Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.3 No.03(2014), Article ID:14019,8 pages
DOI:10.12677/AAM.2014.33021
A New Method for Signal Reconstruction of
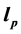 -Norm Optimization
-Norm Optimization
Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot
Email: 1054488585@qq.com
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: May 24th, 2014; revised: Jun. 20th, 2014; accepted: Jun. 29th, 2014
ABSTRACT
With the rapid development of information science and technology, the amount of
information becomes huge. The demand of technology on information processing will
be high and the original traditional information processing methods cannot fully
meet the requirements of people. So the study of compression perception theory is
very important. The main content of this thesis is the reconstruction algorithm,
which has played an important role in the theory of the compressed sensing. In order
to overcome the nonsmooth problem in
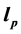 norm, this paper proposed a new Maximum Entropy Function Method (MEFM) to solve
the
norm, this paper proposed a new Maximum Entropy Function Method (MEFM) to solve
the
 optimization problem and proved the convergence of the new algorithm. Numerical
experiments demonstrated that the new algorithm is feasible and effective in signal
reconstruction.
optimization problem and proved the convergence of the new algorithm. Numerical
experiments demonstrated that the new algorithm is feasible and effective in signal
reconstruction.
Keywords:Compressed Sensing, Signal Reconstruction, Nonsmooth Optimization, Maximum Entropy Function

基于光滑逼近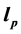 范数的重构信号算法
范数的重构信号算法
赵 真,陈国庆
内蒙古大学,呼和浩特
Email: 1054488585@qq.com
收稿日期:2014年5月24日;修回日期:2014年6月20日;录用日期:2014年6月29日

摘 要
随着信息科学技术的迅猛发展,信息量越来越大,对信息处理的理论技术的要求也就越高,原有的传统信息处理方法不能够完全满足人们的要求。因此对压缩感知理论的研究是十分必要的。而压缩感知理论中最核心的部分就是信号重构。本文用极大熵函数构造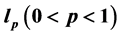 范数的光滑逼近函数,进而实现信号重构,并提出了基于最小
范数的光滑逼近函数,进而实现信号重构,并提出了基于最小 范数问题的MEFM算法,证明了算法的收敛性。数值实验表明验证了新算法是十分可行有效的信号重构方法。
范数问题的MEFM算法,证明了算法的收敛性。数值实验表明验证了新算法是十分可行有效的信号重构方法。
关键词
压缩感知,信号重构,非光滑优化,极大熵函数

1. 引言
当今时代,信息科学技术迅猛发展,大量的数据信息进入我们的生活,需要处理的数据量增大速度惊人。在信息处理过程中,获得信息的最重要途径是对信息进行采样,但传统的采样感知理论受奈奎斯特(Nyqusit)采样定理的限制,要求在采集信号时,信号的频率不能低于信号最高频率的两倍,这样就对相应的信号采集的硬件设备提出了更高要求,很大限制了信号处理的能力。基于此,人们开始找寻一种不受奈奎斯特定理约束的信息采集处理方法。
针对可稀疏压缩信号,Donoho等[1] -[5] 在稀疏分解和信号恢复等思想的基础上提出压缩感知(CS)理论框架。随后该理论得到迅速发展,在2006年Donoho[2] 正式提出了“压缩传感”这一术语。
传统感知的方式是先对信息进行采样后处理,而压缩感知将采样过程和压缩过程同时进行,采样更少但后续处理信息时的计算更多。压缩感知理论中最核心的部分就是信号重构,是指通过压缩测量的低维采样数据,精确或较精确地重构高维原始信息。
对于压缩传感信号重构问题,理想情况下是通过求解最原始的重构模型,即

