Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.
11
No.
12
(
2022
), Article ID:
58711
,
5
pages
10.12677/AAM.2022.1112891
Rn上返回排斥子的Lipschitz结构稳定性
陈员龙,吴小英*
广东金融学院金融数学与统计学院,广东 广州
收稿日期:2022年11月2日;录用日期:2022年11月28日;发布日期:2022年12月5日

摘要
本文研究欧氏空间上返回排斥子的Lipschitz扰动。设f,g是欧氏空间Rn上的连续自映射,如果f具有返回排斥子且g是f的Lipschitz小扰动,则g也有返回排斥子。因此欧氏空间Rn上的返回排斥子是Lipschitz结构稳定的。
关键词
混沌动力系统,Lipschitz扰动,返回排斥子,结构稳定性

The Lipschitz Perturbations of Snapback Repellers in Rn
Yuanlong Chen, Xiaoying Wu*
School of Financial Mathematics and Statistics, Guangdong University of Finance, Guangzhou Guangdong
Received: Nov. 2nd, 2022; accepted: Nov. 28th, 2022; published: Dec. 5th, 2022

ABSTRACT
This note is concerned with the effect of small Lipschitz perturbations of a discrete dynamical system in Rn. Let f, g be continuous map from Rn into itself. If f has snap-back repellers and g is a small Lipschitz perturbations of f, then g has snap-back repellers. In addition, the snap-back repellers are Lipschitz structural stability in Rn.
Keywords:Chaotic Dynamical System, Lipschitz Perturbations, Snapback Repellers, Structural Stability

Copyright © 2022 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
近年来,混沌的研究成为各个领域研究人员的关注的热点 [1] - [11]。数学上,动力系统的混沌有着多种不同的定义,常见的有Li-Yorke混沌 [12]、正熵系统 [13]、Devaney混沌 [8]、分布混沌 [14] 等。它们分别从问题的不同角度反映了系统的复杂性。
这也使得动力系统的混沌研究有着非常丰富的研究成果。因此研究动力系统复杂性的一个重要方向是探究各类混沌之间的关系及其结构稳定,例如:Devaney混沌蕴含Li-Yorke混沌 [9] 及 -混沌 [15],正拓扑熵蕴含Li-Yorke混沌 [13] 及第2类分布混沌 [10], 中返回排斥子的 结构稳定性。
对于一个动力系统 的某种性质P,如果在f的小扰动下仍具有这种性质,则称动力系统 的性质P具有结构稳定性。由于实际应用中,系统的简化或测量误差会造成研究系统与实际系统有细小误差。因此,只有结构稳定性的系统性质才有实际意义。一个直接的问题就是:什么样的混沌系统在一个小扰动下还具有混沌性或者结构稳定性。
对于返回排斥子的扰动,Li等在 [16] 中应用隐函数定理研究了欧氏空间中返回排斥子的 结构稳定性。陈等在 [3] 文中把这一结论推广到Banach空间上,证明了无穷维空间上返回排斥子的 结构稳定性。2020年,陈等在 [5] [7] 中,研究了 及Banach空间上异宿环的的 结构稳定性。本文将考虑 空间上连续条件下的返回排斥子的混沌性及其Lipschitz扰动下的稳定性。
2. 基本定义与引理
在这一节我们给出一些定义及相关引理。首先我们回顾 空间上的扩张映射与可微映射的返回排斥子定义。
定义2.1 设f是从 到自身的连续映射, 为 的某个范数。称f在领域 上是扩张的,如果存在常数 使得对任意 有 ;f的不动点x称为扩张不动点,如果f在x的某个球形领域上是扩张的。
定义2.2 [17] 设 是连续可微映射。f的不动点 称为返回排斥子,如果有
1) 的所有特征值的模大于1;
2) 设在 的某个扩张邻域存在一个点 ,使得 且对每一个 ,,其中 。
注记1:条件 的所有特征值的模大于1等价于存在 的某种范数 ,使得f在 的某个球形邻域扩张。
下面是 上连续映射的返回排斥子定义 [18] [19]。
定义2.3 设 是连续映射。f的不动点 称为返回排斥子,如果有
1) 不动点 是f的扩张不动点,也即存在常数 ,,使得对任意 有
;
2) f有一条连接 的同宿轨 ,也即对任意 且 ,有 ,
,, ;
3) f在同宿轨 上每一点是非退化的,也即对任意 ,存在 使
得对任意 有 。
其中 是 的闭球领域。
引理2.1 设f是从 到自身的连续映射。如果f有一个返回排斥子,则存在正整数 与一个康托集 使得 与符号动力系统 拓扑共轭。因此f具有Devaney混沌、分布混沌、正拓扑熵及 -混沌。
证明:设 为f的返回排斥子,则存在常数 使得对任意 ,。设连接 的同宿轨为 ,也即对任意 且 ,有 ,
,,。因此存在正整数m使得 。由已知同宿轨的非退化性及不动点的扩张性知,存在一致的 ,使得对任意 及任意 有 。由同宿轨的正则性,存在 使得 在
上是同胚及 ,。由 ,可设 满足
,,
这里 表示 限制在 上的逆。
下证存在非空不交的有界闭集 ,对某个 满足引理2.1。因为f在 上扩张,所以存在正整数 使得 。设正整数 使得 ,令
,,
则 满足引理2.1。因为
,
,
所以
即 。根据 的定义知, ,
。进一步,我们还有
。 (1)
因此 有2阶转移不变集 [20],故 与2个符号的符号转移映射 拓扑共轭,定理成立。
3. 主要定理及其证明
在这一小节中,我们将讨论欧氏空间中返回排斥子在Lipschitz小扰动下的结构稳定性。
定理3.1. 设 是 到自身的连续映射。如果f有返回排斥子且g是f的Lipschitz小扰动,那么g也有返回排斥子。因此g具有Devaney 混沌、分布混沌、正拓扑熵及 -混沌。
证明:设 是f的返回排斥子,连接 的同宿轨为 。
设 , 是 上的 Lipschitz映射,由定义2。2的第(1)条,存在 的闭球领域 及 ,使得对任意 有
, (2)
由定义2.2的第(3)条知,对任意 ,,存在一致常数使得对任意 有 。因此对任意 有
, (3)
因为g是f的Lipschitz小扰动,假设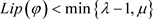 ,其中
,其中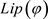 是
是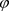 的Lipschitz常数,则g在
的Lipschitz常数,则g在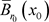 上是扩张的,g在
上是扩张的,g在 上每一点z是非退化的,g在
上每一点z是非退化的,g在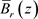 上是同胚。
上是同胚。
