Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.3 No.02(2014), Article
ID:13504,5
pages
DOI:10.12677/AAM.2014.32013
随机脉冲时刻下微分系统的稳定性
Wenbo Han, Caixia GaoSchool of Mathematical Sciences, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot
Email: hwb112358@sina.com, gaocx0471@163.com
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: Mar. 22nd, 2014; revised: Apr. 19th, 2014; accepted: Apr. 27th, 2014
ABSTRACT
This paper studies the stability of impulsive differential systems when the pulses happen in the random time. Under the influence of random pulses, the solutions of impulsive differential equations become the stochastic processes, so the solutions are far different from the deterministic impulsive differential equations’. In this paper, we study how the random pulses affect the stability of the systems, and then the sufficient condition on P-moment stability is established.
Keywords:Impulsive Differential System, P-Moment Exponential Stability, Stochastic Process, Lyapunov’s Direct Method, Sufficient Conditions

随机脉冲时刻下微分系统的稳定性
韩文博,高彩霞
内蒙古大学数学科学学院,呼和浩特
Email: hwb112358@sina.com, gaocx0471@163.com
收稿日期:2014年3月22日;修回日期:2014年4月19日;录用日期:2014年4月27日

摘 要
本文研究了当脉冲时刻是随机变量时,脉冲微分系统的稳定性。因为在随机脉冲时刻的影响下,脉冲微分方程的解为随机过程,这与传统的确定性脉冲时刻的微分方程解的性质相差甚远。本文便研究随机脉冲的发生是如何影响系统稳定性的,并给出使系统P阶指数稳定的充分条件。
关键词
脉冲微分系统,P阶指数稳定性,随机过程,Lyapunov直接法,充分条件

1. 引言
脉冲微分方程描述了某些运动状态在固定或不固定时刻的快速变化或跳跃. 它是对自然界的发展过程更加真实的反映,科学和技术的许多领域和许多方面的变化规律都可以用脉冲微分方程来刻画或描述[1] 。因此大量有关脉冲微分系统的理论应运而生[1] -[3] ,并且得到了广泛的关注。而稳定性对系统来说是重要且基本的内容。因为稳定性是系统能否正常工作的先决条件,因此判别脉冲系统的稳定性以及如何改善其稳定性是系统分析和综合的首要问题[4] [5] 。文献[6] -[11] 分别从不同角度用不同方法研究了脉冲微分系统的稳定性问题。近几年来,在前人的脉冲系统研究的基础上[12] ,运用Lyapunov稳定理论与脉冲系统的比较原理,结合现实工程当中的应用,将时间滞后,参数不确定,耗散性无源性,随机等因素被考虑到脉冲系统模型中来,极大的丰富了经典的脉冲系统稳定性理论。
但是在实际问题中脉冲发生的时刻不全是确定的,而常常是随机的,也就是说,脉冲时刻是随机变量。由于脉冲时刻是随机的,具有随机脉冲时刻的微分方程的所有解均为随机过程,这与传统的确定性脉冲时刻的微分方程解的性质相差甚远,因为一般的确定性脉冲时刻的脉冲系统的解是一个分段函数。而随机脉冲系统的解是一个随机过程。本文便研究随机脉冲的发生是如何影响系统稳定性的,并给出使系统P阶指数稳定的充分条件。
2. 预备知识
考虑线性脉冲微分系统:
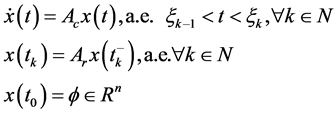 (1)
(1)
其中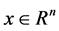 代表系统状态,矩阵
代表系统状态,矩阵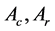 为适合维数的常矩阵。
为适合维数的常矩阵。![]() 是定义在
是定义在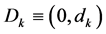 上的随机变量,
上的随机变量,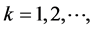 其中
其中 。同时,假设当
。同时,假设当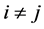 时,
时, 和
和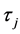 是相互独立的,
是相互独立的,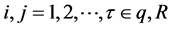 为常数。
为常数。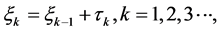 记
记
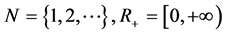
和
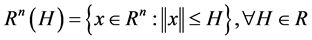
其中![]() 为
为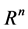 空间中的欧氏范数。
空间中的欧氏范数。
本文中,我们总假设系统(1)的解存在且唯一,并且其解均为右连续的。
令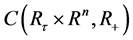 表示所有定义在
表示所有定义在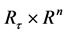 上的非负函数
上的非负函数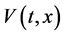 集合,并且
集合,并且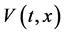 关于
关于![]() 和
和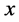 均连续可微。对于
均连续可微。对于 ,定义从
,定义从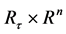 到
到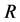 上的算子
上的算子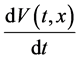
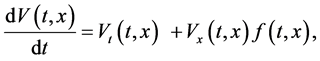
其中
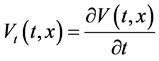
且
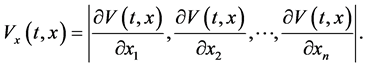
定义1:假设 ,系统(1)的零解被称为
,系统(1)的零解被称为![]() 阶矩指数稳定,如果存在
阶矩指数稳定,如果存在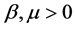 使得
使得

