Advances in Clinical Medicine
Vol.
13
No.
08
(
2023
), Article ID:
71121
,
6
pages
10.12677/ACM.2023.1381894
外耳道原发性腺样囊性癌2例并文献复习
甘柳,黄璐,韩林
三峡大学人民医院病理科,湖北 宜昌
收稿日期:2023年7月26日;录用日期:2023年8月17日;发布日期:2023年8月24日

摘要
目的:探讨外耳道原发腺样囊性癌的临床病理特征及其鉴别诊断。方法:外耳道原发性腺样囊性癌是一种发生于外耳道的一种附属器源性的恶性肿瘤,我们报道2例罕见外耳道原发性腺样囊性癌,结合文献对其临床特征、组织学形态、免疫表型及鉴别诊断等进行综合分析。结果:两例均为左侧外耳道新生物,临床表现侵袭性生长并伴有明显按压痛,一例出现明显听力下降并伴流脓,CT示软组织密度灶,与周围组织界限欠清,并有一例见有骨质破坏。免疫组化:CK7(+),CD117(+),GCDFP-15(−),Ki-67 (<10%)。结论:目前国内外报道的外耳道原发性腺样囊性癌不超过80例,其组织学形态分型有筛状型、管状型、实性型等。本文两例以不规则的腺腔结构为主,高倍镜下细胞异型性明显并伴有明显的核分裂象,但Ki-67增殖指数并不高。目前的治疗方式仍以手术切除为主。但局部复发及转移可能性大,一经确诊,应以扩大切除并辅以局部放疗的综合治疗为主。
关键词
腺样囊性癌,耵聍腺癌,附属器源性肿瘤,外耳道,病理,医学影像学

Two Cases of Primary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the External Auditory Canal and Review of the Literature
Liu Gan, Lu Huang, Lin Han
Department of Pathology, The People’s Hospital of China Three Gorges University, Yichang Hubei
Received: Jul. 26th, 2023; accepted: Aug. 17th, 2023; published: Aug. 24th, 2023

ABSTRACT
Objective: To investigate the clinicopathologic features of primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the external auditory canal and its differential diagnosis. Methods: Primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the external auditory canal is a malignant tumor of appendicular origin that occurs in the external auditory canal. We report two rare cases of primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the external auditory canal, and comprehensively analyze their clinical features, histological patterns, immunophenotypes, and differential diagnosis with the literature. Results: Both cases were neoplasm of the left external auditory canal, with clinical manifestations of invasive growth accompanied by obvious pressure pain, one case showed obvious hearing loss with pus, and CT showed soft tissue density foci with poorly defined boundaries with the surrounding tissues, and bone destruction in one case. Immunohistochemistry: CK7(+), CD117(+), GCDFP-15(−), Ki-67 (<10%). Conclusion: No more than 80 cases of primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the external auditory canal have been reported at home and abroad, and their histologic morphology is typed as sieve-like, tubular, and solid types. The two cases in this paper were dominated by irregular glandular cavity structure, with obvious cellular heterogeneity and obvious nuclear schizophrenia under high magnification, but with low Ki-67 proliferation index. The current treatment is still based on surgical resection. However, the possibility of local recurrence and metastasis is high, and once diagnosed, comprehensive treatment with extended resection supplemented by local radiotherapy should be the mainstay.
