Pure Mathematics
Vol.
13
No.
04
(
2023
), Article ID:
64701
,
11
pages
10.12677/PM.2023.134105
具比例时滞的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络的 稳定性研究
古力加依娜·木合亚提,姑丽加玛丽·麦麦提艾力*
新疆师范大学数学科学学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐
收稿日期:2023年3月19日;录用日期:2023年4月20日;发布日期:2023年4月27日

摘要
本文研究了具有比例时滞的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络的全局指数稳定性。首先通过适当的变换,将比例时滞的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络模型等价的转换为具有常时滞的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络模型。通过应用M-矩阵理论和不等式技巧建立了全局指数稳定性的充分条件。通过数值仿真来验证了所得结论的有效性。
关键词
Cohen-Grossberg神经网络,全局指数稳定,比例时滞,M-矩阵理论

Stability Analysis of Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks with Proportional Delays
Gulijiayina Muheyati, Gulijiamali Maimaitiaili*
School of Mathematical Sciences, Xinjiang Normal University, Urumqi Xinjiang
Received: Mar. 19th, 2023; accepted: Apr. 20th, 2023; published: Apr. 27th, 2023

ABSTRACT
This paper investigates global exponential stability of Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with proportional delays. Firstly, the Cohen-Grossberg neural networks model with proportional delay is equivalent to the Cohen-Grossberg neural networks model with constant delay through appropriate transformation. Sufficient conditions for global exponential stability are established by applying M-matrix theory and inequality techniques. The validity of the obtained conclusions is verified by numerical simulation.
Keywords:Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks, Global Exponential Stability, Proportional Delays, M-Matrix Theory

Copyright © 2023 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
Cohen-Grossberg神经网络 [1] (Cohen-Grossberg neural networks, CGNNs)是一种特殊的递归神经网络。CGNNs比较普遍,涵盖了细胞神经网络 [2] 和Hopfield神经网络 [3] 。递归神经网络在图像处理 [4] [5] [6] 、优化 [7] [8] ,模式识别 [9] [10] ,联想记忆和并行计算等领域得到了广泛的应用。
在实际应用中,要求CGNNs满足一定的稳定性。然而,由于网络在中信号的传输和切换速度是有限的,在网络运行中时滞是不可避免的,时滞会影响或甚至会破坏神经网络的稳定性 [11] 。因此,研究CGNNs的稳定性具有重要的意义。正因如此,关于CGNNs的稳定性已经有了广泛的研究成果:在文献 [12] 中,通过使用一个新的Lyapunov泛函来研究了中立型CGNNs的全局指数稳定性。在文献中 [13] ,利用Banach不动点定理和Lyapunov泛函方法研究了一类具有混合时滞的CGNNs自同构解的存在性和指数稳定性。在文献 [14] 中,利用Lyapunov泛函和积分不等式研究了CGNNs全局指数稳定性。在文献 [15] 中,利用Banach不动点定理、广义Gronwall-Bellman不等式和Lyapunov泛函方法来研究了具有混合时滞CGNNs的渐近自守解的存在性,唯一性和全局指数稳定性。
目前神经网络中涉及的时滞大致分为常时滞 [16] ,时变时滞 [17] [18] [19] 和分布时滞 [20] [21] [22] 。比例时滞 [23] [24] 是一种特殊的时变时滞,存在于物理,生物系统,控制理论等各个领域。因此,研究具有比例时滞的神经网络的稳定性具有重要的理论和应用价值。许多研究者致力于研究比例时滞神经网络稳定性并取得了较大的进展。如在文献 [25] 中,利用参数可调的Lyapunov泛函和不等式技巧研究了具有多个比例时滞CGNNs的全局多项式周期性和全局多项式稳定性。在文献 [26] 中,通过构造Lyapunov泛函和广义Halanay不等式,研究了具有比例时滞的高阶神经网络的稳定性。在文献 [27] 中,通过构造一个具有比例时滞的广义Gronwall积分不等式,研究了具有比例时滞的分数阶神经网络的有限时间的稳定性。
基于上述讨论,本文研究了具有比例时滞的CGNNs的全局指数稳定性。与大多数时滞CGGNs现有结果不同,这里提到的比例时滞是无界且时变的。利用M-矩阵理论和不等式技巧得到了CGNNs的全局指数稳定性的充分条件。该充分条件以M-矩阵的形式给出,这意味着该稳定性充分条件具有更低的计算复杂度。
本文结构安排如下。在第2节中,介绍了具有比例时滞CGGNs的模型以及必要的定义和引理。第3节中给出了具有比例时滞CGGN的全局指数稳定性的判据。在第四节中,给出了一些例子与仿真实验以说明本文结果的有效性。第5节中得出了结论。
2. 数学模型及预备知识
考虑下面的具有比例时滞Cohen-Grossberg神经网络模型:
(2.1)
其中 ,n是神经元个数; 表示t时刻第i个神经元的状态; 表示放大函数; 表示行为函数; 表示激活函数; 表示连接权重, 表示外部输入; 为比例时滞因子,满足 , 为时滞函数,当 时, ,即无界时滞; 为模型初始状态函数, 。
做变换 [23] ,则模型(2.1)就转换为具有常时滞变系数的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络模型:
(2.2)