由定2。2的第(2)条知,存在正整数m,使得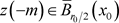 有
有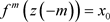 。不是一般性,设
。不是一般性,设
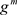 在
在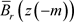 上满足(3)式。因为f在
上满足(3)式。因为f在 上连续,所以f在
上连续,所以f在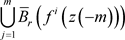 上一致连
上一致连
续。因此对任意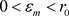 ,存在
,存在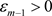 ,使得当
,使得当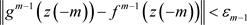 时,有
时,有
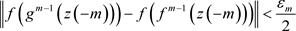 。
。
对任意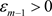 ,存在
,存在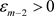 ,使得当
,使得当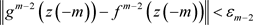 ,有
,有 。递推地,对任意
。递推地,对任意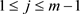 与
与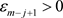 ,存在
,存在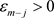 ,使得当
,使得当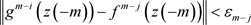 有
有
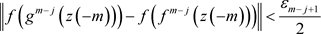 。
。
设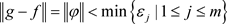 ,那么
,那么
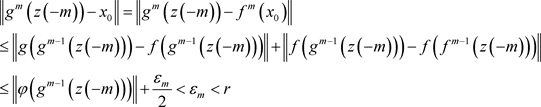
因此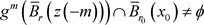 。设
。设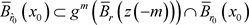 。对
。对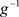 在
在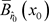 上应用压缩映像定理,则知存在
上应用压缩映像定理,则知存在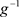 的不动点
的不动点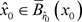 ,也即
,也即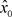 是g的不动点。因为
是g的不动点。因为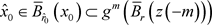 且
在
且
在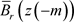 上是同胚,所以存在
上是同胚,所以存在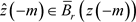 使得
使得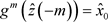 。另一方面g在
。另一方面g在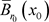 上是扩张的,因此逆向轨
上是扩张的,因此逆向轨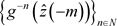 收敛于不动点
收敛于不动点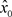 。故g有返回排斥子
。故g有返回排斥子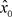 。由引理2.1知,g具有Devane混沌、分布混沌、正拓扑熵及
。由引理2.1知,g具有Devane混沌、分布混沌、正拓扑熵及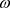 -混沌。
-混沌。
4. 总结
本文研究了欧氏空间上返回排斥子的Lipschitz结构稳定性,获得具有返回排斥子的系统在Lipschitz的小扰动下能够保持,对连续映射的结构稳定性给出理论证明,减弱已有文献的定理条件,对研究一些相对复杂系统可以通过近似处理,获得具有相同性质的简单系统进行研究。比如: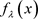 是关于
是关于 的单参数连续映射族。如果
的单参数连续映射族。如果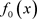 有返回排斥子,则对足够接近0的
有返回排斥子,则对足够接近0的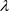 ,那么
,那么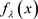 也有返回排斥子,因此
也有返回排斥子,因此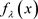 具有Devane混沌、分布混沌、正拓扑熵及
具有Devane混沌、分布混沌、正拓扑熵及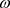 -混沌。
-混沌。
基金项目
本文受广东省普通高校自然科学重点项目(2019KZDXM036)资助。
文章引用
陈员龙,吴小英. Rn上返回排斥子的Lipschitz结构稳定性
The Lipschitz Perturbations of Snapback Re-pellers in Rn[J]. 应用数学进展, 2022, 11(12): 8426-8430. https://doi.org/10.12677/AAM.2022.1112891
参考文献
- 1. Banks, J., Brooks, J., Cairns, G., Davis, G. and Stacey, P. (1992) On Devaney’s Definition of Chaos. The American Mathematical Monthly, 99, 332-334. https://doi.org/10.1080/00029890.1992.11995856
- 2. Chen, Y., Huang, T. and Huang, Y. (2014) Complex Dynamics of a Delayed Discrete Neural Network of Two Nonidentical Neurons. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 24, Article No. 013108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4861756
- 3. Chen, Y., Huang, Y. and Li, L. (2011) The Persistence of Snap-Back Re-peller under Small C1 Perturbations in Banach Spaces. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 21, 703-710. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4861756
