Applied Physics
Vol.
11
No.
05
(
2021
), Article ID:
42455
,
7
pages
10.12677/APP.2021.115034
生长在PLA基片上的Ni81Fe19薄膜的磁性能研究
王禹1*,余涛2*,王传龙1,徐思晨1,朱齐山1,葛水兵1,彭斌3,张万里3,汤如俊1#
1苏州大学物理科学与技术学院,江苏省薄膜重点实验室,江苏 苏州
2贵州雅光电子科技股份有限公司,贵州 贵阳
3电子科技大学,电子薄膜与集成器件国家重点实验室,四川 成都

收稿日期:2021年4月13日;录用日期:2021年5月14日;发布日期:2021年5月21日

摘要
随着电子器件微型化、集成化和柔性化技术的发展,NiFe薄膜器件与人体及其它器件集成化的过程对NiFe薄膜在不同基片,特别是几何弯曲基片上的异质生长提出了新的需求。本文研究了生长在聚乳酸(PLA)基片上Ni81Fe19薄膜的磁学性能,研究了基片的弯曲方向、弯曲程度和弯曲次数对薄膜磁性的影响。结果表明NiFe薄膜的磁性主要受基片弯曲带来的几何形状的影响。薄膜的矫顽力随弯曲半径的增加而增加,薄膜的弯曲半径可以小于1.5 mm。随着弯曲次数的增加,薄膜的矫顽力在略微增加后保持稳定,薄膜的最大弯曲次数可以达到2000次。
关键词
聚乳酸,柔性,NiFe,磁性
Magnetic Properties of Ni81Fe19 Thin Films on PLA Substrate
Yu Wang1*, Tao Yu2*, Chuanlong Wang1, Sichen Xu1, Qishan Zhu1, Shuibin Ge1, Bin Peng3, Wanli Zhang3, Rujun Tang1#
1Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Thin Films, School of Physical Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou Jiangsu
2Guizhou Yaguang Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Guiyang Guizhou
3State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu Sichuan

Received: Apr. 13th, 2021; accepted: May 14th, 2021; published: May 21st, 2021

ABSTRACT
With the development of miniaturization, integration and flexibility of electronic devices, the integration of NiFe thin film devices with other devices puts forward new requirements for the growth of NiFe thin films on different substrates, especially on geometrically bent substrates. The magnetic properties of Ni81Fe19 films grown on polylactic acid (PLA) films were studied. The effects of bending direction, bending degree and bending times on the magnetic properties of the films were studied. The results show that the magnetic properties of NiFe films are mainly affected by the geometry of the substrate. The coercivity increases with the increase of the bending radius, which can be less than 1.5 mm. With the increase of the bending times, the coercivity of the film keeps stable after a slight increase, and the maximum bending times of the film can reach 2000.
Keywords:PLA, Flexible, NiFe, Magnetic Properties

Copyright © 2021 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
坡莫合金(NiFe)作为一种经典的软磁性材料,具有高饱和磁化强度、高剩磁比、低矫顽场和各向异性磁电阻的特点,这使它在弱磁场传感器和薄膜电感等领域有着广阔的应用前景。随着电子设备在日常生活中应用的日益广泛,人们对能够应用于生物集成的传感器的需求不断增加 [1]。与此同时,电子器件的可延展柔性化是微电子器件的革命性发展方向。NiFe薄膜器件与人体及其它器件集成化的过程对NiFe薄膜在不同基片,特别是几何弯曲基片上的异质生长提出了新的需求 [2] - [6]。因此选取合适的柔性基片显得格外重要。
我们选取了聚乳酸(PLA)薄膜。PLA是一种新型可再生生物降解材料,可以生物降解,实现在自然界中的循环,因此是理想的绿色高分子材料 [7]。对柔性PLA基片上NiFe膜生长的研究有助于推动这些材料在柔性电子产品中的应用。本文在柔性PLA基片上制备了不同NiFe厚度的Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜,并对薄膜微观结构和磁性能进行了研究。三层薄膜中底部Ta层设计为过渡层,以便更好地生长NiFe磁性层。顶部Ta层用于保护NiFe层在空气中免受氧化。
2. 实验方法
为了实现在PLA基片上生长的薄膜的性能可以与刚性基片相媲美,并且控制在弯曲和拉伸等形变状态下的磁电性能,同时获得有大形变能力的磁性薄膜。我们通过磁控溅射设备(JGP500)在柔性PLA基片上制备了Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜。使用的是高纯度(99.99%) 的NiFe和Ta金属靶进行沉积。薄膜在室温下1 Pa氩气条件下进行沉积,使用的是直流电源,功率为30 W。通过X射线衍射(XRD, Rigaku D-Max 2000PC)测量样品的成相。在综合物性测量系统(PPMS-9, Quantum Design)中使用振动样品磁强计(VSM)进行磁学测量。对弯曲条件下的磁性测试则是将样品粘贴在不同弯曲半径无磁性模具上后放入仪器测试。如图1(a)所示,为了适配弯曲半径1.5 mm的模具,将NiFe薄膜长度控制小于4 mm。图1(b)是样品放入模具弯曲的照片。
Figure 1. (a) The sample of bending magnetic test; (b) The sample bending in the mold
图1. (a)弯曲磁性测试的样品实物图;(b) 样品放入模具弯曲的实物图
3. 结果与分析
图2是PLA基片上Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜的XRD结果。结果表明,Ta的峰无法被测得。但是在可以观察到NiFe的(111)峰(44.5˚)。由于PLA基片并不具有晶体取向,而且PLA基片上的表面平整度不如刚性样品,这降低了X射线的反射强度,因此NiFe的峰值强度较弱。