 . (1)
. (1)
其中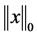 表示
表示 中非零元素的个数。基于
中非零元素的个数。基于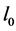 范数重构信号的算法主要是贪婪算法,这其中比较经典的是正交匹配追踪法(Orthogonal
Matching Pursuit, OMP)[6] [7] 。
范数重构信号的算法主要是贪婪算法,这其中比较经典的是正交匹配追踪法(Orthogonal
Matching Pursuit, OMP)[6] [7] 。
由于基于最小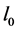 范数进行信号重构的问题是一个NP-hard问题,所以实际中一般用求解最小
范数进行信号重构的问题是一个NP-hard问题,所以实际中一般用求解最小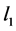 范数来进行信号重构。文献[6]
[7] 证明了问题
范数来进行信号重构。文献[6]
[7] 证明了问题 与
与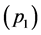 的等价性,并研究了其等价条件。基于最小
的等价性,并研究了其等价条件。基于最小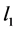 范数进行信号重构问题模型如下:
范数进行信号重构问题模型如下:
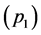
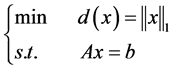 . (2)
. (2)
其中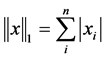 ,基于
,基于 范数最小进行求解的算法中最基本的是基追踪法(Basis
Pursuit, BP)。事实上伪范数
范数最小进行求解的算法中最基本的是基追踪法(Basis
Pursuit, BP)。事实上伪范数 比
比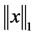 范数更接近原问题中的
范数更接近原问题中的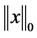 范数。
范数。
图1是多维情况下极小化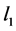 的图形,图2是多维情况下极小化
的图形,图2是多维情况下极小化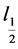 的图形由图1和图2可以看出,恢
的图形由图1和图2可以看出,恢

Figure 1. The minimize of
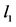
图1. 极小化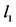

Figure 2. The minimize of
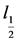
图2. 极小化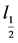
复信号 时
时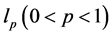 范数优化有时比
范数优化有时比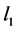 范数优化方法效果会更好。
范数优化方法效果会更好。
伪范数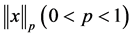 比
比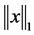 范数更接近原问题中的
范数更接近原问题中的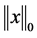 范数。问题模型如下,
范数。问题模型如下,

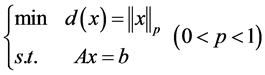 . (3)
. (3)
文献[7] 指出稀疏向量是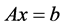 的全局
的全局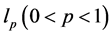 极小解,并且比
极小解,并且比 范数优化方法所需的
范数优化方法所需的 的观测数量更少。同时文献[8]
-[10] 证明了比
的观测数量更少。同时文献[8]
-[10] 证明了比 范数优化方法重构信号要求更弱的充分条件。下面我们用极大熵函数构造
范数优化方法重构信号要求更弱的充分条件。下面我们用极大熵函数构造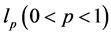 范数的光滑逼近函数,进而实现信号重构。
范数的光滑逼近函数,进而实现信号重构。
由于 范数最小化问题(3)中的目标函数可表示为
范数最小化问题(3)中的目标函数可表示为
 .
.
故问题(3)也可以写成如下形式,
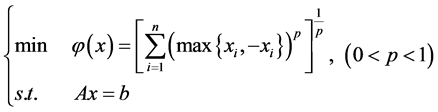 (4)
(4)
由于问题(4)中的目标函数不可导,故光滑约束算法不能使用。本文构造光滑函数去逼近式(4),将问题转变成约束光滑问题,从而用光滑约束算法求解。
2.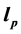 范数的光滑近似
范数的光滑近似
由于最大值函数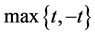 可用极大熵函数
可用极大熵函数 光滑近似[11] ,其中参数
光滑近似[11] ,其中参数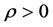 ,
,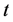 为变量。因此可用极大熵函数
为变量。因此可用极大熵函数 代替式(4)中的函数
代替式(4)中的函数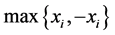 ,得到如下光滑问题:
,得到如下光滑问题:
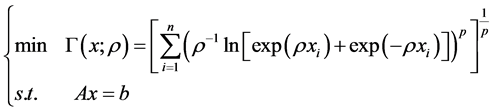 (5)
(5)
引理1[12] 假设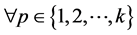 ,
, ,
,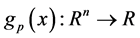 为连续可微的函数,
为连续可微的函数,
 .
.
则函数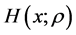 有以下性质:
有以下性质:
1) 和
和 ,有
,有 ;
;
2) 和
和 有
有 ;
;
3)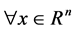 有
有 。
。
引理2 式(5)定义的函数 有如下性质。
有如下性质。 ,
,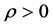 有
有
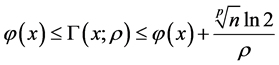 (6)
(6)
证明:由本文引理1知, ,
,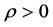 ,有
,有
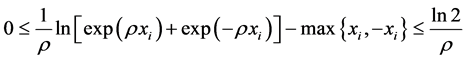 (7)
(7)
由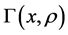 和
和 的定义,有
的定义,有

