Modeling and Simulation
Vol.
12
No.
03
(
2023
), Article ID:
64970
,
9
pages
10.12677/MOS.2023.123163
一种新的基于样条函数的自适应模糊回归模型
蒋珂利*,陆秋君
上海理工大学理学院,上海
收稿日期:2023年2月24日;录用日期:2023年4月29日;发布日期:2023年5月6日

摘要
本文对经典的模糊半参数部分线性模型进行了推广。在本文中,考虑将样条函数和非参方法结合起来进而应用在具有模糊解释变量和模糊响应变量的数据中来,并将模糊响应变量的展形作为模糊响应变量的中心的线性组合,从而构建出一种新的自适应模糊半参数回归模型。模型中重点考虑解释变量的中心与响应变量之间的关系,以简便所构造的模型。然后,提出了一种交叉验证和最小绝对偏差混合的方法来实现所构造的自适应模糊半参数回归的目标函数优化问题,进而估计模糊半参回归模型的非参数部分的带宽和参数部分中待估计的实系数。为了验证所提出模型的有效性,本文中利用了一些常用的拟合指标来检验回归模型的性能。最后将本文中提出的回归模型与所提出的方法进行了对比分析,结果表明所提出的回归模型是较为有效的和准确的。
关键词
LR-型模糊数,截断幂基(TPB),自适应模糊回归,模糊半参数回归

A New Adaptive Fuzzy Regression Model Based on Spline Function
Keli Jiang*, Qiujun Lu
College of Science, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai
Received: Feb. 24th, 2023; accepted: Apr. 29th, 2023; published: May 6th, 2023

ABSTRACT
In this paper, the classical fuzzy semi-parametric partially linear model is extended. A new adaptive fuzzy semi-parametric regression model is constructed by combining spline function and nonparametric method in the data with fuzzy explanatory variable and fuzzy response variable, and taking the spread of fuzzy response variable as the linear combination of the center of fuzzy response variable. The model focuses on the relationship between the center of the explanatory variable and the response variable to simplify the constructed model. Then, a hybrid method of cross validation and minimum absolute deviation is proposed to optimize the objective function of the constructed adaptive fuzzy semi-parametric regression, and then the bandwidth of the non-parametric part of the fuzzy semi-parametric regression model and the real coefficients to be estimated in the parametric part are estimated. In order to verify the validity of the proposed model, some commonly used fitting indexes are used to test the performance of the regression model. Finally, the regression model proposed in this paper is compared with the proposed method, and the results show that the proposed regression model is more effective and accurate.