其中 , , 。
本文我们做以下假设:
假设1: ,并存在常数 使得
假设2:函数 连续且存常数 使得
假设3:激活函数 , 连续且存在常数 使得
记
引理1 [28] 模型(2.1)与模型(2.2)有相同的平衡点,变换前后的两个模型在稳定性上具有等价性。
引理2 [29] 若矩阵 的所有非对角线上元素均非正,且所有主子式均正定,则下列表述是等价的:
1) 矩阵A是非奇异M-矩阵。
2) 存在非零向量 使得 。
定义1 [30] 如果存在常数 , ,使得
其中
则模型(2.2)的平衡点 是全局指数稳定的。
3. 主要结论
定理1如果假设1~假设3成立,且 是非奇异M-矩阵,则模型(2.2)的平衡点是全局指数稳定性的。
证明:设 为模型(2.2)的平衡点,令 则模型(2.2)可以转换为:
(3.1)
其中
因为 非奇异M矩阵,所以由引理2可知,存在非零向量 使得:
(3.2)
构造辅助函数
(3.3)
显然
(3.4)
因为 是连续且可微,所以 是严格单调递增函数。从而我们可以推断出存在常数 ,使得
(3.5)
由此可以推断出,一定存在一个常数 使得:
(3.6)
考虑以下形式的Lyapunov泛函:
(3.7)
对 求右上导:
(3.8)
令 ,则
(3.9)
假设
(3.10)
反正法,若(3.7)式不成立,则存在 ,使得
,且当 时, (3.11)
由式(3.4)和式(3.5)得:
(3.12)
式(3.11)与(3.12)相矛盾。因此式(3.10)成立,则
即
(3.13)
其中 , 。
综上,由定义1和引理1可知模型(2.1)的平衡点是全局指数稳定性的。
4. 数值实验
例1考虑如下具有比例时滞的CGNNs,其中n = 2:
(4.1)
其中:
显然
计算可得:
由引理2可知 是M-矩阵,再由定理1可知模型(2.1)的平衡点 是全局指数稳定的。仿真结果如图1和图2所示。
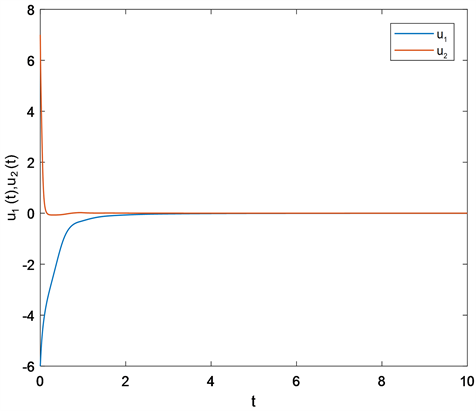
Figure 1. State response of (4.1)
图1. 系统(4.1)的响应图
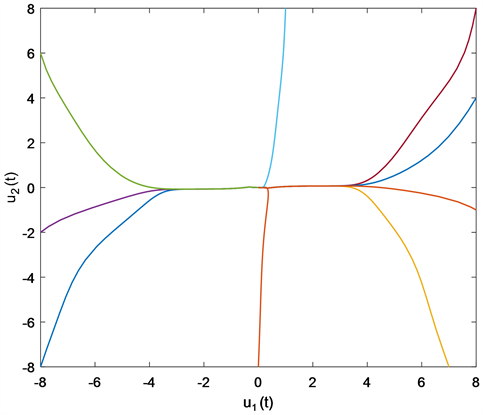
Figure 2. Phase trajectories of system (4.1)
图2. 系统(4.1)的相轨迹
例2考虑如下具有比例时滞的CGNNs,其中n = 2:
(4.2)
其中:
显然
计算可得:
由引理2可知 是M-矩阵,再由定理1可知模型(2.1)的平衡点 是全局指数稳定的。仿真结果如图3和图4所示。
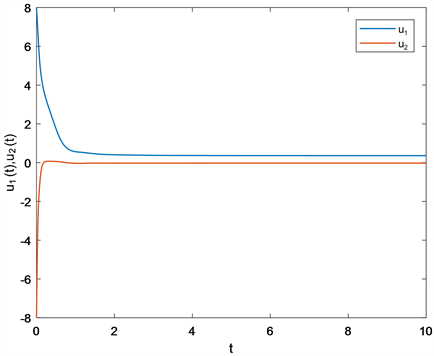
Figure 3. State response of (4.2)
图3. 系统(4.2)的响应图

Figure 4. Phase trajectories of system (4.2)
图4. 系统(4.2)的相轨迹
例3考虑如下具有比例时滞的 CGNNs,其中n = 3:
(4.3)
其中:
显然
计算可得:
由引理2可知 是M-矩阵,再由定理1可知模型(4.3)的平衡点 是全局指数稳定的。仿真结果如图5和图6所示。
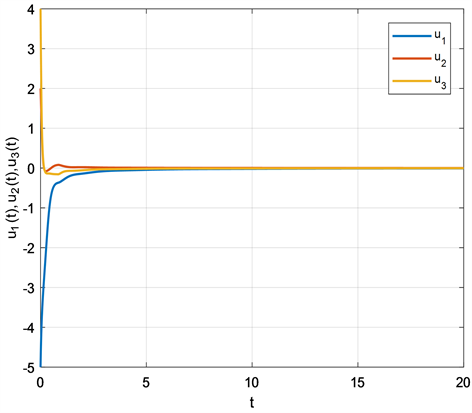
Figure 5. State response of (4.3)
图5. 系统(4.3)的响应图
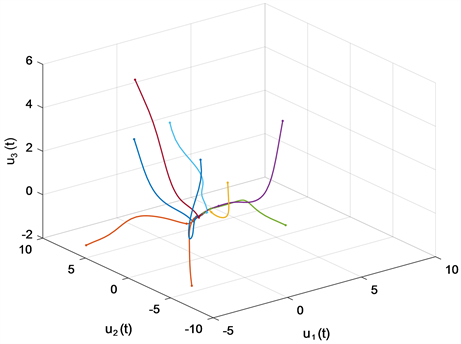
Figure 6. Phase trajectories of system (4.3)
图6. 系统(4.3)的相轨迹
5. 总结
由于CGNNs在Web服务质量路由决策,控制理论,生物系统等领域广泛应用,因而研究CGNNs的稳定性,在实际问题中将具有一定的应用意义。本文中,我们利用M-矩阵理论和不等式技巧研究了具有比例时滞的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络的全局指数稳定性。最后通过数值实验来验证了所得结论的有效性。不难看出,实验证实了我们理论结果的有效性。
文章引用
古力加依娜•木合亚提,姑丽加玛丽•麦麦提艾力. 具比例时滞的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络的稳定性研究
Stability Analysis of Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks with Proportional Delays[J]. 理论数学, 2023, 13(04): 996-1006. https://doi.org/10.12677/PM.2023.134105
参考文献
- 1. Cohen, M.A. and Grossberg, S. (1983) Absolute Stability of Global Pattern Formation and Parallel Memory Storage by Competitive Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, SMC-13, 815-826. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1983.6313075
- 2. Chua, L.O. and Yang, L. (1988) Cellular Neural Networks: Theory. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 35, 1257-1272. https://doi.org/10.1109/31.7600
- 3. Hopfield, J.J. (1982) Neural Networks and Physical Systems with Emergent Collective Computational Abilities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 79, 2554-2558. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.79.8.2554
- 4. Hu, X., Feng, G. and Duan, S. (2015) Multilayer RTD-Memristor-Based Cellular Neural Networks for Color Image Processing. Neurocomputing, 162, 150-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.03.057
- 5. Hu, X., Feng, G. and Duan, S. (2017) A Memristive Multilayer Cellular Neural Network with Applications to Image Processing. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 28, 1889-1901. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2552640