由式(7)可得
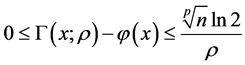
证毕。
引理3 ,
,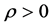 ,有
,有
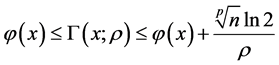
且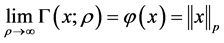 。
。
对问题(3)作如下假设:
矩阵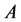 的秩为
的秩为 ,变量
,变量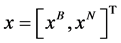 ,其中
,其中 为基变量所对应的向量,
为基变量所对应的向量, 为非基变量所对应的向量;
为非基变量所对应的向量;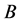 为基变量所对应的矩阵
为基变量所对应的矩阵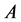 中的
中的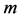 列,
列, 为非基变量所对应的矩阵
为非基变量所对应的矩阵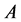 中的
中的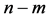 列,矩阵
列,矩阵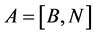 ,可行域
,可行域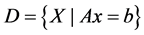 非空。
非空。
在上述假设条件下,(3)中的约束条件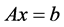 可写成
可写成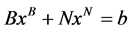 。
。
由此可得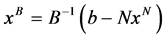 ,将
,将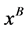 带入问题(5)的目标函数中,则式(5)转化为如下无约束问题:
带入问题(5)的目标函数中,则式(5)转化为如下无约束问题:
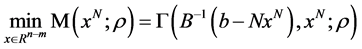 . (8)
. (8)
本文分别用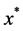 和
和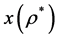 记问题(4)和(5)的最优解。
记问题(4)和(5)的最优解。
3. MEFM算法
算法1(Maximum Entropy Function Method)
步骤1 取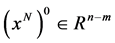 ,误差
,误差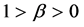 ,
,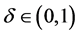 ,
,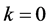 。
。
输入矩阵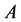 ,
, ,测量值
,测量值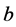 、阀值
、阀值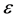 ,步长
,步长 。
。
步骤2 取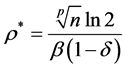 。
。
步骤3 求解式(8),即求解如下问题
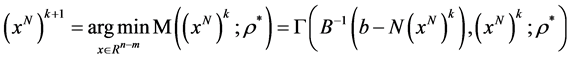
步骤4 若 ,置:
,置: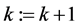 ,返回步骤3;反之,输出
,返回步骤3;反之,输出 。
。
MEFM算法具有如下性质。
定理1 假设式(8)的最优解为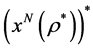 ,且算法1产生的点
,且算法1产生的点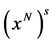 满足
满足
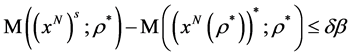 (9)
(9)
则
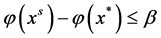 式中
式中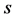 为迭代次数。
为迭代次数。
证明:由 是式(5)的最优解,即
是式(5)的最优解,即
 (10)
(10)
再由式(6)得
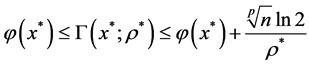