Keywords:Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, Cerumen Adenocarcinoma, Tumors of Accessory Organ Origin, External Ear Canal, Pathology, Medical Imaging

Copyright © 2023 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
外耳道原发恶性肿瘤非常罕见,占所有头颈部恶性肿瘤不到0.2%,且病理类型复杂多样,包括恶性黑色素瘤,梅克尔细胞癌,血管肉瘤,淋巴瘤和附属器癌等等,而耵聍腺癌和腺样囊性癌(adenoid cystic carcinoma, AdCC)则是属于附属器源性的恶性肿瘤 [1] 。临床特征多表现为耳痛、耳鸣、出血、流脓,或耳部饱胀感、听力下降等非特征性的表现,其生长缓慢,病程常可达数年。影像学大多表现为界限不清楚的软组织密度灶,CT值约30~60 HU,增强扫描强化明显,CT检查对观察骨质破坏情况,有无骨膜反应等有很大价值 [2] 。镜下肿瘤表现为浸润性,侵袭性生长,可见形态不规则的腺样或腺腔样结构,腺腔旁的肌上皮细胞通常分泌一种基底膜状物质,积聚于特征性的细胞外假囊性/筛状粘液性和玻璃样细胞外基质沉积中,高倍镜下可见细胞核膜不光滑,染色不均质,且异型性大,核分裂象明显。由于极其罕见,在诊断过程中则需要提高警惕,并与外耳道耵聍腺腺癌、粘液表皮样癌等进行鉴别诊断。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 材料
案例1:患者男,58岁,发现左耳外耳道肿物3年余,伴疼痛半月余,无外耳道流脓,无听力下降等不适。CT:左侧乳突气化欠佳,左侧外耳道见一软组织密度灶,边界清楚,密度均匀,CT值约55 HU,大小约14 × 9 mm,其内见少许钙化灶(图1(a),图1(b))。
案例2:患者女,76岁,左耳闷听力下降伴流脓5年余。CT:左侧外耳道见软组织密度灶填充,左侧外耳道后壁见骨质破坏,左侧部分乳突蜂房内见软组织密度灶(图1(c),图1(d))。
两例患者均在局麻下行左耳外耳道病损切除术。

Figure 1. CT images, and the red arrows in the figure point to the lesion area
图1. CT平扫图像,图中红色箭头所指为病灶区
2.2. 方法
组织标本固定在缓冲福尔马林中,常规包埋,苏木精伊红染色进行组织学检查。对3 µm切片进行免疫组织化学染色:CK7、CD117、GCDFP-15和Ki-67。所有一抗和PV6000试剂盒由北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司提供。
3. 结果
3.1. 专科检查
案例1查体:双耳廓无畸形,左耳外耳道见肿物,表面光滑,鼓膜完整,标志清楚,鼓室内未见积液;
案例2查体:双耳廓无畸形,左耳外耳道见暗灰色新生物阻塞,鼓膜未窥见,左耳前皮肤红肿,按压疼痛明显。
3.2. 组织病理学检查
低倍镜下见癌细胞呈浸润性生长,可见腺腔形成,形态不规则,高倍镜下细胞异型性明显并伴有明显的核分裂象,细胞核染色不均质,呈长椭圆形,核膜染色粗糙,细胞质深染(图2)。

Figure 2. Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining image
图2. 苏木素–伊红染色图像
3.3. 免疫组化
CK7(+),GCDFP-15(−),CD117(+),Ki-67 (<10%) (图3)。
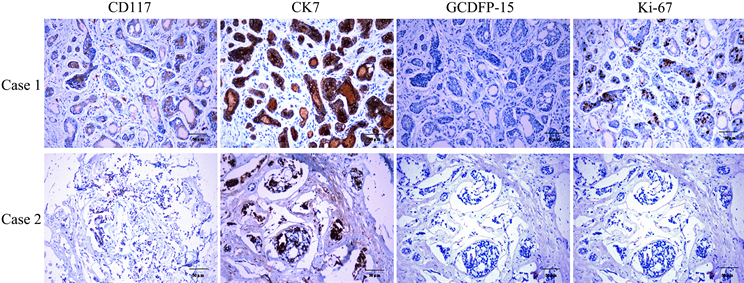
Figure 3. Immunohistochemical staining shows expression of different cell markers
图3. 免疫组化染色显示不同细胞标记物的表达
3.4. 治疗和预后
两例患者术后恢复正常,未行特殊治疗,分别随访8个月,患者暂无复发及转移体征。
4. 讨论
外耳道AdCC是一种发生于成年人的肿瘤,40~60岁是发病高峰,有统计学研究发现,患者中位年龄约为49岁 [3] ,并且外耳道AdCC几乎不发生于儿童和青少年,女性较男性多发,儿童发病则恶性程度更高,预后更差 [4] 。其病因及发病机制尚未完全明确 [5] ,目前认为其可能与反复的炎症刺激(中耳炎或外耳道炎病史)、电离辐射、遗传因素 [4] 或是HPV感染 [6] 等相关。其临床特征多不典型,如耳痛、耳鸣、听力下降、溢液、眩晕或其他因肿瘤扩大压迫周围组织引起的其他症状。常规检查通常为颅骨高分辨率CT,增强MRI等,来明确肿瘤与周围骨质和软组织的关系。