- 6. Li, J. and Peng, Z. (2015) Multi-Source Image Fusion Algo-rithm Based on Cellular Neural Networks with Genetic Algorithm. Optik, 126, 5230-5236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.09.187
- 7. Nagamani, G. and Radhika, T. (2016) A Quadratic Convex Com-bination Approach on Robust Dissipativity and Passivity Analysis for Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks with Time-Varying Delays. Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 39, 3880-3896. https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.3835
- 8. Hayakawa, Y. and Nakajima, K. (2010) Design of the Inverse Function Delayed Neural Network for Solving Combinatorial Optimization Problems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 21, 224-237. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2009.2035618
- 9. Velichko, A., Belyaev, M. and Boriskov, P. (2019) A Model of an Oscillatory Neural Network with Multilevel Neurons for Pattern Recognition and Computing. Electronics, 8, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8010075
- 10. Zhang, Y., Li, Y. and Wang, X. (2017) Synaptic Characteristics of Ag/AgInSbTe/Ta-Based Memristor for Pattern Recognition Applications. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 64, 1806-1811. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2017.2671433
- 11. Baldi, P. and Atiya, A.F. (1994) How Delays Affect Neural Dy-namics and Learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 5, 612-621. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.298231
- 12. Faydasicok, O. (2020) New Criteria for Global Stability of Neutral-Type Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks with Multiple Delays. Neural Networks, 125, 330-337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2020.02.020
- 13. Zhu, H.Y., Zhu, Q.X., Sun, X.B. and Zhou, H.W. (2016) Ex-istence and Exponential Stability of Pseudo Almost Automorphic Solutions for Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks with Mixed Delays. Advances in Continuous and Discrete Models, 2016, Article No. 120. https://advancesindifferenceequations.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13662-016-0831-5
- 14. Zhao, W. (2008) Global Exponential Stability Analysis of Cohen-Grossberg Neural Network with Delays. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 13, 847-856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2006.09.004
- 15. Aouiti, C. and Dridi, F. (2019) New Results on Impulsive Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks. Neural Processing Letters, 49, 1459-1483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9880-y
- 16. Lu, D.J. and Li, C.J. (2013) Exponential Stability of Stochastic High-Order BAM Neural Networks with Time Delays and Impulsive Effects. Neural Computing and Applications, 23, 1-8. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00521-012-0861-1
- 17. Zeng, H.-B., Liu, X.-G. and Wang, W. (2019) A Generalized Free-Matrix-Based Integral Inequality for Stability Analysis of Time-Varying Delay Systems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 354, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.02.009