因此可得

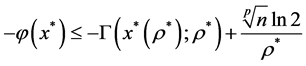 (11)
(11)
由(6)式得
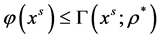 (12)
(12)
式(11)与式(12)相加得
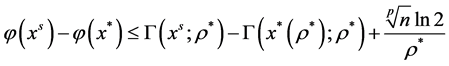 (13)
(13)
再由(8)可得
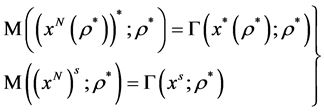 (14)
(14)
由式(9)和式(14)可知
 (15)
(15)
再由式(14)和(15)有
 (16)
(16)
将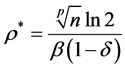 代入式(16)可得
代入式(16)可得 ,
,
证毕。
定理2 假设 是式(3)的最优解。若
是式(3)的最优解。若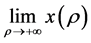 存在,设
存在,设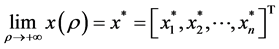 ,若
,若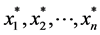 中存在
中存在 时有
时有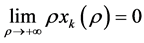 。则
。则 是问题(3)的最优解。
是问题(3)的最优解。
证明:对由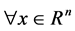 ,有
,有

由引理3得
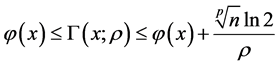 (17)
(17)
式(17)中令 ,并由定理2中的条件(2)可得
,并由定理2中的条件(2)可得
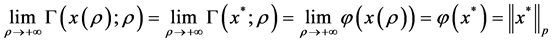
由于 是式(5)的最优解,故对任意满足
是式(5)的最优解,故对任意满足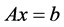 的点
的点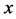 有
有

故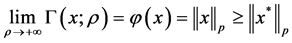 。
。
以下证明 是问题(5)的可行解,由于
是问题(5)的可行解,由于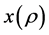 是式(5)的最优解,故有
是式(5)的最优解,故有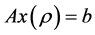 。令
。令 ,可得
,可得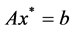 ,即
,即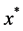 是问题(5)的最优解。
是问题(5)的最优解。
4. 信号重构实例
用MEFM算法和OMP算法对一维信号 进行重构。其中重构信号稀疏度
进行重构。其中重构信号稀疏度 ,信号长度
,信号长度 ,信号观测度
,信号观测度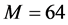 ,
, ,
, ,
,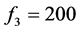 ,
,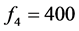 ,
,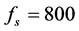 ,
, ,
, ;由图3可以看出重构信号稀疏度K
= 6。
;由图3可以看出重构信号稀疏度K
= 6。

测量值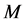 必须满足
必须满足 的,取
的,取 时,采样率
时,采样率 ,取
,取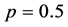 ,
,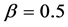 ,
, ,用MEFM算法对信号进行重构,重构效果如图4;用OMP算法重构信号,信号重构效果如图5。由图4和图5可以看出MEFM算法和OMP算法都能够很好的重构信号。
,用MEFM算法对信号进行重构,重构效果如图4;用OMP算法重构信号,信号重构效果如图5。由图4和图5可以看出MEFM算法和OMP算法都能够很好的重构信号。
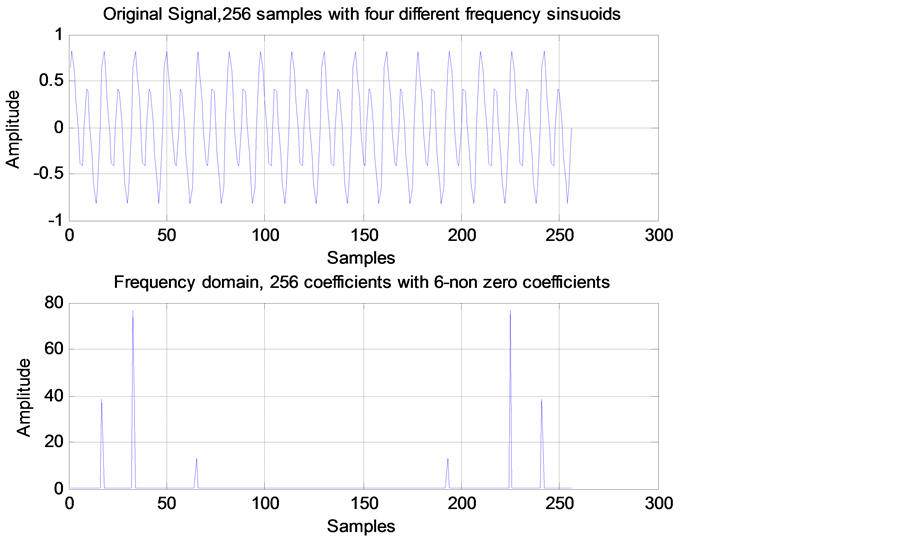
Figure 3. Original signal; Frequency domain
图3. 原始信号;频域信号

