Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.
07
No.
11
(
2018
), Article ID:
27552
,
7
pages
10.12677/AAM.2018.711160
Inertial Manifolds for a Class of Nonlinear Generalized Kirchhoff Equation
Penghui Lv*, Jingxin Lu
School of Information, Tourism and Culture College of Yunnan University, Lijiang Yunnan

Received: Oct. 26th, 2018; accepted: Nov. 7th, 2018; published: Nov. 14th, 2018

ABSTRACT
The paper studies the longtime behavior of solutions to the initial boundary value problem (IBVP) for a class of Kirchhoff models: . The Inertial manifolds are estimated.
Keywords:Generalized Kirchhoff Equation, Spectral Gap Condition, Inertial Manifolds
一类广义非线性Kirchhoff型方程的惯性流形
吕鹏辉*,卢京鑫
云南大学旅游文化学院信息学院,云南 丽江

收稿日期:2018年10月26日;录用日期:2018年11月7日;发布日期:2018年11月14日

摘 要
该文研究了广义Kirchhoff型方程: 的初边值问题的解的长时间行为,证明了方程的惯性流形。
关键词 :广义Kirchhoff型方程,谱间隔条件,惯性流形

Copyright © 2018 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
本文研究下列非线性Kirchhoff型方程的惯性流形:
, (1.1)
, (1.2)
。 (1.3)
其中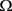 是R中具有光滑边界的有界域,
,且
都是正常数,有关
的假设将会在后文中给出。
是R中具有光滑边界的有界域,
,且
都是正常数,有关
的假设将会在后文中给出。
在非线性偏微分方程无穷维动力系统的长时间行为中,惯性流形起着相当重要的作用,当其存在时,惯性流形是包含整体吸引子的有限维不变光滑流形,并且以指数速率吸引解轨道。对于正在考虑的系统的大部分动力学性态都是在这种流形下产生的,这使得对动力学性态的研究更加简便。同时,在惯性流形的限制下,即使初始系统是无限维的,此时的系统也变成了有限维的。这种系统称为惯性系统,重现了许多初始系统的大部分动力学性态。惯性流形和相应的惯性形式对研究耗散方程的有限维动力学性态是有力的工具 [1] 。
现在普遍认为,惯性流形存在的一个充分条件是线性算子A的谱间隔条件及非线性项的Lipschitz连续性成立( ,其中为q独立于t的Lipschitz常数) [1] - [6] 。
Songmu Zheng和Albert Milani [7] 分别考虑了在一维空间中无粘性的Cahn-Hilliard方程的两种边值问题的奇摄动性。该文证明了基于这两种边值问题的动力系统在相空间 存在指数吸引子和惯性流形。
Xu Guigui,Wang Libo和Lin Guoguang [8] 在时滞时间很小的假设下讨论了一类时滞非线性波方程 的惯性流形的存在性。
Bin Zhao和Guoguang Lin [9] 考虑了基于Cahn-Hilliard的奇异摄动方程上,具有双重扰动的Cahn-Hilliard方程 的惯性流形的存在性。
Guoguang Lin,Penghui Lv和Ruijin Lou [10] 利用了离散挤压性和谱间隔条件研究了一类广义非线性Kirchhoff-Boussinesq型方程 的指数吸引子和惯性流形。
本文主要研究了(1.1)~(1.3)一类广义非线性Kirchhoff型方程的惯性流形,通过论证谱间隔条件成立条件,得到惯性流形存在定理。
本文结构如下:在第一部分中,简要给出惯性流形相比整体吸引子的优势及部分学者的研究成果;在第二部分中,给出主要记号;在第三部分中,对方程惯性流形的讨论。
2. 记号
为叙述方便,我们引入下列符号:
其中
。
为
的共轭空间,
。
是L2-内积下的Sobolev空间。同时
表示
在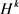 中的闭包(
)。符号
表示H-内积。
中的闭包(
)。符号
表示H-内积。
定义算子 ,
则算子 是正定的且空间 是Hilbert空间
特别的,
是 在 上带有齐次Dirichlet边界条件的第一特征值。
3. 惯性流形
引理3.1 [11] :假定
(H1) , , ,
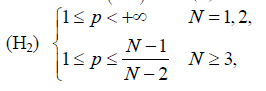
(H2)
,
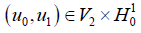 。则问题(1.1)~(1.3)的解
满足
。则问题(1.1)~(1.3)的解
满足
并且问题(1.1)~(1.3)存在唯一解 , 。
评论3.1 [11] :定义映射 , ,其中u是问题(1.1)~(1.3)的解。根据引理3.1, 构成X上的连续算子半群。
定义3.1:设
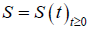 是Banach空间X上的解半群。一个子集
满足:
是Banach空间X上的解半群。一个子集
满足:
1) 是有限维Lipschitz流形,
2) 是正不变的,即 ,
3)
以指数吸引解轨道,即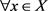 ,存在常数
,使得
,存在常数
,使得
则称 是关于 的一个惯性流形。
设算子
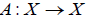 ,设
满足Lipschitz条件:
,设
满足Lipschitz条件:
。 (3.1)
算子A称为满足关于F的谱间隔条件,如果算子A的谱可以分成两部分 和 且 是有限的。
, (3.2)
(3.3)
且有
。 (3.4)
这里满足正交分解: , (3.5)
其中投影是 。
方程(1.1)等价于下列一阶发展方程(研究
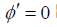 时的情况)。
时的情况)。
, (3.6)
其中:
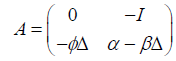 ,
(3.7)
,
(3.7)
令
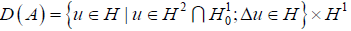 ,
。
,
。
对(3.6)中矩阵型算子的特征值,先定义X中的内积
, (3.8)
, 分别表示 的共轭。
对 ,计算得
(3.9)
又由 ,所以算子A是单调递增且 是非负实数。
我们给出A的特征方程
等价于
(3.10)
从而U满足特征值问题:
(3.11)
