Pharmacy Information
Vol.
07
No.
06
(
2018
), Article ID:
27453
,
12
pages
10.12677/PI.2018.76022
Research Progress on Inhibitors of Natural Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B
Zhongqiu Guo, Xin Wang, Jiajing Han, Yu Liu*
School of Pharmacy, Liaoning University, Shengyang Liaoning

Received: Oct. 17th, 2018; accepted: Nov. 1st, 2018; published: Nov. 8th, 2018

ABSTRACT
Protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B (PTP1B) is a major negative regulator in insulin signal transduction pathways. In recent years, as a new target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, the study of PTP1B inhibitors has attracted extensive attention. PTP1B disrupts the insulin signal transduction by dephosphorylating phosphotyrosine residues of insulin receptor and its substrates. China has plenty of plant resources, through the extraction of natural products, some active PTP1B inhibitors can be obtained. The discovery of highly effective inhibitors of PTP1B can provide a new way to treat type 2 diabetes. In this paper, according to the structural types of PTP1B inhibitors, the research progress of some representative natural PTP1B inhibitors is reviewed, including bromophenol compounds, brass compounds, terpenoid compounds, coumarin compounds and others, which shows that further study of PTP1B and its potent inhibitors have good prospects for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Keywords:Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B, Type 2 Diabetes, Inhibitors, Natural Compound
天然蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1B抑制剂的研究进展
郭忠秋,王欣,韩佳婧,刘宇*
辽宁大学药学院,辽宁 沈阳

收稿日期:2018年10月17日;录用日期:2018年11月1日;发布日期:2018年11月8日

摘 要
蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1B (PTP1B)是胰岛素信号转导途径中重要的负调控因子。PTP1B通过使胰岛素受体及其底物的酪氨酸残基去磷酸化从而破坏胰岛素信号转导。近年来,作为治疗2型糖尿病的新靶点,有关PTP1B抑制剂的研究引起了广泛关注。中国有丰富的植物资源,通过对天然产物进行提取,可以获得一些有活性的PTP1B抑制剂。高效PTP1B抑制剂的发现可以为2型糖尿病的治疗提供新的途径。本文根据PTP1B抑制剂的结构类型,综述了一些具有代表性的天然PTP1B抑制剂的研究进展,包括溴酚类化合物,黄铜化合物,萜类化合物,香豆素类化合物等。表明深入研究PTP1B及其有效的抑制剂对于治疗2型糖尿病具有很好的发展前景。
关键词 :蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1B,2型糖尿病,抑制剂,天然化合物

Copyright © 2018 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