Keywords:LR-Type Fuzzy Number, Truncated Power Basis (TPB), Adaptive Fuzzy Regression, Fuzzy Semi-Parametric Regression

Copyright © 2023 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
回归分析 [1] 是为了研究一个真实现象与其他真实现象之间的依赖关系而采用的统计方法,是一种有着广泛应用背景的数据分析方法。它主要基于观测数据讨论响应变量与一个或多个解释变量之间的相关依赖关系,广泛用于通过对解释变量的观测来描述、控制和预测响应变量的值。然而,由于数据不精确,观测数据与相应的估计值之间存在偏差。提出了模糊回归方法来建立变量间关系的模型。它们还广泛应用于分析复杂系统,包括经济系统、社会系统、工程系统和环境系统,这些系统中人类主观判断的模糊性是有影响的 [2] [3] [4] [5] 。
Tanaka et al. [6] 是最早提出了模糊线性回归问题。他于1982年首次提出模糊线性回归模型,该模型主要用于反映模糊系统中解释变量与响应变量之间的关系。传统回归模型将真实数据与估计值之间的偏差视为观测误差,而模糊回归分析则将这种误差视为系统结构本身的模糊性,将数据与估计值之间的偏差视为系统参数的模糊性,从而通过参数模糊性来解决这一问题。他们最小化了系统的模糊性,以估计回归模型的参数。此后,模糊回归模型引起了一些研究者的兴趣。Yen et al. [7] 将使用对称三角参数的模糊线性回归模型的结果扩展为不对称模糊三角系数的模型。沿着这个思路,后来的研究发展并完善了该模型的缺陷 [8] [9] 。Diamond [10] 研究了模糊回归建模问题中未知参数的最小二乘估计方法。Xu和Li [11] 利用模糊数空间上定义的距离建立了模糊类比,并用最小二乘方法处理了模糊多元线性回归问题。随后一些作者对这种方法进行了研究和改进(例如 [12] [13] )。这些研究都是明确了输入输出之间的关系,从而建立多元线性回归模型,通过各种方法求解未知系数解决实际问题。
对于许多实际问题,输入和输出之间的函数形式往往是未知的,我们无法得到他们之间的具体关系。此时,有非参数技术来改进模糊回归分析。近几年不少学者研究了模糊非参回归模型:Petit-Renaud和Denux [14] 提出了一种基于模糊置信度分配的非参数回归方法。Farnoosh等人 [15] 研究了具有多元实值输入和三角模糊输出的模糊非参数回归模型的岭估计。非参数方法通常存在一些解释性差,数据要求高等缺陷。而由于模糊半参数回归模型集合参数回归和非参数回归,因此,模糊半参回归模型具有了他们的优势,同时更具灵活性。Akbari和Hesamian [16] 扩展了传统的半参数偏线性回归模型,当出现多重共线性和异常值时,该模型具有模糊预测因子和模糊响应。Hesamian et al. [17] 利用非参数估计器构造了一个模糊单变量回归模型,并用混合算法估计了带宽和模糊回归系数。
在过去具有模糊解释变量和模糊响应变量的模糊回归模型中,他们没有研究半参数技术对自适应模糊回归模型中响应变量中心的影响。本文将参数回归和非参数回归方法以及样条基和自适应技术相结合,尝试引入基于样条基的自适应模糊半参数回归模型。因此,本文的主要工作是研究具有模糊输入输出的样条基的自适应模糊半参数回归模型,以预测模糊输出的效果。本文提出了一种常用的两步方法来估计非模糊系数和非模糊平滑函数。为此,采用核函数法和最小绝对偏差法,对自适应模糊半参数回归模型的分量进行估计。在非模糊平滑函数估计中,采用基于交叉验证准则的最小化算法来选择最优带宽。为了进行对比研究,对所提出的基于样条基的自适应模糊半参数回归模型进行了仿真分析,并根据一些著名的拟合优度准则对所提出的方法进行了比较,验证了所提出方法的有效性和优越性。由于所提出的模型应该与现实相关,我们将基于使用真实数据集来说明所提出的方法。数值分析和对比结果表明,该模型较其他模型有较大的优势。
本文的其余部分组织如下。第2节回顾了LR-型模糊数、线性自适应模糊回归模型和模糊半参数部分线性模型。第3节描述了采用样条基的自适应模糊半参数回归模型的形式化。本节中,采用交叉验证方法中的留一法和最小绝对偏差方法来确定未知的光滑参数和待估计的实值系数,然后,从评价模型拟合优度的一些措施方面,报告了模型的不同性能标准。在第4节中,通过应用实例的结果,我们证明了所提模型的有效性。最后,在第5部分对本文的工作做了总结和展望,以供进一步研究。
