Advances in Clinical Medicine
Vol.
13
No.
10
(
2023
), Article ID:
73164
,
6
pages
10.12677/ACM.2023.13102136
十二指肠杜氏病致上消化道出血5例临床分析
张金明1,谢永丰1,郝立亮2,郭明晓2,鲁临3,杜超3*
1锦州医科大学临沂市人民医院研究生培养基地,山东 临沂
2临沂市人民医院普外科,山东 临沂
3临沂市人民医院消化内科,山东 临沂
收稿日期:2023年8月26日;录用日期:2023年9月19日;发布日期:2023年9月26日

摘要
目的:探讨发生于十二指肠的杜氏病(Dieulafoy disease)致上消化道出血的临床表现、诊断方法、治疗和预后,以加强对该病的认识,提高其诊治水平。方法:收集临沂市人民医院2020年1月~2023年3月诊断的5例发生在十二指肠的杜氏病致上消化道出血病人的临床资料,分析其临床表现、内镜下特征、治疗方式及预后等特点,并复习相关文献。结果:5例杜氏病患者均因“呕血、黑便”入院。均由胃镜确诊为“杜氏病”。镜下:病灶4例位于十二指肠球部,1例位于十二指肠降部。位于球部的表面可见破裂血管残端及血凝块,伴活动性渗血,其中1例可见“火柴头”样改变;降部的病例胃镜下可见裸露血管残端及血痂。治疗上给予质子泵抑制剂(PPI)针剂、生长抑素、补液等,无效后行急诊内镜检查及治疗:予金属钛夹 + 粘膜下注射1:10,000肾上腺素高渗盐水治疗。预后:经3个月~3年随访,2例病灶复发。结论:杜氏病是上消化道出血少见但重要的病因,多发生于胃,发生于十二指肠和其他部位的较少,但我们分析发现:发生在十二指肠的杜氏病与胃部杜氏病的临床特征并无明显差异。诊断主要依靠电子内镜检查,且内镜下止血治疗是杜氏病的诊治关键,无效时应尽快进行急诊外科手术治疗,此病较为罕见,但因其出血部位隐匿和易反复等特点,必须加强认识,有效降低死亡率。
关键词
杜氏病,十二指肠,上消化道出血,临床特征

Clinical Analysis of 5 Cases of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Caused by Duodenal Dieulafoy’s Disease
Jinming Zhang1, Yongfeng Xie1, Liliang Hao2, Mingxiao Guo2, Lin Lu3, Chao Du3*
1Graduate Training Base of Linyi People’s Hospital, Jinzhou Medical University, Linyi Shandong
2Department of General Surgery, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi Shandong
3Department of Gastroenterology, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi Shandong
Received: Aug. 26th, 2023; accepted: Sep. 19th, 2023; published: Sep. 26th, 2023

ABSTRACT
Objective: To investigate the clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment, and prognosis of Dieulafoy’s disease in the duodenum causing upper gastrointestinal bleeding, in order to enhance understanding of the disease and improve its diagnosis and treatment. Methods: Clinical data of five patients diagnosed with duodenal Dieulafoy’s disease causing upper gastrointestinal bleeding, from January 2020 to March 2023 at Yiyi City People’s Hospital, were collected. The clinical manifestations, endoscopic features, treatment modalities, and prognosis were analyzed, and relevant literature was reviewed. Results: All five patients were admitted with the chief complaints of “hematemesis and melena”. Diagnosis of “Dieulafoy’s disease” was confirmed by gastroscopy in all cases. Microscopically, four lesions were located in the duodenal bulb, and one lesion was located in the descending part of the duodenum. In the bulb region, ruptured vascular remnants and blood clots with active bleeding were observed, with matchstick-like changes seen in one case. In the descending part, exposed vascular remnants and blood scabs were visible. Treatment included proton pump inhibitor (PPI) injections, somatostatin, fluid resuscitation, and blood transfusion. Emergency endoscopy and treatment were performed when conservative management failed, with titanium clips and submucosal injection of 1:10,000 epinephrine saline solution used. Prognosis: Follow-up ranging from 3 months to 3 years revealed lesion recurrence in two cases. Conclusions: Dieulafoy’s disease is a rare but important cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, with a higher incidence in the stomach and a lower incidence in the duodenum and other locations. However, our analysis found that there was no clear difference in the clinical features of Duchenne disease in the duodenum and in the stomach. Diagnosis primarily relies on electronic endoscopy, and endoscopic hemostasis is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of Dieulafoy’s disease. In cases of treatment failure, prompt emergency surgical intervention should be considered. Due to its rarity, concealed bleeding sites, significant blood loss, and propensity for recurrence, understanding of this disease should be enhanced to effectively reduce mortality rates.