Figure 2. XRD θ-2θ spectrum of Ta/NiFe/Ta tri-layer film on flexible PLA substrate
图2. PLA基片上的 Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜的XRD结果

Figure 3. In-plane and out-of-plane hysteresis loops of Ta/NiFe/Ta tri-layer films on flexible PLA substrate
图3. PLA基片上的Ta/NiFe/Ta 三层薄膜的面内外磁滞回线
图3是PLA基片上NiFe薄膜的磁滞回线。对于沉积在PLA基片上的Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜,其面内磁滞回线具有NiFe软磁薄膜的典型特征。面内和面外磁滞回线之间有明显的差别,这表明NiFe薄膜的磁各向异性和易磁化轴位于薄膜面内 [8]。PLA上NiFe的矫顽场为4.94 Oe,高于Si/SiO2基片上NiFe的0.84 Oe。弯曲的NiFe膜中的应变 可以用以下公式近似计算 [9]:
(1)
其中R是曲率半径, 和 分别是基片和薄膜的厚度。如下图所示正和负 值表示拉伸和压缩平面应变。图4(a)是不同磁场方向测试的示意图。图4(b)、图4(c)和图4(d)是在不同弯曲半径和弯曲方向(拉伸和压缩) PLA基片上NiFe薄膜磁滞回线的比较。由螺旋测微仪测得PLA的基片厚度为15微米。利用上式,计算出弯曲半径R = 5 mm和R = 1.5 mm的弯曲应变分别为 = 0.5%和 = 1.66%。以上结果表明,附着在柔性基片上的NiFe膜可以承受 = 1.66%的弯曲应变。磁场分别沿交叉和面外方向施加到膜表面,图中显示,当沿面内方向施加磁场时,磁滞回线在拉伸和压缩弯曲下几乎没有变化。这表明弯曲曲率和弯曲方向并未导致NiFe膜面内磁化翻转过程的显着变化。当从交叉和面外方向施加磁场时,磁滞回线会略有变化。但是当R为5 mm时,磁滞回线变化很小。当R减小到1.5 mm时,磁滞回线变化显著。
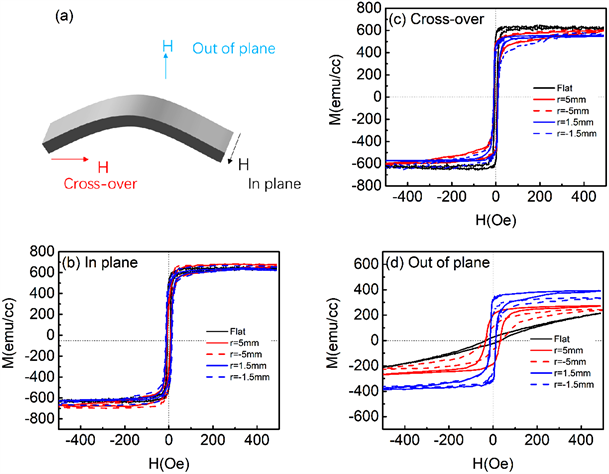
Figure 4. (a) Schematic diagram of different magnetic field directions; hysteresis loops in (b) In-plane; (c) Cross and (d) Out of plane directions of films on PLA substrate under different bending radius R (1.5 mm and 5 mm) and bending strain (tensile r > 0 and compressive r < 0)
图4. (a)不同磁场方向测试的示意图;不同弯曲半径r (1.5 mm和5 mm)和弯曲应变(拉伸r > 0和压缩r < 0)下PLA基片上薄膜(b)面内、(c)交叉和(d)面外方向磁滞回线
图5是不同弯曲半径相关的矫顽力 和饱和磁化强度 。图5(a)中显示当施加磁场沿面内(面内和交叉)方向时, 略微增大。施加面外方向磁场时, 却显著减小,这是因为薄膜弯曲后与磁场不完全垂直,此时的薄膜磁矩处于面内到面外的一个中间态。图5(b)中显示当沿面内方向和面外方向施加磁场时,饱和磁化强度 会发生显着变化。交叉方向 的减小对应着面外方向 的等量增加。而面内方向的磁矩并无明显变化,这是由于磁场沿此方向与膜面保持平行。
图5显示拉伸弯曲和压缩弯曲之间的 变化差异不大,在拉伸和压缩应变下,平面外矫顽力Hc的变化是几乎对称的。NiFe膜的总各向异性能在相同应变大小、不同弯曲方向下由于不同正负的应力各向异性有轻微的差别。为了更好地理解弯曲半径与磁性的物理机制,我们假设β是M与弯曲应变 的夹角,磁弹各向异性能量可以表示为:
(2)
其中 和 分别是NiFe薄膜的饱和磁致伸缩常数和杨氏模量。而在磁致伸缩合金薄膜的情况下,应变与几何形状变化是导致磁性能变化可能的机制。因此,不同应变方向下 变化差异不大表明NiFe薄膜的磁化反转过程不受弯曲应变的影响,而是受薄膜弯曲几何形状影响的结果。这可能是柔性NiFe的低饱和磁致伸缩常数造成的,也可能是薄膜中可能存在的弯曲裂纹释放了弯曲应变。但是,轻微不对称则可能是磁致伸缩效应造成的。