其中 这里及以后,
这里及以后,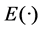 表示数学期望。
表示数学期望。
3. 主要结果
引理1 对于系统(1),任意的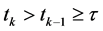 ,
,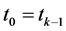 ,假设存在
,假设存在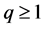 以及函数
以及函数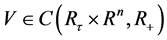 满足
满足
i)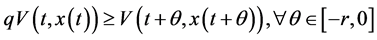 有
有
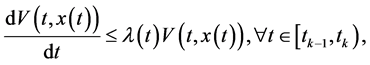
其中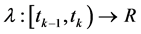 。
。
ii) 
那么,对任意的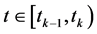 ,
,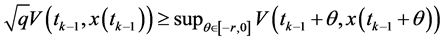 就有
就有
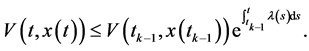
证明过程见参考文献[13] 。
在提供稳定性条件之前,需要指出,该分析利用了一类在紧集上满足线性微分包含的拟二次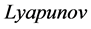 函数[9] [14] 。更确切地说,我们使用的函数:
函数[9] [14] 。更确切地说,我们使用的函数:
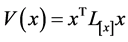
其中![]() 为依赖于系统系统状态的李雅普诺夫矩阵,并满足齐次性,即
为依赖于系统系统状态的李雅普诺夫矩阵,并满足齐次性,即
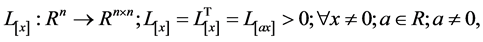
而在本文中,我们只需令![]() 为对称正定常矩阵
为对称正定常矩阵 即可,即取
即可,即取
![]()
定理1:假设存在函数 ,对称正定矩阵
,对称正定矩阵 和正常数
和正常数 满足下列条件
满足下列条件
i) 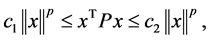
ii)![]() 有
有
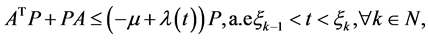
其中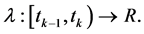
iii) 存在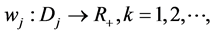 使得
使得
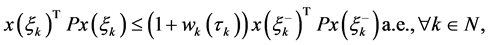
iv) 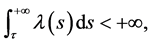
v) 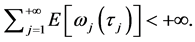
则系统(1)的零解是![]() 阶矩指数稳定的。
阶矩指数稳定的。
证:我们假设 对任意的
对任意的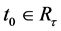 ,由条件i),我们得到
,由条件i),我们得到

那么对所有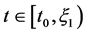 ,由引理1得到:
,由引理1得到:
 (2)
(2)
接下来,我们将证明
 (3)
(3)
对任意的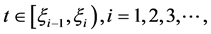 当
当![]() 时,
时,
在![]() 的情况下,由式(2),则能推出(3)。假设对
的情况下,由式(2),则能推出(3)。假设对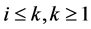 (3)成立,也就是说对所有
(3)成立,也就是说对所有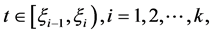 有
有
 (4)
(4)
因此,对所有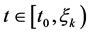 有
有
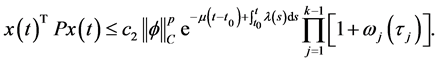
进一步,条件iii)意味着
 (5)
(5)
对任意的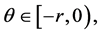 如果
如果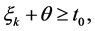 那么由式(4)和(5),有
那么由式(4)和(5),有
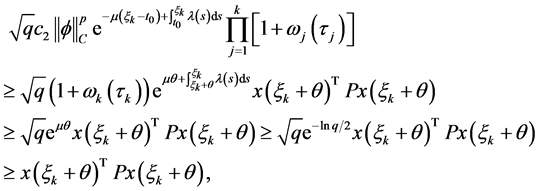
反之如果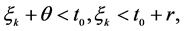 那么由式(4)和(5),有
那么由式(4)和(5),有
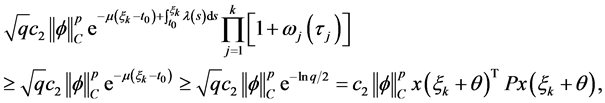
综上,对任意 我们有
我们有
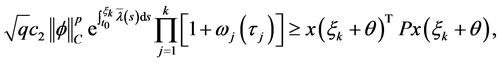
由(5)以及引理1,对于所有的 我们得到
我们得到