Keywords:Dieulafoy’s Disease, Duodenum, Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Clinical Features

Copyright © 2023 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
杜氏病(Dieulafoy disease)是上消化道出血的罕见原因 [1] ,可发生于消化道的任何部位,最常见于胃 [2] 。最初由Gallard于1884年提出,后来在1896年被法国外科医生Georges Dieulafoy更准确地描述为“单纯性溃疡”,他报告了3例因黏膜下层动脉扩张引起致命性胃出血,随后以自己的名字命名。杜氏病亦可称为Dieulafoy溃疡、胃动脉瘤、胃动脉硬化、粘膜下动脉畸形、环状动脉瘤、黏膜下恒径动脉综合征和孤立性单纯性溃疡等 [3] 。在不明原因胃肠道出血中,杜氏因起病隐匿、易反复出血并且难以诊断,成为最危及生命的病因之一,死亡率高达80% [4] 。因杜氏病发病率低,发生于十二指肠的少之又少,检索相关文献,国内仅有零星的病例报道,近五年只有1篇名为“1例ACS患者并发十二指肠杜氏病的临床护理”的文章发表 [5] 。因此本文收集了经内镜证实发生在十二指肠的5例杜氏病引起上消化道出血的患者的临床资料,分析其临床表现、内镜下表现、治疗及预后,并结合相关文献,探究杜氏病在诊断、治疗方面的特点,以提高对该疾病的认识。
2. 临床资料
收集2020年1月~2023年3月临沂市人民医院经内镜证实的5例杜氏病患者的相关资料,分析其临床表现、内镜特征、诊疗方法及预后。其中男性患者3例,女性患者2例,年龄13~71岁,中位年龄50岁,平均年龄44.4岁。电话随访患者,截止时间为2023年6月。
3. 结果
3.1. 临床特征
5位患者均无明显诱因出现大出血,2例内镜检查出合并十二指肠溃疡,1例有饮酒史,1例有肝病病史。其中3例均表现为呕血、黑便,1例表现为反复晕厥,均有贫血、乏力,余1例为无症状健康查体患者。血常规结果血红蛋白明显低于正常值。
3.2. 镜下特征
5例病灶中,4例位于十二指肠球部:表面可见破裂血管残端及血凝块,伴活动性渗血(图1(A)),其中1例可见“火柴头”样改变(图1(B));1例位于十二指肠降部:可见裸露血管残端及血痂。

Figure 1. Gastroscopic findings. (A) A vascular stump can be seen in the duodenal bulb cavity with active bleeding; (B) Ulceration can be seen on the posterior wall of the bulb cavity, and a “matchhead” like change can be seen in the center
图1. 胃镜下表现。(A) 十二指肠球腔可见一血管残端,伴活动性出血;(B) 球腔后壁可见溃疡,中央可见“火柴头”样改变
3.3. 治疗与预后
治疗上起初都给予质子泵抑制剂(PPI)针剂、生长抑素、营养补液治疗,重者予间断输注悬浮红细胞每次2U,效果欠佳,后均行急诊胃镜检查,确诊为十二指肠杜氏病引起的上消化道出血。后进行内镜下治疗,给予金属钛夹 + 粘膜下注射1:10,000肾上腺素高渗盐水(图2),均成功止血,好转出院。随访3个月~3年,1例复查胃镜,金属钛夹已脱落,恢复良好,2例未复查,也未再发生上消化道出血,2例复发。
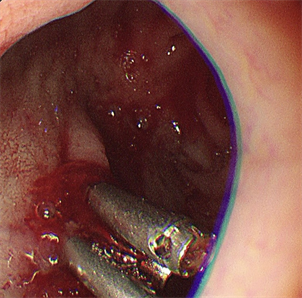
Figure 2. Three metal titanium clips are given for endoscopic treatment
图2. 胃镜下给予三枚金属钛夹治疗
4. 讨论
4.1. 临床特征
