Mine Engineering
Vol.
09
No.
01
(
2021
), Article ID:
40047
,
7
pages
10.12677/ME.2021.91012
CO2分压对N80钢腐蚀影响的研究
王媛媛
延长石油集团油气勘探公司采气一厂,陕西 延安

收稿日期:2020年12月20日;录用日期:2021年1月20日;发布日期:2021年1月27日

摘要
为获得CO2分压对N80钢腐蚀的影响规律,提高对N80钢油气管线的腐蚀防护效果。应用高温高压釜实验装置,采用挂片对比试验方法,借助扫描电镜手段,研究了不同CO2分压条件下,N80钢挂片腐蚀产物膜表面形貌、腐蚀产物膜下金属基体表面形貌、挂片横截面腐蚀产物膜特点以及挂片腐蚀速率和挂片表面腐蚀产物膜生长特点。随着CO2分压的增加,挂片表面产生的腐蚀产物膜由薄到厚,由平滑到粗糙;腐蚀速率逐渐增加,且存在峰值腐蚀速率;腐蚀产物膜生成初期,生成过程不均匀,导致局部腐蚀或者蚀斑;腐蚀产物膜存在内、中间、外3层结构,由内到外逐层减薄;内层与中间层结合较差,内层与外层之间存在明显的空隙,易发生严重局部腐蚀。输送含CO2油气管线的腐蚀防护,关键是在投产初期抑制局部腐蚀的发生,一旦腐蚀产物膜均匀发展,将对管线产生较好的防护。
关键词
高压釜,CO2腐蚀,CO2分压,腐蚀产物膜,局部腐蚀
Study on the Effect of CO2 Partial Pressure on the Corrosion of N80 Steel
Yuanyuan Wang
Yanchang Petroleum Group Exploration Company First Gas Plant, Yan’an Shaanxi

Received: Dec. 20th, 2020; accepted: Jan. 20th, 2021; published: Jan. 27th, 2021

ABSTRACT
In order to obtain the influence rule of partial pressure of CO2 on corrosion of N80 steel and improve the corrosion protection effect of N80 steel oil and gas pipeline. With the aid of scanning electron microscope, the effect of CO2 partial pressure on the temperature and pressure of CO2 was studied, the surface morphology of corrosion product film on N80 steel hangers, the surface morphology of metal substrate under the corrosion product film, the characteristics of corrosion product film on Cross section of hangers, the corrosion rate of hangers and the growth characteristics of corrosion product film on hangers surface. With the increase of the partial pressure of CO2, the corrosion product film on the surface of the hanging plate changes from thin to thick, from smooth to rough, the corrosion rate increases gradually with the existence of peak corrosion rate, and the formation process of the corrosion product film is not uniform at the initial stage, there are three layers in the corrosion product film, which are inner, middle and outer layers, and thin from the inner layer to the outer layer, the inner layer and the middle layer combine badly, there is obvious gap between the inner layer and the outer layer, and serious local corrosion occurs easily. The key to the corrosion protection of oil and gas pipelines containing CO2 is to restrain the local corrosion at the beginning of operation.
Keywords:Autoclave, CO2 Corrosion, CO2 Partial Pressure, Corrosion Product Membrane, Local Corrosion

Copyright © 2021 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
随着上世纪80年代,北海油田的大规模开采,尤其是最近十几年注CO2驱油技术在北海油田的大规模应用,西欧、北欧等众多国家均建立了专门的CO2腐蚀研究机构,建设了一流的试验装置,荟萃了众多高水平专业人才,通过对CO2、 、Cl−、流动特性、含水量、腐蚀产物膜等进行模拟研究,获得了大量相关科研成果,有力的指导了管材CO2腐蚀防护。近十年来,水驱、CO2驱等开采技术逐渐应用于国际多数大型油田,含CO2多相流腐蚀引起的腐蚀失效事故越来越多,高温高压恶劣条件下的多相流CO2腐蚀机理引起了国际上相关科研人员的研究热情也取得了有益的科研成果:美国的Zhou以及Vuppu等 [1] - [6] 考虑了多相湍流中CO2分压对腐蚀过程的影响,阐述了原油输送含水,沙子存在、CO2分压以及高Cl−含量等对腐蚀的影响。美国腐蚀专家Jepson教授利用建立的等比例多相流试验环路,开展了高压条件下的段塞流腐蚀试验研究,应用电化学、力学以及微观测试等手段,深入分析了不同CO2分压条件下,段塞流内部空泡对腐蚀产物膜的破坏作用以及由此导致的严重局部腐蚀行为 [7] [8] [9] [10] [11]。美国的Southwestern Louisiana大学 [12]、Illinois大学 [13]、挪威能源研究所 [14],S. Nesic [15],J. Villarreal [16] 等均做了许多有益的工作。本文着重研究湿气环境下,CO2分压对N80钢腐蚀的影响。
2. 实验
实验工具为高温高压釜,不仅可以进行静态实验,亦可进行动态实验,高压釜内配置磁力转动装置,最高转速达到1200 n/min。该设备可同时进行6组对比实验,实验温度0℃~250℃,实验压力0~25 MPa。
实验采用挂片失重法计算腐蚀速率,并借助扫描电镜(SEM)手段从微观层面予以验证。实验选择油套管常用管材N80钢,图1表示N80钢制成的实验挂片和挂片的电镜扫描图,表1表示本次试验所选用N80钢的化学成分(Wt%)。如不做特别说明,采用对比试验,每组试验设置2片相同挂片,每组试验时间168 h,试验温度60℃。