现如今,随着人们生活水平的提高,糖尿病已经逐渐成为威胁人类健康的重大疾病。糖尿病是由胰岛素分泌不足或胰岛素抵抗引起的一种疾病,以高血糖为典型的临床症状,它可以引发视网膜病变、心血管疾病等一系列并发症,严重时甚至危及生命 [1] 。2型糖尿病在糖尿病患者中占绝大多数,主要是由于胰岛素抵抗作用,使靶细胞对胰岛素的敏感性下降,对葡萄糖的摄取能力降低,最终导致血液中的葡萄糖含量升高 [2] 。随着人们对胰岛素生理功能研究的不断深入,发现了一些治疗糖尿病的新靶点。其中,蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1B (protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B, PTP1B)是胰岛素信号传导重要的负调控因子,在胰岛素信号的传递过程中起着十分重要的作用,通过抑制PTP1B的活性可以提高靶细胞对胰岛素的敏感性 [3] ,在糖尿病的治疗中有着十分广阔的应用前景。
2. PTP1B简介
PTP1B是蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶家族(PTPs)的一员,于1988年从人胎盘组织中分离出来,是一种由435个氨基酸残基构成的胞内酶,可以在内质网表面广泛富集 [4] 。PTP1B的N末端含有由半胱氨酸残基(Cys215)和精氨酸残基(Ary221)组成的催化活性中心,指向胞浆方向,可以与胰岛素受体结合 [5] 。以C末端的35个特异性氨基酸将PTP1B定位在内质网表面 [6] 。PTP1B通过与蛋白酪氨酸激酶(protein tyrosine kinases, PTK)协同作用维持细胞内蛋白酪氨酸磷酸化水平的动态平衡,是细胞信号转导机制的重要组成部分。PTP1B是胰岛素信号传导重要的负调控因子,可以去磷酸化蛋白酪氨酸,阻碍胰岛素信号的传导,引发2型糖尿病。
PTP1B的结构特征包括:1) 活性位点,PTP1B的催化结构域是由240个氨基酸残基组成的序列,是PTP酶家族共有的保守区域 [7] 。其中PTP1B的催化活性中心由Cys215残基组成,可以与底物的磷酸基结合从而发生水解作用,是保持PTP1B的酶活性必不可少的结构 [8] 。2) WPD环,含有Asp181残基,可以参与酶的催化过程,促进底物去磷酸 [9] 。结合底物之后,该环的构象会改变,促进与底物之间的作用。3) 第二结合位点,该位点不在PTP1B的保守区域,位于活性中心附近 [10] 。根据以上结构分析,为我们筛选具有更高亲和性和选择性的PTP1B抑制剂奠定了重要的理论基础。PTP1B的结构见图1。
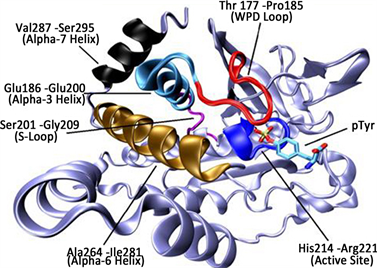
Figure 1. X-ray crystallography of PTP1B
图1. PTP1B的X衍射图
3. PTP1B与2型糖尿病的关系
PTP1B的高表达与2型糖尿病的发生有着密切的联系,当细胞内PTP1B的浓度较高时会引起胰岛素抵抗,从而引发2型糖尿病 [11] 。McGuire等人发现,与胰岛素敏感受试者相比胰岛素抵抗的受试者具有更高的体脂百分比和更高的血糖,肌肉组织中具有较高水平的PTP1B [12] 。Dadke等人发现PTP1B可以与胰岛素受体相互作用从而阻碍胰岛素信号的传导,PTP1B敲除的小鼠具有较强的胰岛素敏感性,胰岛素抵抗的糖尿病大鼠体内发现了较高水平的PTP1B [13] 。在瞬时转染的脂肪细胞中发现了高水平的PTP1B,PTP1B的过度表达会导致GLUT4介导的葡糖糖转运减少 [14] 。
3.1. PTP1B与胰岛素抵抗
PTP1B是胰岛素信号转导重要的负调控因子,可以使胰岛素受体及其底物去磷酸化而失活,阻断胰岛素信号的传导。Cicirelli等人通过向爪蟾卵母细胞中注射PTP1B来研究其体内葡萄糖的代谢水平,结果显示PTP1B可以抑制胰岛素信号途径 [15] 。Klaman等人通过基因敲除研究发现,PTP1B基因敲除的小鼠对胰岛素的敏感性要显著强于野生型小鼠,肝脏组织中胰岛素受体磷酸化水平显著增强(P < 0.05) [16] 。
3.2. PTP1B与胰岛β细胞损伤
研究发现,在2型糖尿病动物模型的中存在明显的β细胞功能受损的现象,会导致β细胞分泌胰岛素减少 [17] 。吴鸿采用Ad-PTP1B腺病毒转染实验,构建胰岛β细胞PTP1B过表达模型,观察PTP1B的含量对胰岛β细胞的分泌功能的影响。观察到PTP1B在胰岛细胞中的表达对β细胞胰岛素分泌功能有显著降低作用 [18] 。Kushner等人通过实验证明,PTP1B敲除小鼠胰岛β细胞的面积明显小于正常小鼠,胰岛素分泌量减少。如果同时剔除PTP1B和胰岛素受体底物-2,则小鼠胰岛β细胞的面积变大 [19] 。由此可见PTP1B可以调节胰岛β细胞的动态平衡。
3.3. 参与瘦素信号传导
瘦素是一种可以调节人体脂肪含量的激素,它是由脂肪组织分泌的 [20] 。研究发现,在糖尿病动物模型中存在着瘦素代谢紊乱的现象,瘦素代谢异常会导致肥胖的发生。PTP1B在瘦素信号的传导过程中起着重要作用,可以使瘦素受体相关激酶JAK-2去磷酸化而失活 [21] ,从而阻断瘦素信号的传导。与野生型小鼠相比,PTP1B基因敲除的小鼠瘦素敏感性升高,瘦素引起的下丘脑转化及转录活化因子-3酪氨酸磷酸化水平升高 [22] ,最终导致其食欲受到抑制,脂肪组织减少,体重下降。