黏膜下恒径动脉破裂出血是消化道出血的罕见原因,称为“杜氏病”,是消化道血管畸形的一种特殊类型 [6] ,约占上消化道大出血病因的0.28%,大约是上消化道大出血手术的1.3%~2.3% [7] 。杜氏病的确切病因和发病发病机制尚不明确,多数研究人员认为本病与遗传有关,是一种先天性血管病变 [8] 。可发生于任何年龄,平均发病年龄为50岁,且如今国内外均已有儿童发病病例 [9] [10] 。男性的发病率是没有特定家族史的女性的两倍,Tonguç等人认为:发生于胃的杜氏病好发于男性考虑可能是因为雌激素通过增加前列腺素的合成来保护胃,从而减少胃酸和胃蛋白酶的侵蚀,十二指肠则不然 [11] 。并且使用非甾体抗炎药、阿司匹林或抗血小板药物是杜氏病形成和出血的危险因素 [12] 。本次研究收集的病例未见明显诱因,仅有1例有吸烟、饮酒史,1例有肝病病史。Baxter等人表明:此病可发生于消化道的任何部位:71%发生在胃内,15%发生在十二指肠,8%发生在食管内,6%发生在小肠和结肠 [13] ,也有发生于阑尾 [14] 、支气管 [15] 的病例。杜氏病的临床表现与胃肠道出血相似,包括便血、黑便、吐血、低血压、晕厥及心动过速 [16] ,十二指肠病变患者通常表现为上消化道出血症状,本次研究5例患者中3例有呕血、黑便症状,1例出现反复晕厥。
4.2. 诊断方法
起初杜氏病由于病灶小、周围黏膜外观正常以及出血的间歇性而难以快速做出诊断 [17] ,但是随着内镜的出现,大多数杜氏病(约80%)可在内镜检查中确诊 [18] ,有些病例往往需要多次内镜检查才能做出诊断,本研究中有2例患者行二次胃镜确诊。十二指肠管腔的出血也可能因其他伴随病变(如溃疡)而被忽略,而无经验内镜医生可能会因血凝块或两旁憩室而忽略杜氏病,所以本次我们主要讨论杜氏病的内镜下特点。大致可总结为以下三条:1) 病灶小,多为孤立性黏膜或浅表溃烂,中央可见小动脉破裂出血;2) 非活动性杜氏病病灶呈点状样渗血;3) 黏膜局部浅表溃疡中间有血管走行,呈“火柴头”样表现,常附血凝块或有血痂 [19] 。与典型的消化性溃疡不同,病变部位粘膜缺损没有被炎性细胞浸润包围,并且暴露的动脉具有较大的直径 [20] 。本次研究的十二指肠病例中,胃镜下特征符合上述3条。对于内镜未能发现出血部位的杜氏病,也可行选择性腹动脉造影检查以及手术探查 [21] 。
4.3. 鉴别诊断
十二指肠杜氏病致上消化道出血临床较少见,且临床表现缺乏特异性,易漏诊和误诊。需与以下疾病相鉴别:1) 十二指肠溃疡(DU):十二指肠溃临床上多于胃溃疡,两者之比为3:1,且男性发病率明显高于女性,发生机制与黏膜自身防御–修复因素之间失衡有关,空腹上腹痛是其典型症状,出血是最常见的并发症 [22] ,与杜氏病都是由胃镜检查确诊,十二指肠溃疡镜下可见类圆形或圆形的粘膜缺损,呈单发或多发,表面被覆白苔,周围粘膜充血水肿,或红色新生上皮覆盖。累及血管时则可引起出血,所以可根据临床症状和镜下特点来进行两者鉴别;2) 胃十二指肠动脉瘤(GADD):可分为真性动脉瘤和假性动脉瘤,也是引起上消化道出血的罕见病因,发病率小于0.1%,女性多于男性,约占内脏动脉瘤的1.5%,一旦破裂,死亡率高达70%,确诊的金标准为选择性血管造影 [23] 。3) 十二指肠癌:是一种罕见的癌症,发病率小于0.0005% [24] 。由于其发病率和患病率较低,多数就诊时已属中晚期,首发症状主要为体重减轻和腹痛,还可出现上消化道出血、贫血、消瘦、黄疸和腹部包块,主要依靠十二指肠镜取检做病理检查确诊,手术切除是十二指肠腺癌最基本、最有效的治疗方法。
4.4. 治疗与预后
杜氏病是上消化道出血的原因之一,治疗主要取决于临床表现以及病变部位。患者的血流动力学状态是决定治疗方式的最重要的因素。血流动力学稳定的患者,内镜 + 注射疗法为首选治疗方法,若当患者血流动力学不稳定和内镜治疗失败时,则必须立即进行手术治疗 [11] ,血管造影和栓塞也成为治疗流程中的重要工具 [25] 。Wang等人研究资料显示经及时诊断和内镜治疗的杜氏病治愈率 > 99%,预后良好,死亡率 < 1%,但只经保守治疗患者死亡率则达28% [26] 。本次入组的5个病人全部经内镜下治疗,2人复发,余3人预后良好。