Figure 1. The surface morphology of N80 on no corrosion coupon
图1. 未腐蚀N80钢挂片表面形貌
Table 1. N80 steel composition (Wt %)
表1. N80钢化学成分(Wt%)
3. 实验结果分析
长期以来,CO2腐蚀问题一直是研究热点。干燥的CO2本身不具备腐蚀性,对油气生产系统不产生危害,但溶解在水中的CO2能参与到钢和水相的电化学反应中,CO2在碳氢化合物中的溶解度甚至更大,高达3:1。油气藏中大都会含有一定比例的CO2。因此,CO2会溶解在水和轻烃,对油气生产产生影响。相比其他酸性腐蚀介质,CO2溶于水中形成碳酸或碳酸氢盐导致的腐蚀速率均大于预期,产生碳酸虽为弱酸,但与矿物酸相比,它并没有完全分离,因此CO2溶于水导致的碳酸腐蚀是一个持续过程。碳酸反应的步骤如下 [1]:
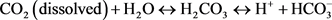
关于CO2腐蚀机理的争论一直存在,但明显的是CO2腐蚀速率与CO2分压有极大关系这将确定溶液pH值和溶解度。事实上,CO2腐蚀电化学反应的完整链要比上述步骤复杂得多。本文主要研究CO2分压对CO2腐蚀机理的影响。
3.1. 腐蚀形貌分析
图2表示CO2分压分别为0.1 MPa、0.5 MPa、1 MPa、2 MPa、2.5 MPa条件下带腐蚀产物膜和不带腐蚀产物膜试验挂片腐蚀形貌。试验后左侧挂片表面不作处理,右侧挂片依据文献 [17] 方法清除腐蚀产物膜。从图2可以看出,试验后挂片表面覆盖一层腐蚀产物膜,但膜厚不均匀,清除腐蚀产物膜后,露出挂片基体金属原色,可以看出挂片出现了不同程度的腐蚀。
 0.1 MPa
0.1 MPa
 0.5 MPa
0.5 MPa
 1 MPa
1 MPa
 2 MPa
2 MPa
 2.5 MPa
2.5 MPa
Figure 2. Test corrosion coupon of different CO2 partial pressure conditions (with corrosion product membrane and scavenging corrosion product membrane)
图2. 不同CO2分压条件试验腐蚀挂片(带腐蚀产物膜、清除腐蚀产物膜)
图3表示应用日立S4800型场发射扫描电子显微镜观测到的CO2分压分别0.1 MPa、0.5 MPa、1 MPa、2 MPa、2.5 MPa条件下试验挂片腐蚀表面形貌聚焦显微图(清除腐蚀产物膜)。从图3中可以看出CO2分压0.1 MPa时,清除腐蚀产物膜后,挂片基体相对完好,但在中部位置存在明显的局部腐蚀,腐蚀产物膜较薄,且表面较光滑,清除腐蚀产物膜后,局部腐蚀深度约为10 μm;CO2分压0.5 MPa时,腐蚀产物膜较薄,表面较光滑,清除腐蚀产物膜后,挂片基体仍然相对完好,挂片表面呈现金属基色,但挂片表面部分呈现暗色斑点,从三维分析图可以看出,虽有斑点,但并未形成局部腐蚀,挂片表面高差仅3 μm;CO2分压1 MPa时,形成的腐蚀产物膜较厚,表面相对光滑,清除腐蚀产物膜后,挂片表面未呈现金属基色,挂片表面成片暗色,且挂片表面颜色呈现波浪状变化,从三维分析图可以看出,挂片表面呈现均匀腐蚀特征,未有明显的局部腐蚀,挂片表面高差仅3 μm;CO2分压2 MPa时,形成的腐蚀产物膜较厚,且腐蚀产物膜表面粗糙,清除腐蚀产物膜后,挂片表面未呈现金属基色,挂片表面呈现明显的局部腐蚀特征,从三维分析图可以看出,局部腐蚀特征明显,挂片表面高差高达15 μm;CO2分压2.5 MPa时,与2 MPa时类似,形成的腐蚀产物膜较厚,表面粗糙,清除腐蚀产物膜后,挂片表面呈暗色,从三维分析图可以看出,局部腐蚀特征明显,挂片表面高差高达18 μm。
 0.1 MPa
0.1 MPa
 0.5 MPa
0.5 MPa
 1 MPa
1 MPa
 2 MPa
2 MPa
 2.5 MPa
2.5 MPa
Figure 3. Micrograph of surface topography of the corrosion hanging surface of different CO2 partial pressure condition (scavenging corrosion product membrane)
图3. 不同CO2分压条件腐蚀挂片表面形貌聚焦显微图(清除腐蚀产物膜)
3.2. 腐蚀产物膜分析
试验挂片腐蚀形貌分析初步了解了不同CO2分压条件对挂片腐蚀的影响,但很难清楚的解释局部腐蚀和均匀腐蚀产生的原因,更不能量化挂片的腐蚀速率。图4表示典型的带腐蚀产物膜挂片横截面聚焦显微图,从图4可以看出挂片横截面腐蚀产物膜呈现明显的内、中、外三层结构,其特点包括:1) 腐蚀产物膜由内到外逐层减薄;2) 腐蚀产物膜内层与中间层之间的结合较差(图中阴影部分明显),内层与外层之间存在明显的空隙,极易渗入腐蚀介质,产生严重的缝隙腐蚀,进而导致严重的局部腐蚀;3) 内层腐蚀产物膜与金属基体之间结合较紧密,但也存在部分阴影,导致如图4所示的局部腐蚀,说明腐蚀产物膜在形成的过程中易形成局部腐蚀,这较好的解释了2.1节中CO2分压0.1、0.5MPa时,挂片表面腐蚀产物膜较薄,如图5所示,试验挂片表面易形成局部腐蚀;CO2分压2、2.5MPa时,挂片表面腐蚀产物膜虽然较厚(如图5所示),但仍产生严重的局部腐蚀。