4. 天然PTP1B抑制剂的研究进展
PTP1B是胰岛素信号传导过程中重要的负调节因子,是近年来发现的用于治疗2型糖尿病的新靶点。在胰岛素敏感细胞中使用PTP1B抑制剂可以促进胰岛素受体及其底物的磷酸化,增加葡萄糖的摄取,对糖尿病的治疗可以产生显著效果。抑制PTP1B可以增强胰岛素的敏感性、调节脂肪代谢,对2型糖尿病、肥胖症和高血脂都具有很好的治疗效果 [23] 。我国植物资源丰富,通过对天然产物进行提取,可以得到一些具有活性的PTP1B抑制剂。以此类天然产物为母核结构,对其化学结构进行修饰,从而制备高效的2型糖尿病治疗药物,具有广泛的研究前景。近年来,对天然产物的开发和利用逐渐成为科学研究的热点,引起了国内外研究人员的广泛重视。我国研究人员充分利用丰富的植物资源,从天然产物中分离出大量结构新颖的PTP1B抑制剂,为2型糖尿病的治疗提供了广阔的研究平台。本文将根据天然PTP1B抑制剂的类型,对其进行简要综述。
4.1. 溴酚类化合物
研究发现,海藻中富含种类丰富的天然卤酚类化合物,其中,溴酚类化合物不仅具有新颖的化学结构,还表现出广泛的药理活性,包括PTP1B抑制活性、抗肿瘤活性、α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性等 [24] 。Liu等人从红藻中纯化出溴酚化合物1、2,显示非常有效的PTP1B抑制活性,IC50值分别为3.9和3.5 μM [25] 。这些初步数据表明溴酚衍生物中溴原子和侧链的数量可能影响其PTP1B的抑制活性。朱承根,田金英等人在大量前期研究的基础上,制备了新型溴酚衍生物3~11,并初步探讨了其结构中羟基、溴原子的数目及位置的变化以及苄基醚烷基链的长度对PTP1B抑制活性的影响 [26] 。体外PTP1B抑制活性实验结果显示:烷基链为三个碳原子的溴酚化合物活性最好;二溴代物比单溴、三溴代物活性好,就二溴代物而言,两个溴原子处于邻位的活性高于处于对位的活性;酚羟基被甲醚化后化合物的活性降低。杨猛等人通过对海洋藻类的提取分离得到了溴酚类化合物BPN,通过对BPN进行结构修饰得到了新型结构的HPN,其体外PTP1B抑制活性增强。通过对HPN的异丙氧基进行修饰,设计合成新型化合物12、13 [27] 。体外PTP1B抑制活性检测结果显示:接入噻唑环结构的化合物PTP1B酶抑制活性较高,在溴酚类化合物中引入噻唑环结构,可以模拟磷酸化酪氨酸(pTyr)底物,竞争性地与PTP1B的活性位点结合,从而抑制PTP1B的作用,改善化合物的活性。吴国耀等人利用杂环化合物(2,4-噻唑烷二酮、海因)对海藻中提取的卤代苯酚类化合物进行结构修饰,合成化合物14~19,提高对PTP1B的抑制活性 [28] 。通过对结构进行分析发现酚羟基的引入,溴原子数目的增加能够提高对PTP1B的抑制作用。化合物1~19的结构见图2。
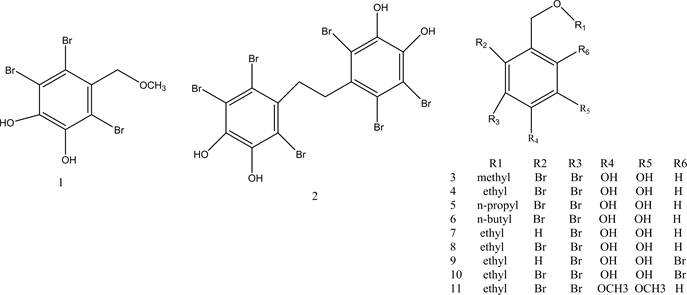

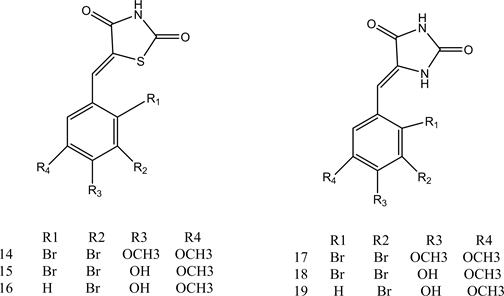
Figure 2. Structure of compounds 1~19
图2. 化合物1~19的结构
4.2. 黄铜类化合物
类黄铜是广泛分布于植物界的多酚化合物,由15个碳原子组成,其基本结构特征是由两个苯环通过3碳键连接而成 [29] 。研究发现黄铜类化合物具有广泛的生物性质,包括抗过敏,抗炎,抗糖尿病等,一些类黄酮还具有PTP1B抑制活性 [30] 。Paoli等人通过大量前期研究发现morin具有潜在的抗糖尿病活性,可以激活胰岛素代谢途径并充当胰岛素敏化剂,具有较强的PTP1B抑制活性 [31] 。并通过进一步筛选得到了具有较好PTP1B抑制活性的类黄酮化合物20~22。研究表明槲皮素 [32] ,木犀草素 [33] ,芹菜素 [34] 和山奈酚 [35] 等类黄酮都具有PTP1B抑制活性。Progenca等人以上述物质为原料合成类黄酮化合物23~27 [36] 。对其体外PTP1B抑制活性进行测定,结果显示化合物26、27具有最佳抑制活性,IC50值分别为10 ± 1 μM和16 ± 2 μM。表明弱极性取代基,-OBn和-OMe基团增加了PTP1B抑制能力。Quang的观点与其一致,他认为黄酮类化合物存在极性较小的取代基结构通常有利于对PTP1B的抑制活性,而添加极性基团,如-OH,可能会降低它们抑制PTP1B的能力 [37] 。Cui等人通过对刺桐类植物的研究,分离出具有PTP1B抑制活性的黄酮类化合物28-30,提出了化合物具有异戊二烯基结构会表现出强烈的PTP1B抑制活性 [38] 。这表明异戊二烯基部分在黄酮类抑制剂中起重要作用。Zhang等人合成了一系列唑基黄酮类化合物,通过对其PTP1B抑制活性进行考察发现三唑基黄酮化合物31具有最佳抑制活性,IC50值为1.6 μM,且具有较低的细胞毒性 [39] 。化合物20~31的结构见图3。
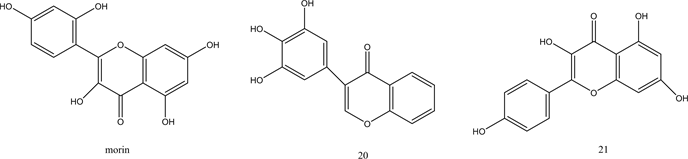
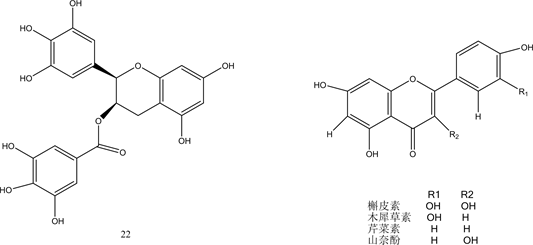
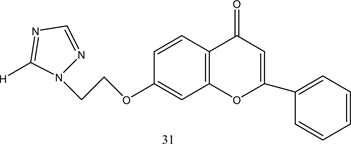