- 18. Zhang, C.-K., He, Y. and Jiang, L. (2016) Stability Analysis of Systems with Time-Varying Delay via Relaxed Integral Inequalities. Systems & Control Letters, 92, 52-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysconle.2016.03.002
- 19. Li, Z., Yan, H. and Zhang, H. (2020) Stability Analysis of Linear Systems with Time-Varying Delay via Intermediate Polynomial-Based Functions. Automatica, 113, Article ID: 108756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108756
- 20. Bazighifan, O., Elabbasy, E.M. and Moaaz, O. (2019) Oscillation of Higher-Order Differential Equations with Distributed Delay. Journal of Inequalities and Applica-tions, 2019, 55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13660-019-2003-0
- 21. Cao, Y. (2019) Bifurcations in an Internet Con-gestion Control System with Distributed Delay. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 347, 54-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2018.10.093
- 22. Zhao, Y., Li, X. and Cao, J. (2020) Global Exponential Stability for Impulsive Systems with Infinite Distributed Delay Based on Flexible Impulse Frequency. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 386, Article ID: 125467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2020.125467
- 23. Zhou, L.Q. (2013) Delay-Dependent Exponential Stability of Cellular Neural Networks with Multi-Proportional Delays. Neural Processing Letters, 38, 347-359. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11063-012-9271-8
- 24. Zhou, L. (2014) Global Asymptotic Stability of Cellular Neural Networks with Proportional Delays. Nonlinear Dynamics, 77, 41-47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1271-y
- 25. Zhou, L. and Zhao, Z. (2022) Global Polynomial Periodicity and Polynomial Stability of Proportional Delay Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks. ISA Transactions, 122, 205-217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2021.04.041
- 26. Shen, W., Zhang, X. and Wang, Y. (2020) Stability Analysis of High Order Neural Networks with Proportional Delays. Neurocomputing, 372, 33-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.09.019
- 27. Yang, Z., Zhang, J. and Hu, J. (2021) New Results on Fi-nite-Time Stability for Fractional-Order Neural Networks with Proportional Delay. Neurocomputing, 442, 327-336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.02.082
- 28. Zhou, L. (2013) Delay-Dependent Exponential Stability of Cellular Neural Networks with Multi-Proportional Delays. Neural Processing Letters, 38, 347-359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-012-9271-8
- 29. Cao, J. and Wang, J. (2003) Global Asymptotic Stability of a General Class of Recurrent Neural Networks with Time-Varying Delays. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 50, 34-44. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2002.807494
- 30. Zhang, J. (2003) Globally Exponential Stability of Neural Net-works with Variable Delays. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 50, 288-290. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2002.808208
NOTES
*通讯作者。