2. 预备知识
在本节中,我们介绍了LR-型模糊数的一些概念,线性自适应模糊回归模型和模糊半参数部分线性模型的基本原理。这两个模型在提供信息以支持本文讨论的背景、方法和预测过程方面都很重要。
2.1. LR-型模糊数
一个LR-型模糊数 是由下面的隶属函数定义 [18] 得到:
(1)
可以看出,LR-型模糊数的隶属函数是由中心值 ,左右展值 , ( 是严格递减的形状函数),且 组成。一个LR-型模糊数 可以记作 。若形状函数由 定义,那么 是一个三角模糊数,记为 。
对于LR-型模糊数的代数运算,我们在Zadeh可拓原理的基础上得到如下结果(详见 [18] )。令 和 为两个LR-型模糊数, 为实数。
;
。
由Kelkinnama和Taheri [19] 所定义的两个LR-型模糊数之间的距离:
(2)
其中, , 。
2.2. 线性自适应模糊回归模型
考虑n组LR-型模糊数据,即 。其中 是解释变量, 是响应变量 。D’urso [20] 得到了具有实值系数的模糊输入与模糊输出之间真实关系的方程并提出了一种基于三个子模型(一个核心回归模型和两个展形回归模型)的自适应模糊线性回归模型。模糊回归模型可以写成:
(3)
以上表达式中, , 和 分别表示第i个响应变量的估计值的中心,左展和右展; , 和 是关于响应变量估计值中心的回归模型的系数;u,v,g和z是关于响应变量估计值左右展形的回归模型的系数; , 和 分别表示回归模型中心、左展和右展的残差。D’Urso采取了基于两个LR-型模糊数之间的平方欧氏距离来估计模糊回归模型的未知参数。
2.3. 模糊半参数部分线性模型
给定一组具有n个的模糊观测数据 ,可以建立模糊半参数部分线性模型 [21] :
(4)
其中, 是一个未知的实系数; 是一个取值范围在0到1 (包含0和1)的协变量,当 时,有 ; 是未知的光滑函数,其中光滑函数的左右展 都大于等于0; 是一个均值为零的随机误差。由(4)指出,在模糊半参数部分线性模型中使用常数 代替 ,可以将模糊半参数部分线性模型简化为模糊线性回归模型。因此,模糊线性回归问题转向寻找最优实系数 ,使估计输出 与观测输出在一定意义上一致。模糊半参数部分线性模型由两部分组成,一部分是参数部分,另一部分是非参数部分。参数分量用于分析确定性影响因素,非参数分量用于表征随机干扰。可见,模糊半参数部分线性模型与参数回归模型相结合具有解释性好、简单的优点,非参数回归模型的回归函数形式可以任意,可以有效地处理非线性问题,较好地拟合样本数据。
3. 模糊输入、模糊输出回归模型的建立
本节提出了一种基于模糊输入和模糊输出数据的半参数自适应模糊回归方法。
3.1. 基于TPB自适应模糊半参数回归模型
考虑LR-型模糊数 ,其中 , , 。回归样条的使用通常为分析人员制定探索性分析提供了额外的灵活性。截断幂基是一个在 处具有结点的某阶样条,并且在每个区间上是一个d次的实值多项式函数。对此,我们考虑以下应用TPB的自适应模糊半参数回归模型:
(5)
其中, , ,u,v,g和z是上述模型中待估计的实系数; 是关于解释变量中心的节点; , 和 表示残差; 是未知的光滑函数,其中 是协变量。
根据Nadaraya-Watson [22] ,那么估计光滑函数 可以是:
(6)
其中 和 为核函数 的带宽。
将(6)式代入(5)式中的第一个表达式中,得到关于输出中心的估计值:
(7)
3.2. 估计模型未知参数的算法
由于光滑函数 中涉及光滑参数h,因此在估计光滑函数时,先估计未知的光滑参数带宽h。本文中,采取交叉验证中的留一法获取h:
, (8)
其中, 表示去掉第i个样本之后 的估计值。
根据最优带宽 ,估计模糊回归系数的最优值是考虑两个LR-型模糊数之间的绝对距离来确定回归模型中的未知参数:
。 (9)
针对上述优化问题,本文提出了以下算法来寻找带宽和回归系数的最优值:
步骤1:选择一个核函数,通过(8)计算最优带宽。
步骤2:通过最小化(9)的方法估计回归系数。
3.3. 回归模型的评价指标
为了检验所提出的基于样条基的自适应模糊半参数回归模型的性能,本文采用以下常用的拟合指标测度,以获得预测精度。在模糊环境中,我们可以使用Kim和Bishu ( [23] )提出的隶属函数拟合的误差作为拟合优度的度量。假设 和 分别是基于所建立模型的实际输出和估计输出。使用Kim和Bishu提出的距离的误差均值(ME)定义为公式:
(10)
其中,积分只在包含模糊数支撑的区间内计算。