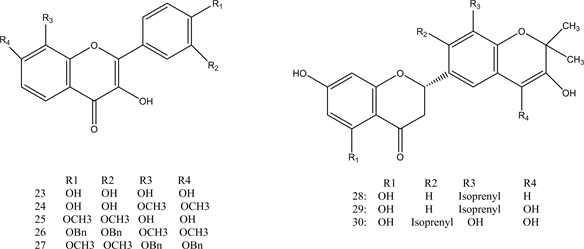
Figure 3. Structure of compounds 20~31
图3. 化合物20~31的结构
4.3. 萜类化合物
倍半萜类被认为是具有PTP1B抑制活性的化合物,许多科学家都发现了倍半萜类PTP1B抑制剂。Huang等人从海绵中提取了具有强烈PTP1B抑制活性的倍半萜类化合物32,其IC50值为1.9 μg/mL [40] 。Choi等人从雪莲花根中提取了倍半萜类PTP1B抑制剂33、34 [41] 。Abdjul等人从海绵中提取了具有强烈PTP1B抑制活性的倍半萜类化合物35~38 [42] 。Jung等人从龙牙草的根中提取出一系列二帖类化合物,其中化合物39、40具有强烈的PTP1B抑制活性 [43] ,表明二萜类化合物的分子类型和分子中存在的取代基种类对化合物的活性至关重要。来自G. pentaphyllum的三萜类化合物41-44显示出较强的PTP1B抑制活性 [44] 。Li等人报道了七种类型的三萜类化合物45~51,具有对PTP1B的强抑制作用,具有4.1至13.6 μM的低IC50值 [45] 。以上信息说明,天然来源的萜类化合物可能是PTP1B抑制剂的良好候选物。化合物32~51的结构见图4。

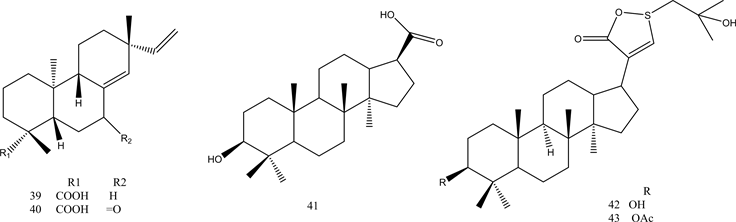
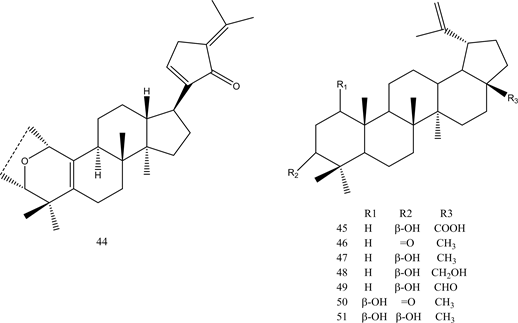
Figure 4. Structure of compounds 32~51
图4. 化合物32~51的结构
4.4. 香豆素类化合物
香豆素是天然存在的芳香杂环类的一种,于1822年首次从Dipteryx odorata中分离出来 [46] ,具有广泛的生物活性,如抗微生物,抗肿瘤、抗血小板聚集和抗癌活性等 [47] 。两种来自Artemisia capillaris的香豆素衍生物52、53表现出良好的PTP1B抑制活性 [48] 。Ali等人从草本植物Angelica decursiva中鉴定出有效的抗糖尿病药物,对其进行进一步提取分离出天然香豆素衍生物54~57,并对其PTP1B抑制活性进行评估,结果显示所有香豆素均具有显著PTP1B抑制活性 [49] 。来自Angelica keiskei的茎的香豆素衍生物58~61,经证实具有PTP1B的抑制活性 [50] 。化合物52~61的结构见图5。
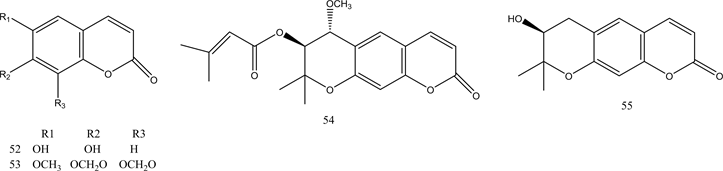
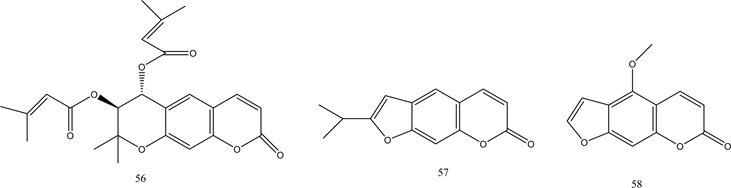
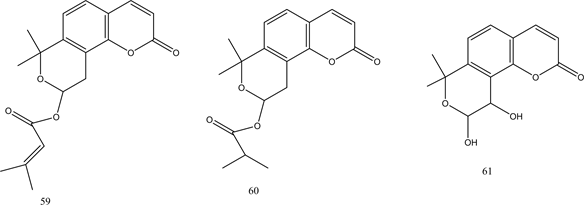
Figure 5. Structure of compounds 52~61
图5. 化合物52~61的结构
4.5. 其他类化合物
Henki等人从海绵中提取出新型PTP1B抑制剂Cladosporamide A,其IC50值为48 μM [51] 。Feng等人从绿藻中分离出了2个具有PTP1B抑制活性的香草酸类化合物62、63 [52] 。Liang等人发现多羟基类固醇PTP1B抑制剂64 [53] 。化合物65、66是从绿藻中提取的两种生物碱,显示有效的PTP1B抑制活性 [54] 。另外,Steinmann等人提出饱和脂肪酸如棕榈酸、硬脂酸、花生酸,不饱和脂肪酸如岩芹酸、油酸、亚麻酸均可以表现出对PTP1B的强烈抑制 [55] 。这些脂肪酸的PTP1B抑制作用与双键的数目无关,它们取决于碳原子的数量。从海洋真菌中提取出来的具有不饱和脂肪酸侧链的化合物67,对PTP1B活性显示出强烈的抑制作用 [56] 。Chen等人从黄莲中发现了具有PTP1B抑制活性的木质素类化合物68~72 [57] 。化合物62~72的结构见图6。

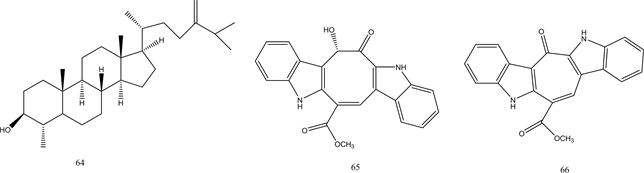
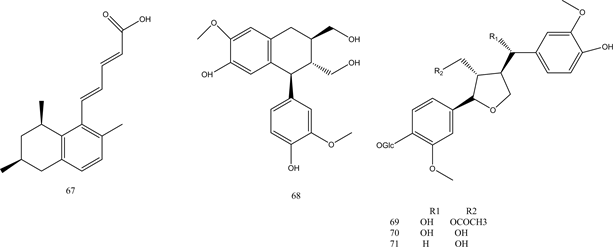
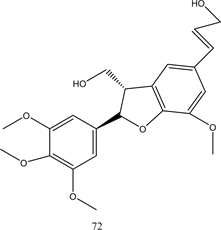
Figure 6. Structure of compounds 62~72
图6. 化合物62~72的结构
5. 展望
作为抗2型糖尿病的新靶点,关于PTP1B及其抑制剂的研究引起了国内外研究人员的广泛关注。我国开展了大量有关PTP1B抑制剂的药物设计和合成研究,发现了大量选择性高的特异性抑制剂。目前,虽然很多PTP1B抑制剂都表现良好的生物活性,但是PTP1B与PTPs的活性结构和结合位点有一定的相似性,使其抑制剂对PTP1B的选择性较差,限制了它的成药性,因此开发高效的PTP1B抑制剂是未来的研究重点。中国植物资源丰富,植物药开发潜力巨大,加强抑制PTP1B天然植物活性成分的研究可以为2型糖尿病的治疗提供新的途径。
文章引用
郭忠秋,王 欣,韩佳婧,刘 宇. 天然蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1B抑制剂的研究进展