总之,临床上十二指肠杜氏病致上消化道出血较为罕见,因其临床表现缺乏特异性,诊断较为困难,易漏诊误诊,需与其他十二指肠致上消化道出血疾病相鉴别,但其与发生在胃部的杜氏病的临床特征并无明显差异,诊断必须依靠内镜、手术探查及选择性腹动脉造影,一经确诊,也要优先考虑内镜治疗,所以,掌握相关知识,及时诊断和治疗本病,对于挽救患者生命具有十分重要的意义。
基金项目
山东省自然科学基金资助项目(ZR2021MH183和ZR2021MH362)。
声明
本研究已获得病人的知情同意。
文章引用
张金明,谢永丰,郝立亮,郭明晓,鲁 临,杜 超. 十二指肠杜氏病致上消化道出血5例临床分析
Clinical Analysis of 5 Cases of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Caused by Duodenal Dieulafoy’s Disease[J]. 临床医学进展, 2023, 13(10): 15268-15273. https://doi.org/10.12677/ACM.2023.13102136
参考文献
- 1. 黄爱红, 张敏, 孙凯. 杜氏病临床病理分析[J]. 饮食保健, 2021(15): 41.
- 2. Baxter, M. and Aly, E.H. (2010) Dieulafoy’s Lesion: Current Trends in Diagnosis and Management. The Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, 92, 548-554. https://doi.org/10.1308/003588410X12699663905311
- 3. Chaer, R.A. and Helton, S.W. (2003) Dieulafoy’s Disease. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 196, 290-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1072-7515(02)01801-X
- 4. Batouli, A., Kazemi, A., Hartman, M.S., Heller, M.T., Mid-ian, R. and Lupetin, A.R. (2015) Dieulafoy Lesion: CT Diagnosis of This Lesser-Known Cause of Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Clinical Radiology, 70, 661-666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2015.02.005
- 5. 王飞. 1例ACS患者并发十二指肠杜氏病的临床护理[J]. 当代护士(上旬刊), 2018, 25(6): 156-157.
- 6. Al-Mishlab, T. (1999) Dieulafoy’s Lesion: An Obscure Causes of GI Bleeding. Journal of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh, 44, 222-225.
- 7. 赵发宽, 杨家成, 梁伟纲, 吴春波. 腹腔镜胃腔内手术联合胃镜治疗贲门杜氏溃疡出血[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2023, 26(5): 428.
- 8. 周智岱, 詹善治, 夏紫琴, 等. 以胃黏膜下隆起为表现的无症状Dieulafoy病1例并文献复习[J]. 胃肠病学, 2022(6): 26-32.
- 9. 张勇, 涂远艳, 何少珊, 周新龙, 李桢, 王永培. 儿童杜氏病1例报告[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2017, 35(7): 537-539.