- 4. Chen, Y., Huang, Y. and Zou, X. (2013) Chaotic Invariant Sets of a De-layed Discrete Neural Network of Two Non- Identical Neurons. Science China Mathematics, 56, 1869-1878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-013-4640-y
- 5. Chen, Y., Li, L., Wu, X. and Wang, F. (2020) The Structural Sta-bility of Maps with Heteroclinic Repellers. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 30, Article No. 2050207. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127420502077
- 6. Chen, H. and Li, M. (2015) Stability of Symbolic Embeddings for Difference Equations and Their Multidimensional Perturbations. Journal of Differential Equations, 258, 906-918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jde.2014.10.008
- 7. Chen, Y. and Wu, X. (2020) The C1 Persistence of Heteroclinic Re-pellers in Rn. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 485, Article ID: 123823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2019.123823
- 8. Devaney, R. (1989) An Introduction to Chaotic Dynamical Sys-tems. 2nd Edition, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Redwood City.
- 9. Huang, W. and Ye, X. (2002) Deva-ney’s Chaos or 2-Scattering Implies Li-Yorke’s Chaos. Topology and Its Applications, 117, 259-272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-8641(01)00025-6
- 10. Li, J. and Ye, X. (2016) Recent Development of Chaos The-ory in Topological Dynamics. Acta Mathematica Sinica, English Series, 32, 83-114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10114-015-4574-0
- 11. Lu, K., Yang, Q. and Xu, W. (2019) Heteroclinic Cycles and Chaos in a Class of 3D three-Zone Piecewise Affine Systems. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 478, 58-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2019.04.070
- 12. Li, T. and Yorke, J. (1975) Period Three Implies Chaos. The American Mathematical Monthly, 82, 985-992. https://doi.org/10.1080/00029890.1975.11994008
- 13. 叶向东, 黄文, 邵松. 拓扑动力系统概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008.
- 14. Marotto, F. (1978) Snap-Back Repellers Imply Chaos in Rn. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 63, 199-223. https://doi.org/10.1080/00029890.1975.11994008
- 15. Li, S. (1993) ω-Chaos and Topological Entropy. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 339, 243-249. https://doi.org/10.1090/S0002-9947-1993-1108612-8
- 16. Li, M. and Lyu, M. (2020)9 A Simple Proof for Pre-sistence of Snap-Back Repellers. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 352, 669-671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2008.11.021
- 17. Li, Z., Shi, Y. and Zhang, C. (2008) Chaos Induced by Heteroclin-ic Cycles Connecting Repellers in Complete Metric Spaces. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 36, 746-761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2006.07.014
- 18. Schweizer, B. and Smital, J. (1994) Measures of Chaos and a Spectral Decomposition of Dynamical Systems on the Interval. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 344, 737-754. https://doi.org/10.1090/S0002-9947-1994-1227094-X
- 19. 吴小英, 陈员龙, 王芬. 完备度量空间中的混沌判定[J]. 数学学报: 中文版, 2021, 64(2): 225-230. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0583-1431.2021.02.004
- 20. 周作领. 符号动力系统[M]. 上海: 上海科技教育出版社, 1997.
NOTES
*通讯作者。