Research Progress on Inhibitors of Natural Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B[J]. 药物资讯, 2018, 07(06): 129-140. https://doi.org/10.12677/PI.2018.76022
参考文献
- 1. 刘永贵, 解学星, 吴疆, 等. 治疗2型糖尿病的新靶点药物研究进展[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2015, 30(2): 222-227.
- 2. 孟艳秋, 刘文虎, 刘凤鑫, 等. 抗2型糖尿病药物研究进展[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2013, 28(3): 461-464.
- 3. Maheshwari, N., Karthikeyan, C., Trivedi, P., et al. (2018) Recent Advances in Protein Tyrosine Phos-phatase 1B Targeted Drug Discovery for Type II Diabetes and Obesity. Current Drug Targets, 19, 551-575.
- 4. Chen, X., Gan, Q., Feng, C.G., et al. (2018) Virtual Screening of Novel and Selective Inhibitors of Protein Tyrosine Phospha-tase 1B over T-Cell Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Using a Bidentate Inhibition Strategy. The Journal of Chemical In-formation and Modeling, 58, 837-847. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00040
- 5. 王欣, 许潇, 孙瑞, 等. 蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶1B及其小分子抑制剂的研究进展[J]. 北方药学, 2014, 11(11): 92-94.
- 6. 刘霞, 冯长根. 蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1B抑制剂研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2012, 30(10): 72-79.
- 7. Hajfg, B.J. (2015) Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Substrates and Metabolic Regulation. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 37, 58-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.09.020
- 8. Barford, D., Flint, A.J. and Tonks, N.K. (1994) Crystal Struc-ture of Human Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B. Science, 263, 1397-1404. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8128219
- 9. Xiao, P., Wang, X., Wang, H.M., et al. (2014) The Second-Sphere Residue T263 Is Important for the Function and Catalytic Activity of PTP1B via Interaction with the WPD-Loop. Inter-national Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 57, 84-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2014.10.004
- 10. Puius, Y.A., Zhao, Y., Sullivan, M., et al. (1997) Indentification of a Second Aryl Phosphate-Binding Site in Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B: A Paradigm for Inhibitor Design. Bio-chemistry, 94, 13420-13425.