这就表示,当 时,式(3)成立。经过以上数学推导,我们证明了对于所有
时,式(3)成立。经过以上数学推导,我们证明了对于所有 式(3)成立。
式(3)成立。
对于任意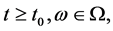 如果存在一个
如果存在一个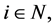 使得
使得 那么我么从式(3)得到
那么我么从式(3)得到
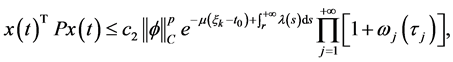
否则,如果不存在这样的![]() ,那么
,那么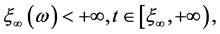 这时式(11)意味着:
这时式(11)意味着:
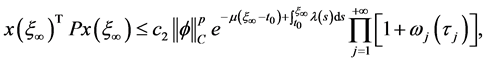
因此,由引理1
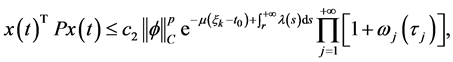
综上,对任意 有
有

因此对所有的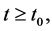 由条件i)
由条件i)
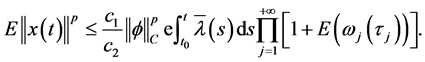 (6)
(6)
对任意的 存在
存在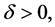 满足
满足 其中
其中
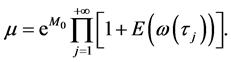
当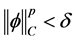 时,由(6)得到,对所有的
时,由(6)得到,对所有的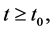
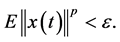
4. 结论
由于受到脉冲随机发生的影响,脉冲微分方程的解成为了一个随机过程,本文以Lyapunov直接法为基础,通过运用拟二次Lyapunov函数给出使线性随机脉冲微分系统P阶指数稳定的充分条件。
致 谢
作者衷心感谢导师高彩霞副教授的悉心指导和热心鼓励,感谢中国自然科学基金(基金编号:11261033)的资助。向给予转载和引用权的资料、文献、研究思想和设想的所有者、表示感谢。感谢审稿人的审稿意见。
项目基金
中国自然科学基金(基金编号:11261033)。
参考文献 (References)
- Lakshmikantham, V., Bainov, D.D. and Slmeonov, P.S. (1989) Theory of impulsive differential equations. World Scientific, Singapore.
- Yang, T. (2001) Impulsive control theory. Vol. 272, Springer.
- Samoilenko, A.M., Perestyuk, N.A. and Chapovsky, Y. (1995) Impulsive differential equations. World Scientific, Singapore.
- Liu, X. (1993) Impulsive stabilization of nonlinear systems. IMA Journal of Mathematical Control and Information, 10, 11-19.
- Reinfelds, A. and Sermone, L. (2013) Stability of impulsive differential systems. Abstract and Applied Analysis, Vol. 2013, Hindawi Publishing Corporation.
- Stamova, I.M. and Stamov, G.T. (2001) Lyapunov-Razumikhin method for impulsive functional differential equations and applications to the population dynamics. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 130, 163-171.
- Kou, C.H., Zhang, S.N. and Wu, S.J. (2002) Stability analysis in terms of two measures for impulsive differential equations. Journal of the London Mathematical Society, 66, 142-152.
- Naghshtabrizi, P., Hespanha, J.P. and Teel, A.R. (2008) Exponential stability of impulsive systems with application to uncertain sampled-data systems. Systems & Control Letters, 57, 378-385.
- Hetel, L., Kruszewski, A., Perruquetti, W. and Richard, J. (2011) Discrete and inter-sample analysis of systems with aperiodic sampling. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 56, 1696-1701.
- Liu, K. and Fridman, E. (2012) Wirtingers inequality and lyapunov-based sampled-data stabilization, Automatica, 48, 102-108.
- Hetel, L., Daafouz, J., Tarbouriech, S., Prieur, C., et al. (2013) Stabilization of linear impulsive systems through a nearly-periodic reset. Nonlinear Analysis: Hybrid Systems, 7, 4-15.
- Lakshmikantham, V. and Devi, J.V. (1993) Strick stability for impulsive differential systems. Nonlinear Analysis, 21, 785-794.
- Wu, S.J. and Han, D. (2005) Exponential stability of impulsive functional differential systems with random impulsive moments. Computers & Mathematics with Applications‚ 50‚ 321-328.
- Molchanov, A.P. and Pyatnitskiy, Y.S. (1989) Criteria of asymptotic stability of differential and difference inclusions encountered in control theory. Systems and Control Letters, 13, 59-64.