输出的中心、左展、右展( 、 和 )的平均绝对百分比误差分别用于比较和评估回归模型的准确性。
(11)
(12)
(13)
另外,平均相似度(MSM)的评价指标亦可以对模型进行评价:
(14)
其中 和 表示模糊数空间上的交集和并集。
4. 算例分析
在本节中,我们研究了所提出的自适应模糊回归求解过程的可行性和有效性。我们可以令 。平滑函数是triweight核函数。
在这里,我们使用的数据集包括1988年1月至1991年10月5家不同航空公司的每日股价(见https://sci2s.ugr.es/keel/dataset.php?cod=77/)。该数据集包含150个连续变量的数值观测数据。在这五个变量中,数据集中的第五个变量被认为是响应变量,其余四个变量根据数据集中的顺序被索引为解释变量。然后He et al. ( [24] )将所有变量转化为三角模糊数,对所选数据进行模糊化如下处理:
其中 , 分别是均值和方差。 和 可以由下面的表达式确定:
。
利用TPB对这些数据导出的自适应模糊半参数回归模型为:
作为对比,提出的模型的性能与其他研究人员D’Urso [20] ,Chen和Hsueh [25] ,Choi和Buckley [26] ,Chachi和Taheri [27] ,Hesamian et al. [21] 和Chen and Nien [28] 提出的模型进行了比较。
从表1可以看出,与文献中已有的方法相比,我们的方法具有显著的拟合性和效率。
Table 1. The fitting performance of fuzzy regression model
表1. 模糊回归模型的拟合性能
如图1所示为拟合示意图。如图1所示,可以很明显看出,与文献中已有的方法相比,我们的方法的拟合指标结果最优,从而本文提出的方法更有效。
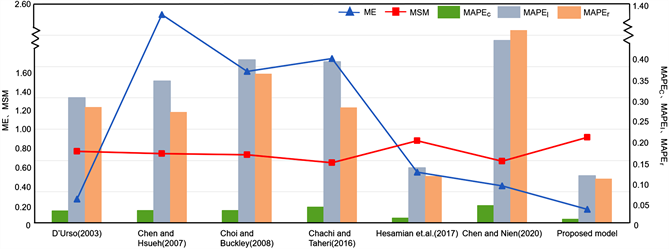
Figure 1. The fit of the model
图1. 模型的拟合性
5. 总结与未来展望
利用样条基函数研究了一种输入模糊、输出模糊的自适应模糊半参数回归模型。所提出的回归模型是基于著名的线性自适应模糊回归模型。
首先,定义了自适应模糊回归模型,并结合半参数技术和TPB,利用绝对偏差度量优化目标函数,同时估计回归系数和平滑函数。然后,我们讨论了我们的结果,并与一些经典的和最近提出的方法进行了比较。该模型优于其他模型,是提高预测精度的一种有效合理的方法。
根据所获得的结果,进一步的工作可以将所提出的方法扩展到更复杂的模糊回归模型(例如:模糊逻辑回归)以及发展与传统方法的比较研究。
致谢
在此,我要感谢陆老师为改进这篇论文的呈现提出的宝贵意见。
基金项目
本文由Priority discipline project of Shanghai Grant No. T0502和Foundation of Hujiang Grant No. B14005资助。
文章引用
蒋珂利,陆秋君. 一种新的基于样条函数的自适应模糊回归模型
A New Adaptive Fuzzy Regression Model Based on Spline Function[J]. 建模与仿真, 2023, 12(03): 1760-1768. https://doi.org/10.12677/MOS.2023.123163
参考文献
- 1. Thrane, C. (2019) Applied Regression Analysis: Doing, Interpreting and Reporting. Taylor and Francis, New York. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429443756
- 2. Burrows, W.R. (1999) Combining Classification and Regression Trees and the Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System for Environmental Data Modeling. Proceedings of 18th International Conference of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society-NAFIPS (Cat. No. 99TH8397), New York, 10-12 June 1999, 695-699.