- 11. Panzhinskiy, E., Ren, J. and Nair, S. (2013) Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B and Insulin Resistance: Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress/Reactive Oxygen Species/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Axis. PLoS ONE, 8, e77228. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077228
- 12. Mcguire, M.C., Fields, R.M., Nyomba, B.L., et al. (1991) Ab-normal Regulation of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Activities in Skeletal Muscle of Insulin-Resistant Humans. Diabetes, 40, 939-942. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.40.7.939
- 13. Dadke, S.S., Li, H.C., Kusari, A.B., et al. (2000) Elevated Expression and Activity of Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B in Skeletal Muscle of Insulin-Resistant Type II Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 274, 583-589. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.3188
- 14. Chen, H., Wertheimer, S.J., Lin, C.H., et al. (1997) Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatases PTP1B and Syp Are Modulators of Insulin-Stimulated Translocation of GLUT4 in Transfected Rat Adi-pose Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 8026-8031. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.12.8026
- 15. Cicirelli, M.F., Tonks, N.K., Diltz, C.D., et al. (1990) Microinjection of a Protein-Tyrosine-Phosphatase Inhibits Insulin Action in Xenopus Oocytes. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of USA, 87, 5514-5518. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.14.5514
- 16. Klaman, L.D., Boss, O., Peroni, O.D., et al. (2000) Increased Energy Expenditure, Decreased Adiposity, and Tissue Specific Insulin Sensitivity in Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B-Deficient Mice. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 20, 5479-5489. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.20.15.5479-5489.2000
- 17. Fernandez, R.R., Vieira, E., Garcia, R.P.M., et al. (2014) Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B Modulates Pancreatic β-Cell Mass. PLoS ONE, 9, e90344. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090344
- 18. 吴鸿. 蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶1B对β细胞胰岛素分泌功能及其胰岛素信号转导通路的影响[D]: [博士学位论文]. 上海: 第二军医大学内分泌与代谢病专业, 2009.