AdCC组织学分型有:1) 筛状型:筛状结构大于70%,伴或不伴有少量管状或实性结构,镜下看似筛状孔囊性腔隙,与藕的断面类似;2) 管状型:管状结构大于70%,伴或不伴有少量筛状或实性结构,管腔内可见粉染粘液,PAS染色强阳性,管状型的肿瘤细胞常分化较好;小管由2~3列细胞形成,衬覆导管或腺样结构的微小的立方状细胞,偶尔为柱状细胞,其外围绕非腔面的肌上皮细胞;3) 实性型:实性结构大于30%,伴或不伴有中心性坏死、少量筛状或管状结构;肿瘤细胞分化较差,肿瘤细胞大片状排列,只要是肌上皮细胞,内含不多见的导管样孔隙,内衬明确的腺上皮细胞层;成团的肿瘤细胞中常可见核分裂象,且核异型性大,可出现核仁、核内空泡;此种类型的AdCC恶性程度较高。
3种组织学类型中以实性型诊断最为困难,尤其容易与基底样鳞状细胞癌混淆。基底样鳞状细胞癌排列成小叶、缎带或条索状,边缘成栅栏状排列,免疫组织化学可以帮助鉴别,基底样鳞状细胞癌肿瘤细胞CK5、p63弥漫阳性,CD117、CK7阴性。其他需要与外耳道AdCC鉴别的还有基底细胞腺瘤、多形性腺瘤等。而且在病理诊断中就出现过冰冻病理报告基底细胞癌,最后常规诊断为外耳道耵聍腺的AdCC的报道 [7] 。耵聍腺癌在表皮下常分化较好,深部分化差,呈条索状,而AdCC和粘液表皮样癌形态特点则近似于发生于涎腺者 [8] [9] 。有报道发现外耳道AdCC患者易复发,存在一定的致死率,且首次治疗时晚期患者死亡率明显高于早期患者,远处转移是致死的主要原因 [3] 。虽然镜下无法区分外耳道AdCC与涎腺ACC,但是外耳道AdCC比涎腺ACC侵袭性高的多,恶性程度更高,且预后更差。
腺样囊性癌的特征性生物学表现为肿瘤沿神经生长,且易复发,易发生远处转移 [10] [11] 。腺样囊性癌可沿Santorini裂隙(外耳道软骨切迹)侵犯腮腺 [12] 和颞颌关节,亦可转移到颈部淋巴结或肺。不仅如此,肿瘤可沿神经周围生长,侵犯神经衣和神经纤维束,引起神经症状,同时也可沿着或围绕着血管生长,使血管收缩机能障碍,引起手术时出血,脉管内瘤栓也常见 [13] 。肿瘤可沿着血管、神经、胶原纤维扩散至腺组织和邻近其他组织。
外耳道腺样囊性癌一般生长缓慢,有报道从最初出现症状到做出诊断平均为时7.7年 [14] 。该病虽然生长缓慢,但远期生存率较差,10年生存率约为38.1% [15] 。AdCC的治疗方法目前仍为积极的手术切除和辅助性的放射治疗这种综合治疗策略,但其仍有转移及复发的风险 [16] ,局部复发 [17] 常见,脑、肺 [18] 以及腰椎 [19] 等及远处转移则风险低。并有数据分析,其总生存率不受放疗、肿瘤类型或局部与区域疾病的影响 [17] 。因此,本病确诊仍然是依靠病理学检查,且应早期诊断,一经病例确诊应扩大切除。CT、MRI等影像学检查可为确定病变部位以及与周围组织的关系、累及范围等提供参考依据,对术中定位有重要价值。
文章引用
甘 柳,黄 璐,韩 林. 外耳道原发性腺样囊性癌2例并文献复习
Two Cases of Primary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the External Auditory Canal and Review of the Literature[J]. 临床医学进展, 2023, 13(08): 13561-13566. https://doi.org/10.12677/ACM.2023.1381894
参考文献
- 1. Verma, R.R. and Verma, R. (2022) Syringocystadenocarcinoma Papilliferum of External Auditory Canal: First Case Re-port in English Literature. Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 74, 3700-3705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02434-x
- 2. 尹宏博, 全松石. 外耳道耵聍腺样囊性癌一例[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2019, 38(3): 567.