Figure 4. Reconstruction effect of one-dimensional signal
图4. MEFM算法重构信号

Figure 5. Reconstruction effect of one-dimensional signal
图5. OMP算法重构信号
表1. 重构误差
表1分别列出了MEFM算法和OMP重构算法的重构误差,可以看出,在相同采样率的情况下,MEFM算法的信号重构误差为2.9716e−024,OMP算法的信号重构误差为7.2093e−004。即采样率相同时,MEFM算法比OMP重构算法的重构效果更好,重构误差更小;OMP算法在运行时需已知信号稀疏度 ,而MEFM算法运行时不需要已知信号稀疏度
,而MEFM算法运行时不需要已知信号稀疏度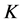 ;OMP算法是基于
;OMP算法是基于 范数最小化问题,是非光滑的,而MEFM算法是基于极大熵函数光滑化的
范数最小化问题,是非光滑的,而MEFM算法是基于极大熵函数光滑化的 最小化问题,一些基于求导求解的方法都适用,所以计算更方便,效率更高。
最小化问题,一些基于求导求解的方法都适用,所以计算更方便,效率更高。
参考文献 (References)
- [1] Candes, E.J., Romberg, J. and Tao, T. (2006) Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52, 489-509.
- [2] Donoho, D.L. (2006) Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52, 1289-1306.
- [3] Donoho, D.L. and Tsaig, Y. (2006) Extensions of compressed sensing. Signal Processing, 86, 533-584.
- [4] Candes, E. (2006) Compressive sampling. Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians, 3, 1433- 1452.
- [5] Candes, E. and Romberg, J. (2006) Quantitative robust uncertainty principles and optimally sparse decompositions. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 6, 227-254.
- [6] Chen, S.B., Donoho, D.L. and Saunders, M.A. (1998) Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 20, 33-61.
- [7] Donoho, D.L., Elad, M. and Temlyakov, V. (2006) Stable recovery of sparse overcomplete representations in the presence of noise. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52, 6-18.
- [8] Gribonval, R. and Nielsen, M. (2003) Sparse representation in unions of bases. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 49, 3320-3325.
- [9] Zelinski, A., Wald, L., Setsompop, K., et al. (2008) Sparsity-enforced slice-selective MRI RF excitation pulse design. IEEE Transaction on Medical Imaging, 27, 1213-1229.
- [10] Levin, A., Fergus, R., Durand, F. and Freeman, W.T. (2007) Image and depth from a conventional camera with a coded aperture. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 26, 70.
- [11] Donoho, D.L. and Elad, M. (2003) Optimally sparse representation in general (nonorthogoinal) dictionaries via L1 minimization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 100, 2197-2202.
- [12] Li, X.S. and Fang, S.C. (1997) On the entropic regularization method for solving max-min problems with application. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 46, 119-130.