- 19. Kushner, J.A., Haj, F.G., Klaman, L.D., et al. (2004) Islet-Sparing Effects of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B Deficiency Delays Onset of Diabetes in InsRS2 Knockout Mice. Diabetes, 53, 61-66. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.53.1.61
- 20. 郭伍斌, 马新, 刘翔. 血清胰岛素、瘦素及CRP在乳腺癌合并2型糖尿病患者中的表达水平及其临床意义[J]. 中国医学创新, 2017, 14(3): 13-16.
- 21. Lund, I.K., Hansen, J.A., Andersen, H.S., et al. (2005) Mechanism of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B-Mediated Inhibition of Leptin Signalling. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 34, 339-351. https://doi.org/10.1677/jme.1.01694
- 22. Cheng, A., Uetanli, E.N., Simoncic, P.D., et al. (2002) Attenuation of Leptin Action and Regulation of Obesity by Protein Tyrosine Phos-phatase 1B. Developmental Cell, 2, 497-503. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00149-1
- 23. 张雪莲, 郑海洲, 郑智慧. PTP1B作为药物靶点的研究进展[J]. 国外医药抗生素分册, 2017, 38(4): 173-178.
- 24. Liu, M., Han-sen, P.E. and Lin, X.K. (2011) Bromophenols in Marine Algae and Their Bioactivities. Marine Drugs, 9, 1273-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9071273
- 25. Liu, X., Li, X.M., Gao, L.X., et al. (2011) Extraction and PTP1B Inhibi-tory Activity of Bromophenols from the Marine Red Alga Symphyocladia latiuscula. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 29, 686-690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-0136-1
- 26. 朱承根, 田金英, 叶菲, 等. 溴酚衍生物的合成及其蛋白酪氨酸磷脂酶1B抑制剂活性研究[J]. 中国药物化学杂志, 2015, 25(6): 424-429.
- 27. 杨猛, 高天虹. 原料药HPN制备工艺的优化以及新型PTP1B抑制剂的设计、合成以及生物活性研究[D]: [硕士学位论文]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2015.
- 28. 吴国耀. 蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶1B抑制剂的化学合成及活性研究[D]: [硕士学位论文]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2015.
- 29. Halbwirth, H. (2010) The Creation and Physiological Relevance of Divergent Hydroxylation Pat-terns in the Flavonoid Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 11, 595-621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11020595
- 30. Kumar, S. and Pandey, A.K. (2013) Chemistry and Biological Activities of Flavonoids: An Overview. The Scientific World Journal, 2013, Article ID: 162750.
- 31. Paoli, P., Cirri, P., Caselli, A., et al. (2013) The Insulin-Mimetic Effect of Morin: A Promising Molecule in Diabetes Treatment. Biochimica et Bio-physica Acta, 1830, 3102-3111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.01.017
- 32. Jiang, L., Numonov, S., Boba-kulov, K., et al. (2015) Phytochemical Profiling and Evaluation of Pharmacological Activities of Hypericum scabrum L. Molecules, 20, 11257-11271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200611257
- 33. Choi, J.S., Islam, M.N., Ali, M.Y., et al. (2014) The Effects of Cglycosylation of Luteolin on Its Antioxidant, Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease, Anti-Diabetic, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 37, 1354-1363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0351-3
- 34. Choi, J.S., Islam, M.N., Ali, M.Y., et al. (2014) Effects of C-Glycosylation on Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Apigenin. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 64, 27-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.020
- 35. Na, B., Nguyen, P.H., Zhao, B.T., et al. (2016) Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) Inhibitory Activity and Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of Compounds Isolated from Agrimo-nia pilosa. Pharmaceutical Biology, 54, 474-480. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2015.1048372
- 36. Progenca, C., Freitas, M., Ribeiro, D., et al. (2017) Inhibi-tion of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B by Flavonoids: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 111, 474-481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.11.039
- 37. Quang, T.H., Ngan, N.T.T., Yoon, C.S., et al. (2015) Protein Tyro-sine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors from the Roots of Cudrania tricuspidata. Molecules, 20, 11173-11183. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200611173
- 38. Cui, L., Thuong, P.T., Lee, H.S., et al. (2008) Flavanones from the Stem Bark of Erythrina abyssinica. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 16, 10356-10362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2008.10.012
- 39. Zhang, L., Ge, Y., Song, H.M., et al. (2018) Design, Synthesis of Novel Azolyl Flavonoids and Their Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B Inhibitory Activities. Bioorganic Chemistry, 80, 195-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.06.008
- 40. Huang, X.C., Li, J., Li, Z.Y., et al. (2008) Sesquiter-penes from the Hainan Sponge Dysidea septosa. Journal of Natural Products, 71, 1399-1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/np8002035