- 10. Shibutani, S., Obara, H., Ono, S., Kabeshima, Y., Kawakubo, H., Shito, M., Kakefuda, T., Omori, T., Sato, H., Narimatsu, Y., et al. (2011) Dieulafoy Lesion in the Ileum of a Child: A Case Report. Journal of Pediatric Sur-gery, 46, e17-e19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.01.028
- 11. Ylmaz, T.U. and Kozan, R. (2017) Duode-nal and Jejunal Dieulafoy’s Lesions: Optimal Management. Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology, 10, 275-283. https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S122784
- 12. Shin, H.J., Ju, J.S., Kim, K.D., Kim, S.W., Kang, S.H., Kang, S.H., Moon, H.S., Sung, J.K. and Jeong, H.Y. (2015) Risk Factors for Dieulafoy Lesions in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. Clinical Endoscopy, 48, 228-233. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.228
- 13. Baxter, M. and Aly, E. (2010) Dieulafoy’s Lesion: Current Trends in Diagnosis and Management. Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, 92, 548-554. https://doi.org/10.1308/003588410X12699663905311
- 14. Johnson, A., Oger, M. and Capovilla, M. (2014) Dieulafoy Lesion of the Appendix. Digestive and Liver Disease, 46, E11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2014.04.001
- 15. Lai, L., Lu, Y., Xi, Z., Liu, F., Qian, L., Wang, L. and Zhao, Q. (2023) Pediatric Bronchial Dieulafoy’s Disease with Bronchial Artery Embolization: Two Case Reports. Translational Pediatrics, 12, 79-85. https://doi.org/10.21037/tp-22-294
- 16. Senger, J.-L. and Kanthan, R. (2012) The Evolution of Dieulafoy’s Lesion Since 1897: Then and Now—A Journey Through the Lens of a Pediatric Lesion with Literature Review. Gastroenterol-ogy Research and Practice, 2012, Article ID: 432517. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/432517
- 17. Ibrarullah, M. and Wagholikar, G.D. (2003) Dieulafoy's Lesion of Duodenum: A Case Report. BMC Gastroenterology, 3, Article No. 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-3-2
- 18. Baettig, B., Haecki, W., Lammer, F. and Jost, R. (1993) Dieulafoy’s Disease: Endoscopic Treatment and Follow up. Gut, 34, 1418-1421. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.34.10.1418
- 19. 严利, 陈娟. 杜氏病致消化道出血案例分析[J]. 医学信息, 2019, 32(14): 192.
- 20. Miko, T.L. and Thomázy, V.A. (1988) The Caliber Persistent Artery of the Stomach: A Unifying Approach to Gastric Aneurysm, Dieulafoy's Lesion, and Submucosal Arterial Malformation. Human Pathology, 19, 914-921. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0046-8177(88)80006-6
- 21. 蔡龙娇, 刘媛, 吴蓉, 冷爱民. 小肠血管畸形的治疗进展[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2023, 32(5): 564-568.
- 22. 闫小燕, 王秀敏. 经消化内镜治疗胃溃疡十二指肠溃疡出血的临床效果评价[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志, 2023, 33(3): 76-79.
- 23. 余薇, 杨阳, 邬颖华. 胃十二指肠动脉瘤伴活动性出血1例[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2021, 26(7): 934-935+939.
- 24. Jiang, S., Zhao, R., Li, Y., Han, X., Liu, Z., Ge, W., Dong, Y. and Han, W. (2018) Prognosis and Nomogram for Predicting Postoperative Survival of Duo-denal Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Study in China and the SEER Database. Scientific Reports, 8, Article No. 7940. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26145-6
- 25. Rodriguez, C.T., Bittle, J.S.H., Kwarcinski, T.J., Juarez, S. and Hinshelwood, J.R. (2020) Dieulafoy Lesions and Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Baylor University Medical Center Proceed-ings, 33, 633-634. https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2020.1778405
- 26. 汪兴伟, 张世荣, 陈志惠, 沈小春, 崔红利, 颜綦先, 兰春慧, 王军, 陈东风. 中国消化道Dieulafoy病5145例回顾性文献分析[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2017, 37(7): 462-465.
NOTES
*通讯作者。