糊控制器总输入 ,代入分数阶Chen混沌系统,对分数阶不确定Chen混沌系统进行稳定化控制。当 时,初值取 做分数阶Chen混沌系统(7)的仿真图,图2是加了控制后的分数阶Chen混沌系统的状态曲线,图3是系统的控制曲线,可以看到分数阶Chen混沌系统的状态曲线和控制曲线很快趋向于原点。此时,在控制器的作用下分数阶Chen混沌系统是可镇定的。

Figure 2. Control results of the fractional order Chen system
图2. 添加了控制后的分数阶Chen混沌系统的状态曲线
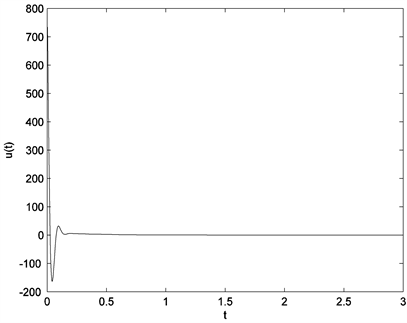
Figure 3. Control curve of the fractional order Chen system
图3. 分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制曲线
4. 结论
本文讨论了分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制问题。首先介绍了分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统及其稳定化条件。接着对分数阶Chen混沌系统建立了分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统模型,利用建模得到的分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统的稳定化条件对分数阶Chen混沌系统进行控制。本文对阶数 的Chen混沌系统进行了仿真,验证了分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊系统对分数阶Chen混沌系统控制的有效性。
基金项目
陕西省教育厅科研计划项目资助(项目编号:17JK0394);西安航空学院校级科研基金项目(2017ky0208)。
文章引用
李玉婷. 基于分数阶Takagi-Sugeno模糊模型的分数阶Chen混沌系统的控制
Stability of Fractional Order Chen Chaos Based on Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Model[J]. 运筹与模糊学, 2020, 10(02): 115-121. https://doi.org/10.12677/ORF.2020.102012
参考文献
- 1. Lorenz, E.N. (1963) Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 20, 130-141. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1963)020<0130:DNF>2.0.CO;2
- 2. Chen, G. and Ueta, T. (1999) Yet Another Chaotic Attractor. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 9, 1465-1466. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127499001024
- 3. Ueta, T. and Chen, G. (2000) Bifurcation Analysis of Chen’s Equation. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 10, 1917-1931. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127400001183
- 4. Sprott, J.C. (2015) New Chaotic Regimes in the Lorenz and Chen Systems. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 25, Article ID: 1550033. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127415500339
- 5. Zhang, F., Liao, X., Mu, C., et al. (2017) On Global Boundedness of the Chen System. Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems-B, 22, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3934/dcdsb.2017080
- 6. Algaba, A., Domínguez-Moreno, M.C., Merino, M., et al. (2015) Study of the Hopf Bifurcation in the Lorenz, Chen and Lü Systems. Nonlinear Dynamics, 79, 885-902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1709-2
- 7. Leonov, G.A. and Kuznetsov, N.V. (2015) On Differences and Similarities in the Analysis of Lorenz, Chen, and Lu Systems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 256, 334-343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2014.12.132
- 8. El-Sayed, A.M.A., Nour, H.M., Elsaid, A., et al. (2016) Dynamical Behaviors, Circuit Realization, Chaos Control, and Synchronization of a New Fractional Order Hyperchaotic System. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 40, 3516-3534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2015.10.010
- 9. Odibat, Z., Corson, N., Aziz-Alaoui, M.A., et al. (2017) Chaos in Fractional Order Cubic Chua System and Synchronization. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 27, Article ID: 1750161. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127417501619
- 10. Khamsuwan, P., Sangpet, T. and Kuntanapreeda, S. (2018) Chaos Synchronization of Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems with Input Saturation. Journal of Computational and Nonlinear Dynamics, 13, Article ID: 090903. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4039681
- 11. Čermák, J. and Nechvátal, L. (2019) Stability and Chaos in the Frac-tional Chen System. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 125, 24-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2019.05.007
- 12. Takagi, T. and Sugeno, M. (1985) Fuzzy Identification of Systems and Its Applications to Modeling and Control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, SMC-15, 116-132. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313399
- 13. Tanaka, K. and Sugeno, M. (1992) Stability Analysis and Design of Fuzzy Control Systems. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 45, 135-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(92)90113-I
- 14. Asemani, M.H. and Vatankhah, R. (2017) NON-PDC Observer-Based T-S Fuzzy Tracking Controller Design and Its Application in CHAOS Control. Asian Journal of Control, 19, 969-982. https://doi.org/10.1002/asjc.1451
- 15. Yang, C.H., Wu, C.L., Chen, Y.J., et al. (2015) Reduced Fuzzy Controllers for Lorenz-Stenflo System Control and Synchronization. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 17, 158-169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0032-5
- 16. Chadli, M. and Zelinka, I. (2014) Chaos Synchronization of Unknown Inputs Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy: Application to Secure Communications. Com-puters & Mathematics with Applications, 68, 2142-2147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2013.01.013
- 17. Podlubny, I. (1999) Fractional Differential Equations. Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
- 18. Li, Y. and Li, J. (2014) Stability Analysis of Fractional Order Systems Based on T-S Fuzzy Model with the Fractional Order . Nonlinear Dynamics, 78, 2909-2919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1635-3