- 41. Choi, J.Y., Na, M., Hwang, I.H., et al. (2009) Isolation of Betulinic Acid, Its Methyl Ester and Guaiane Sesquiterpenoids with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from the Roots of Saussurea lappa C.B. Clarke. Molecules, 14, 266-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14010266
- 42. Abdjul, D.B., Yamazaki, H., Takahashi, O., et al. (2016) Sesquiterpene Hydroquinones with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activities from a Dysidea sp. Marine Sponge Collected in Okinawa. Journal of Natural Products, 79, 1842-1847. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00367
- 43. Jung, H.J., Jung, H.A., Kang, S.S., et al. (2012) In-hibitory Activity of Aralia continentalis Roots on Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B and Rat Lens Aldose Reductase. Ar-chives of Pharmacal Research, 35, 1771-1777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1009-7
- 44. Zhang, X.S., Bi, X.L., Wan, X., et al. (2013) Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Effect by Dammarane-Type Triterpenes from Hydrolyzate of Total Gynostemma pentaphyl-lum Saponins. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 23, 297-300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.10.097
- 45. Li, J.L., Lli, N., Zhang, N., et al. (2014) Lupane Terpenoids Iso-lated from Betula platyphylla Suk of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity. Natural Product Research and Development, 26, 1398-1401.
- 46. Jain, P.K. and Joshi, H. (2012) Coumarin: Chemical and Pharmacological Profile. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 2, 236-240.
- 47. Ishita, I.J., Nurul, I.M., Kim, Y.S., et al. (2016) Couma-rins from Angelica decursiva Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Nitrite Oxide Production in RAW 264.7 Cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 39, 115-126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0668-6
- 48. Nuru, I.M., Jung, H.A., Sohn, H.S., et al. (2013) Potent a-Glucosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors from Artemisia capillaris. Archives of Pharmacal Re-search, 36, 542-552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0069-7
- 49. Ali, M.Y., Jannat, S., Jung, H.A., et al. (2016) Coumarins from Angelica decursiva Inhibit a-Glucosidase Activity and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 252, 93-101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.04.020
- 50. Li, J.L., Gao, L.X., Meng, F.W., et al. (2015) PTP1B Inhibitors from Stems of Angelica keiskei (Ashitaba). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 25, 2028-2032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.04.003
- 51. Henki, R., Hiroyuki, Y., Shino, S., et al. (2018) Cladosporamide A, a New Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitor, Produced by an Indonesian Marine Sponge-Derived Cladosporium sp. Journal of Natural Medicines, 72, 779-783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1193-y
- 52. Feng, Y.J., Carroll, A.R., Addepalli, R., et al. (2017) Vanillic Acid Derivatives from the Green Algae Cladophora socialis as Potent Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors. Journal of Natural Products, 70, 1790-1792. https://doi.org/10.1021/np070225o
- 53. Liang, L.F., Wang, X.J., Zhang, H.Y., et al. (2013) Bioactive Polyhydrox-ylated Steroids from the Hainan Soft Coral Sinularia depressa Tixier-Durivault. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Let-ters, 23, 1334-1337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.12.087
- 54. Yang, H., Liu, D.Q., Liang, T.J., et al. (2014) Racemosin C, a Novel Minor Bisindole Alkaloid with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B Inhibitory Activity from the Green Alga Caulerpa racemosa. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, 16, 1158-1165. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2014.965162
- 55. Steinmann, D., Baumgarther, R.R., Heiss, E.H., et al. (2012) Bioguided Isolation of (9Z)-Octadec-9-Enoic Acid from Phellodendron amurense Rupr. and Identification of Fatty Acids as PTP1B Inhibitors. Planta Medica, 78, 219-224. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1280377
- 56. Quang, T.H., Ngan, N.T.T., Ko, W., et al. (2014) Tanzawaic Acid Derivatives from a Marine Isolate of Penicillium sp. (SF-6013) with Anti-Inflammatory and PTP1B Inhibitory Activities. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 24, 5787-5791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.10.035
- 57. Chen, G.C., Li, X.L., Chen, G., et al. (2016) Isolation and Identification of Lignans Chemical Constituents from Coptis chinen-sis and Their Inhibitory Activity to Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B. China Pharm, 27, 2197-2199.
NOTES
*通讯作者