Figure 4. Micrograph of the cross-section focusing of the corrosion product film
图4. 带腐蚀产物膜挂片横截面聚焦显微图

Figure 5. Micrograph of the cross-section focusing of the corrosion product film in 0.5 MPa and 2.5 MPa CO2 partial pressure
图5. 0.5 MPa和2.5 MPa CO2分压条件带腐蚀产物膜挂片横截面聚焦显微图
3.3. 腐蚀速率分析
图6表示挂片均匀腐蚀速率和腐蚀产物膜质量随CO2分压的变化,从图6可以看出随着CO2分压的增加,产生的腐蚀产物膜质量不断增加,但增速逐渐减缓,直至稳定,这表明外层与中间层腐蚀产物膜的结合力较小,不易形成较厚、且结合力紧密的腐蚀产物膜。均匀腐蚀速率随CO2分压的增加,先增大后减小,当CO2分压达到2.5 MPa时,挂片腐蚀速率达到最高,随着CO2分压继续增加,均匀腐蚀速率反而减少,依据2.2节的分析,可以知道CO2分压持续增加,虽然均匀腐蚀速率减小,但局部腐蚀或缝隙腐蚀会增加,管线极易出现穿孔泄露甚至断裂。

Figure 6. Corrosion rate and corrosion product film quality of different CO2 subpressure conditions
图6. 不同CO2分压条件挂片腐蚀速率和腐蚀产物膜质量
4. 结论
1) 随着CO2分压的增加,挂片表面产生的腐蚀产物膜由薄到厚,逐渐增加;腐蚀速率也逐渐增加,但不同的CO2分压,存在峰值腐蚀速率,峰值腐蚀速率的存在不意味着腐蚀会随着CO2分压增加而减弱,反而会产生严重的局部腐蚀或缝隙腐蚀。
2) 不同CO2分压条件下,腐蚀产物膜生成初期,虽然较致密,与金属基体的结合要较强,但因生成过程的不均匀,导致初期局部腐蚀或者蚀斑已经存在,为以后严重局部腐蚀的发展埋下了隐患,因此输送含CO2油气管线腐蚀的防护,关键是在投产初期抑制局部腐蚀的发生,一旦腐蚀产物膜均匀发展,将对管线产生较好的防护。
3) 不同CO2分压条件下,腐蚀产物膜存在内、中间、外3层结构,腐蚀产物膜由内到外逐层减薄;腐蚀产物膜内层与中间层之间的结合较差,内层与外层之间存在明显的空隙,极易渗入腐蚀介质,进而导致严重的局部腐蚀;内层腐蚀产物膜与金属基体之间结合虽然较紧密,但在腐蚀产物膜形成过程中易形成局部腐蚀。
文章引用
王媛媛. CO2分压对N80钢腐蚀影响的研究
Study on the Effect of CO2 Partial Pressure on the Corrosion of N80 Steel[J]. 矿山工程, 2021, 09(01): 81-87. https://doi.org/10.12677/ME.2021.91012
参考文献
- 1. Crolet, J.L. (1994) Predicting CO2 Corrosion in the Oil and Gas Industry. The Institute of Materials, London.
- 2. Hong, T., Sun, Y.H. and Jepson, W.P. (2002) Study on Corrosion Inhibitor in Large Pipelines Under Multiphase Flow Using EIS. Corrosion Science, 44, 101-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(01)00052-X
- 3. Wang, S.H. and Nesic, S. (2003) On Corrosion and Multiphase Flow Models. CORROSION/03, Paper No. 631, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 4. Choi, Y.S., Nesic, S. and Young, D. (2010) Effect of Impurities on the Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in Supercritical CO2-Water Environments. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 23, 9233-9238. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102578c
- 5. Choi, Y.S. and Nesic, S. (2009) Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in Supercritical CO2-Water Environments. CORROSION/2009, Paper No. 09256, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 6. 陈长风, 路民旭, 赵国仙, 白真权, 等. N80 钢 CO2 腐蚀电极过程交流阻抗分析[J]. 金属学报. 2002, 38(7): 770-774. http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2002.07.021
