Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.
08
No.
12
(
2019
), Article ID:
33432
,
4
pages
10.12677/AAM.2019.812230
The Dynamics of Lotka Volterra Competition Model
Sheng Xiao, Huayong Zhang*
North China Electric Power University, Beijing

Received: Nov. 20th, 2019; accepted: Dec. 6th, 2019; published: Dec. 13th, 2019

ABSTRACT
In this paper, an improved Lotka-Volterra model is established. Through the dynamic analysis of the model, the stability of the equilibrium point and the occurrence conditions of several kinds of bifurcations are explored.
Keywords:Equilibrium Point, Bifurcation, Dynamics

Lotka-Volterra竞争模型的动力学研究
肖晟,张化永*
华北电力大学,北京

收稿日期:2019年11月20日;录用日期:2019年12月6日;发布日期:2019年12月13日

摘 要
本文建立了一个Lotka-Volterra改进模型,通过对模型的动力学分析探究平衡点的稳定性以及几类分岔的发生条件。
关键词 :平衡点,分岔,动力学

Copyright © 2019 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
食物网动力学模型一直是理论生态学的重要模型之一 [1],食物网动力学模型能够产生复杂的动力学行为,如分岔,混沌,极限环等 [2] [3] [4]。研究者们对食物网的动力学进行了广泛研究,分析不同环境下各种系统的动力学行为,如资源–消耗系统 [5],植物–草食动物系统 [6],浮游植物–浮游动物系统 [7],种间竞争系统 [8] 等。本文建立了一个Lotka-Volterra竞争模型 [9],通过对模型的动力学分析探究平衡点的稳定性以及几类分岔的发生条件 [10]。
本文所研究的Lotka-Volterra改进模型如下:
(1)
其中,u和v是两个竞争物种在t时刻的物种密度。该模型模拟了两个竞争物种在同一被捕食环境下的动态变化,两个物种被同一高级捕食者捕食,两个物种会分摊被捕食压力。
, :物种的内在增长率;
:物种u的被捕食系数;
:物种v的被捕食系数;
:物种v对u的竞争系数;
:物种u对v的竞争系数。
基于实际的生态学意义,上述参数均大于等于零,u和v为零说明该物种灭绝。
2. 系统的平衡点极其稳定性分析
2.1. 平衡点
对于上述竞争模型,有三类平衡点:
1) 在任意参数下, 都是该模型的一个平衡点;
2) 当u或v有一方灭绝时, 或 也是该系统边界平衡点,此时一个物种灭绝,另一物种的种内竞争与内在增长率相同;
3) 非零平衡点,即共存平衡点 ,其中 , , 且 。
2.2. 稳定性分析
平衡点的稳定性对于系统至关重要,特别是共存平衡点的稳定性,它是各个物种是否够长久共存的关键所在。
设A为该系统的雅克比矩阵,则有以下结论:
1) 若矩阵A所有特征值实部为负,则系统在平衡点 处是渐进稳定的;
2) 若矩阵A的特征值中有一个具有正实部,则系统在平衡点 处是不稳定的;
3) 若矩阵A的特征值中有一个实部为零,则系统的稳定性与高阶项有关。
对于系统(1),其雅克比矩阵为:
(2)
其共存平衡点 处时的雅可比矩阵为:
(3)
其中 ; ; ; ;
雅可比矩阵在平衡点 处的特征方程为:
(4)
其中 ; ;
特征值 ; ;
若平衡点 为渐进稳定平衡点,则 且 。
3. 几类分岔的条件
3.1. N-S分岔
系统想要发生N-S分岔,我们首先需要对模型进行离散化。我们知道:
(5)
我们令 ,结合模型(1)可得:
(6)
这样我就将模型(1)离散化了。
N-S分岔的条件:
对于上诉离散模型(6),我们同样可以用第二章的方法(2) (3) (4)求出特征值 。
对于 ,要求:
条件1: 且 。
条件2:特征值 与
与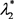 都是虚数且共轭。
都是虚数且共轭。
满足上述两个条件即可发生N-S分岔。
3.2. flip分岔
系统想要发生flip分岔,我们同样需要对模型离散化,离散过程如(5) (6)所示。
同样的,我们可以求出特征值 。
。
对于flip分岔,只需 或
或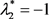 即可。
即可。
只要任意一个特征值为−1即可发生flip分岔。
致谢
感谢导师和审稿人给出的宝贵意见。
文章引用
肖 晟,张化永. Lotka-Volterra竞争模型的动力学研究
The Dynamics of Lotka Volterra Competition Model[J]. 应用数学进展, 2019, 08(12): 2002-2005. https://doi.org/10.12677/AAM.2019.812230
参考文献
- 1. Baretta-Bekker, J.G., Baretta, J.W. and Rasmussen, E.K. (1995) The Microbial Food Web in the european Regional Seas Ecosystem Model. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 33, 363-379.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0077-7579(95)90053-5 - 2. Becks, L., Hilker, F.M., Malchow, H., Jürgens, K. and Arndt, H. (2005) Experimental Demonstration of Chaos in a Microbial Food Web. Nature, 435, 1226-1229.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03627 - 3. Kooi, B.W., Kuijper, L.D.J. and Boer, M.P. (2002) Numerical Bifurcation Analysis of a Tri-Trophic Food Web with Omnivory. Mathematical Biosciences, 177-178, 201-228.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5564(01)00111-0 - 4. Perhar, G. and Arhonditsis, G.B. (2009) The Effects of Seston Food Quality on Planktonic Food Web Patterns. Ecological Modelling, 220, 805-820.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2008.12.019 - 5. Crowley, D.M., Jones, D.E. and Greenberg, M.T. (2012) Resource Consumption of a Diffusion Model for Prevention Programs: The PROSPER Delivery System. Journal of Adolescent Health Official Publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine, 50, 256-263.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2011.07.001 - 6. Room P.M. (1990) Ecology of a Simple Plant-Herbivore System: Biological Control of Salvinia. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 5, 74-79.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(90)90234-5 - 7. Sarkar, R.R., Pal, S. and Chattopadhyay, J. () Role of Two Toxin-Producing Plankton and Their Effect on Phytoplankton-Zooplankton System—A Mathematical Study Supported by Experimental Findings. Biosystems, 80, 11-23.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2004.09.029 - 8. Riegman, R. and Kuipers, B.R. (1994) Resource Competition and Selective Grazing of Plankton in a Multispecies Pelagic Food Web Model*. Marine Ecology, 15, 153-164.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0485.1994.tb00050.x - 9. Matsuda, H., Ogita, N. and Sasaki, A. (1992) Statistical Mechanics of Population: The Lattice Lotka-Volterra Model. Progress of Theoretical Physics, 88, 1035-1049.
https://doi.org/10.1143/ptp/88.6.1035 - 10. Prasad, A., Dana, S.K., Karnatak, R., et al. (2008) Universal Occurrence of the Phase-Flip Bifurcation in Time-Delay Coupled Systems. Chaos, 18, Article ID: 023111.
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2905146