- 3. Liu, S.C., Kang, B.H., Nieh, S., et al. (2012) Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the External Auditory Canal. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association, 75, 296-300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2012.04.007
- 4. Young, A. and Okuyemi, O.T. (2023) Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors.
- 5. Sahara, S., Herzog, A.E. and Nor, J.E. (2021) Systemic Therapies for Salivary Gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. American Journal of Cancer Research, 11, 4092-4110.
- 6. Bishop, J.A. andreasen, S., Hang, J.F., et al. (2017) HPV-Related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma: An Expanded Series of 49 Cases of the Tumor Formerly Known as HPV-Related Carcinoma with Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma-Like Features. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 41, 1690-1701. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000944
- 7. Ebelhar, A.E., West, D.S. and Aouad, R.K. (2017) Cerumi-nous Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of External Auditory Canal. The Journal of International Advanced Otology, 13, 292-294. https://doi.org/10.5152/iao.2017.3929
- 8. Vickers, T.W., Clifford, D.L., Garcelon, D.K., et al. (2015) Pathology and Epidemiology of Ceruminous Gland Tumors among Endangered Santa Catalina Island Foxes (Urocyon littoralis catalinae) in the Channel Islands, USA. PLOS ONE, 10, e143211. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143211
- 9. Malli, M. and Shoukat, A.M. (2022) External Auditory Canal Pleomorphic Adenoma: A Rare Case Presentation. Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 74, 4106-4109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02862-9
- 10. Coca-Pelaz, A., Rodrigo, J.P., Bradley, P.J., et al. (2015) Ade-noid Cystic Carcinoma of the Head and Neck—An Update. Oral Oncology, 51, 652-661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
- 11. de Sousa, L.G., Jovanovic, K. and Ferrarotto, R. (2022) Metastatic Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Genomic Landscape and Emerging Treatments. Current Treatment Options in Oncology, 23, 1135-1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-022-01001-y
- 12. Da, S.F., Carvalho, D.A.J.J., Ralph, A., et al. (2023) Salivary Glands Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: A Molecular Profile Update and Potential Implications. Frontiers in Oncology, 13, Article ID: 1191218. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1191218
- 13. Cantu, G. (2021) Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. An Indolent but Aggressive Tumour. Part B: Treatment and Prognosis. Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica, 41, 296-307. https://doi.org/10.14639/0392-100X-N1729
- 14. Dong, F., Gidley, P.W., Ho, T., et al. (2008) Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the External Auditory Canal. Laryngoscope, 118, 1591-1596. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e31817c42a8
- 15. 刘明波, 周其友, 武文明, 等. 外耳道腺样囊性癌24例临床分析[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2009, 7(1): 5-7.
- 16. Shimoda, H., Teshima, M., Murase, T., et al. (2023) Prognostic Scores for Patients with Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma without Lymph Node Metastasis. Oral Oncology, 145, Ar-ticle ID: 106491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2023.106491
- 17. Wanner, B., Rismiller, K. and Carr, D.R. (2022) Treat-ment and Survival Outcomes of Ceruminous Carcinomas of the External Auditory Canal: A SEER Database Analysis and Literature Review. Archives of Dermatological Research, 314, 583-591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-021-02257-4
- 18. Zheng, Q.Y., Zheng, L.M., Song, F.L., et al. (2021) Recurrence of Ceruminous Gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma with Intracranial Dissemination: Report of a Case. Chinese Journal of Pathology, 50, 405-408.
- 19. Shen, Y.W., Yang, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2022) Metastatic Ceruminous Adenoid Cystic Car-cinoma of the Lumbar Spine Causing Neurological Compromise: A Case Report. Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Re-habilitation, 13. https://doi.org/10.1177/21514593221111357