- 3. Lin, J.G., Zhuang, Q.Y. and Huang, C. (2012) Fuzzy Statistical Analysis of Multiple Regression with Crisp and Fuzzy Covariates and Applications in Analyzing Economic Data of China. Computational Economics, 39, 29-49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-010-9223-1
- 4. Roldan, L., de Hierro, A.F., Martinez-Moreno, J., Aguilar-Pena, C., Lopez, R. and de Hierro, C. (2016) A Fuzzy Regression Approach Using Bernstein Polynomials for the Spreads: Computational Aspects and Applications to Economic Models. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 128, 13-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2016.03.012
- 5. Mirzaei, F., Delavar, M., Alzoubi, I. and Arrabi, B.N. (2018) Model-ing and Predict Environmental Indicators for Land Leveling Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) and Re-gression. International Journal of Energy Sector Management, 12, 484-506. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJESM-02-2017-0003
- 6. Tanaka, H., Uejima, S. and Asai, K. (1982) Linear Regression Analy-sis with Fuzzy Model. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 12, 903-907. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1982.4308925
- 7. Yen, K.K., Ghoshray, S. and Roig, G. (1999) A Linear Regression Model Using Triangular Fuzzy Number Coefficients. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 106, 167-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(97)00269-8
- 8. Liu, X.L. and Chen, Y.Z. (2013) A Systematic Approach to Opti-mizing Value for Fuzzy Linear Regression with Symmetric Triangular Fuzzy Numbers. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2013, Article ID: 210164. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/210164
- 9. de Andrés-Sánchez, J. (2017) An Empirical Assessment of Fuzzy Black and Scholes Pricing Option Model in Spanish Stock Option Market. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 33, 2509-2521. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-17719
- 10. Diamond, P. (1988) Fuzzy Least Squares. Information Sciences, 46, 141-157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-0255(88)90047-3
- 11. Xu, R.N. and Li, C.L. (2001) Multidimensional Least-Squares Fitting with a Fuzzy Model. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 119, 215-223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(98)00350-9
- 12. Shen, S.L., Mei, C.L. and Cui, J.L. (2010) A Fuzzy Varying Coefficient Model and Its Estimation. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 60, 1696-1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2010.06.049
- 13. Chachi, J. (2018) A Weighted Least Squares Fuzzy Regression for Crisp Input-Fuzzy Output Data. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 27, 739-748. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2868554
- 14. Petit-Renaud, S. and Denœux, T. (2004) Nonparametric Regression Analysis of Uncertain and Imprecise Data Using Belief Functions. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 35, 1-28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0888-613X(03)00056-2
- 15. Farnoosh, R., Ghasemian, J. and Solaymani, F.O. (2012) A Modi-fication on Ridge Estimation for Fuzzy Nonparametric Regression. Iranian Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 9, 75-88.
- 16. Akbari, M.G. and Hesamian, G. (2019) A Partial-Robust-Ridge-Based Regression Model with Fuzzy Predictors-Responses. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 351, 290-301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2018.11.006
- 17. Hesamian, G., Akbari, M.G. and Shams, M. (2021) Parameter Estimation in Fuzzy Partial Univariate Linear Regression Model with Non-Fuzzy Inputs and Triangular Fuzzy Outputs. Iranian Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 18, 51-64.
- 18. Zimmermann, H.J. (2011) Fuzzy Set Theory and Its Applications. Springer Science & Business Media, New York.
- 19. Kelkinnama, M. and Taheri, S.M. (2012) Fuzzy Least-Absolutes Regression Using Shape Preserving Operations. Information Sciences, 214, 105-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2012.04.017
- 20. D’Urso, P. (2003) Linear Regression Analysis for Fuzzy/Crisp Input and Fuzzy/Crisp Output Data. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 42, 47-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9473(02)00117-2
- 21. Hesamian, G., Akbari, M.G. and Asadollahi, M. (2017) Fuzzy Semi-Parametric Partially Linear Model with Fuzzy Inputs and Fuzzy Outputs. Expert Systems with Applications, 71, 230-239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.11.032
- 22. Cai, Z.W. (2001) Weighted Nadaraya—Watson Regression Estimation. Statistics & Probability Letters, 51, 307-318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7152(00)00172-3
- 23. Kim, B. and Bishu, R.R. (1998) Evaluation of Fuzzy Linear Regres-sion Models by Comparing Membership Functions. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 100, 343-352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(97)00100-0
- 24. He, Y.L., Wang, X.Z. and Huang, J.Z. (2016) Fuzzy Nonlinear Re-gression Analysis Using a Random Weight Network. Information Sciences, 364, 222-240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.037
- 25. Chen, L.H. and Hsueh, C.C. (2007) A Mathematical Programming Method for Formulating a Fuzzy Regression Model Based on Distance Criterion. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 37, 705-712. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2006.889609
- 26. Choi, S.H. and Buckley, J.J. (2008) Fuzzy Regression Using Least Absolute Deviation Estimators. Soft Computing, 12, 257-263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-007-0198-3
- 27. Chachi, J. and Taheri, S.M. (2016) Multiple Fuzzy Regression Model for Fuzzy Input-Output Data. Iranian Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 13, 63-78.
- 28. Chen, L.H. and Nien, S.H. (2020) A New Approach to Formulate Fuzzy Regression Models. Applied Soft Compu-ting, 86, Article 105915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105915
NOTES
*通讯作者。