由(3.10)知,相应的特征函数
, , (3.12)
对任意的整数 ,有
。 (3.13)
因此将 带入(3.11)中u的位置,两边用 取内积,并将(3.13)带入得到特征值
。 (3.14)
引理3.2:
是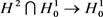 的整体有界和整体Lipschitz函数。
的整体有界和整体Lipschitz函数。
证明:
定理3.1:设l是g的Lipschitz常数, 且
满足
且
满足
, (3.15)
则算子A满足谱间隔条件(3.4)。
证明:由 是减函数。
令N满足(3.15),可将A的特征值分解为
, , (3.16)
相应的X可分解为
, 。 (3.17)
下面将找出正交空间,对 和 ,将证明(3.4)成立。
进一步分解
,
。 (3.18)
由 得
。 (3.19)
所以 与 不正交, 与 正交。
要证 与 正交,则需要重新定义X的内积,并与(3.9)等价。
定义 。
由 得
。
由 ,所以 。
。
所以在重新定义的内积下, 与 正交,即 正交。
下面估计 的Lipschitz常数 。
。
因此
。
由此只需说明 成立,则谱间隔条件(3.4)成立。
,
,
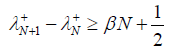 。
。
由(3.15)得:
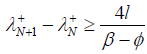 。
。
到此说明谱间隔条件(3.4)成立。
综上我们有惯性流形的存在性定理。
定理3.2:若 ,其中 是一个常数,则方程(1.1)存在惯性流形 ,具有形式
。
其中 是Lipschitz连续的,Lipschitz常数为 , 表示图。
文章引用
吕鹏辉,卢京鑫. 一类广义非线性Kirchhoff型方程的惯性流形
Inertial Manifolds for a Class of Nonlinear Generalized Kirchhoff Equation[J]. 应用数学进展, 2018, 07(11): 1374-1380. https://doi.org/10.12677/AAM.2018.711160
参考文献
- 1. Temam, R. (1990) Intertial Manifolds. The Mathematical Intelligencer, 12, No. 4.
- 2. Marion, M. (1989) Intertial Manifolds Associated to Partly Dissipative Reaction-Diffusion Systems. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 143, 295-326. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-247X(89)90043-7
- 3. Rezounenko, A.V. (2002) Inertial Manifolds for Retarded Second Order in Time Evolution Equations. Nonlinear Analysis, 51, 1045-1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0362-546X(01)00878-1
- 4. Huy, N.T. (2012) Inertial Manifolds for Semi-Linear Parbolic Equations in Admissible Spaces. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 386, 894-909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2011.08.051
- 5. Foias, C. (1988) Inertial Manifolds for Nonlinear Evolutionary Equations. Journal of Differential Equations, 73, 309-353. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0396(88)90110-6
- 6. Liu, W.J. and Haller, G. (2004) Inertial Manifolds and Completeness of Eigenmodes for Unsteady Magnetic Dynamos. Physica D, 194, 297-319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2003.03.002
- 7. Zheng, S.M. and Milani, A. (2004) Exponential Attractors and Inertial Manifolds for Singular Perturbations of the Cahn-Hilliard Equations. Nonlinear Analysis, 57, 843-877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.na.2004.03.023
- 8. Xu, G.G., Wang, L.B. and Lin, G.G. (2014) Inertial Manifolds for a Class of the Retarded Nonlinear Wave Equations. Mathematica Applicata, 27, 887-891.
- 9. Zhao, B. and Lin, G.G. (2013) Inertial Manifolds for Dual Perturbations of the Cahn-Hilliard Equations. Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics, 77, 113-136.
- 10. Lin, G.G., Lv, P.H. and Lou, R.J. (2017) Exponential Attractors and Inertial Manifolds for a Class of Nonlinear Generalized Kirchhoff-Boussinesq Model. Far East Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 101, 1913-1945. https://doi.org/10.17654/MS101091913
- 11. Lv, P.H., Lu, J.X. and Lin, G.G. (2016) Global Attractors for a Class of Nonlinear Generalized Kirchhoff Models. Journal of Advances in Mathematics, 12, 6452-6462.
NOTES
*通讯作者。