- 7. Jepson, W.P., Stitzel, S., Kang, C. and Gopal, M. (1997) Model for Sweet Corrosion in Horizontal Multiphase Slug Flow. CORROSION/97, Paper No. 11, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 8. Gopal, M. and Rajappa, S. (1999) Effect of Multiphase Slug Flow on the Stability of Corrosion Product Layer. CORROSION/99, Paper No.46, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 9. Hong, T., Shi, H., Wand, H., Gopal, M. and Jepson, W.P. (2000) EIS Study of Corrosion Product Film in Pipelines. CORROSION, Paper No.44, National As-sociation of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 10. Wang, S.H. and Nesic, S. (2003) On Coupling CO2 Corrosion and Multiphase Flow Models. CORROSION/03. Paper No. 631, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Hou-ston.
- 11. Wang, H.W., Cai, J.Y. and Jepson, W.P. (2002) CO2 Corrosion Mechanistic Modeling and Prediction in Porizontal Slug Flow. CORROSION/02, Paper No. 238, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Hou-ston.
- 12. Garber, J.D. and Palaki, V. (1998) Modeling Corrosion Rates in Non-Annular Gas Condensate Wells Con-taining CO2. CORROSION/98, Paper No. 53, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 13. Heuer, J.K. and Stubbins, J.F. (1998) Microstructure Analysis of Coupons Exposed to Carbon Dioxide Corrosion in Multiphase Flow. CORROSION, 54, 566-575. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3284885
- 14. Nyborg, R., Andersson, P. and Nordsveen, M. (2000) Implementation of CO2 Corrosion Models in a Three-phase Fluid Flow Model. CORROSION, Paper No. 48, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 15. Yang, Y., Bruce, B. and Srdjan, N. (2010) Mechanical Strength And Removal of a Protectiveiron Carbonate Layer Formed on Mild Steel in CO2 Corrosion. CORROSION/2010, Paper No. 10383, National Association of Colleges and Employers, Houston.
- 16. Villarreal, J., Laverde, D. and Fuentes, C. (2006) Carbon-Steel Corrosion in Multiphase Slug Flow and CO2.Corrosion Science, 48, 2363-2379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.09.003
- 17. 崔铭伟. 多相流海管CO2内腐蚀及剩余强度研究[D]: [博士学位论文]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2014.