Figure 5. (a) Coercive field Hc and (b) saturation magnetization Ms of NiFe films on PLA substrates with different bending radius R (1.5 mm and 5 mm) and bending strains (tensile r > 0 and compressive r < 0)
图5. 不同弯曲半径r (1.5 mm和5 mm)和弯曲应变(拉伸r > 0和压缩r < 0)PLA基片上NiFe薄膜的(a)矫顽场Hc和(b)饱和磁化强度Ms变化
图6是在不同弯曲次数(0到2000次)下NiFe薄膜的面内磁滞回线。图6显示,随着弯曲次数的增加,PLA基片上的面内磁滞回线的变化并不明显。图6(b)中的折线图表明,经过多次弯曲后,矫顽场 轻微增加,而饱和磁化强度 略有减少,最后都趋于平稳。弯曲2000次后,面内磁滞回线基本没有变化,这表明NiFe薄膜有着优异的抗疲劳性能。而 的增加和 的降低可能是由于弯曲后引起的细小裂纹引起的。

Figure 6. The changes of (a) In-plane hysteresis loops and (b) Coercive field Hc and saturation magnetization Ms of NiFe films on PLA substrates with different bending times N (0, 500, 1000 and 2000)
图6. 不同弯曲次数N (N = 0、500、1000和2000次)下PLA基片上NiFe膜的(a)面内磁滞回线和(b)矫顽场Hc和饱和磁化强度Ms变化
4. 总结
综上所述,我们通过磁控溅射的方法,在PLA基片上制备了Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜。研究了各种压缩或拉伸应变以及不同弯曲次数对PLA上的Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜的面内面外等方向磁性产生的影响。结果表明,NiFe薄膜的磁性主要受弯曲几何形状的影响,样品可以承受 = 1.66%的弯曲应变,在不同应变(弯曲半径可达1.5 mm)和弯曲次数达到2000次后仍然能够保持优异的软磁性。证明PLA基片上的Ta/NiFe/Ta三层薄膜具有出色的稳定性和延展性,同时有应用到生物集成磁性传感器上的巨大潜力。
致谢
本论文感谢科技部国家重点研发计划项目(No. 2017YFB0406401)的支持。
文章引用
王 禹,余 涛,王传龙,徐思晨,朱齐山,葛水兵,彭 斌,张万里,汤如俊. 生长在PLA基片上的Ni81Fe19薄膜的磁性能研究
Magnetic Properties of Ni81Fe19 Thin Films on PLA Substrate[J]. 应用物理, 2021, 11(05): 289-295. https://doi.org/10.12677/APP.2021.115034
参考文献
- 1. Someya, T., Sekitani, T., Iba, S., Kato, Y., Kawaguchi, H. and Sakurai, T. (2004) A Large-Area, Flexible Pressure Sensor Matrix with Organic Field-Effect Transistors for Artificial Skin Applications. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 9966-9970. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0401918101
- 2. Bauer, S., Bauer-Gogonea, S., Graz, I.., Kaltenbrunner, M., Keplinger, C. and Schwdiauer, R. (2014) 25th Anniversary Article: A Soft Future: From Robots and Sensor Skin to Energy Harvesters. Advanced Materials, 26, 149-162. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201303349
- 3. Ren, X., Pei, K., Peng, B., Zhang, Z., Wang, Z., Wang, X. and Chan, P.K.L. (2016) A Low-Operating-Power and Flexible Active-Matrix Organic-Transistor Temperature-Sensor Array. Ad-vanced Materials, 28, 4832-4838. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201600040
- 4. Hines, L., Petersen, K., Guo, Z.L. and Sitti, M. (2017) Soft Actua-tors for Small-Scale Robotics. Advanced Materials, 29, Article ID: 1603483. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603483
- 5. Choi, M.K., Yang, J., Dong, C.K., Dai, Z., Kim, J., Seung, H., Kale, V.S., Sung, S.J., Chong, R.P. and Lu, N. (2018) Extremely Vivid, Highly Transparent, and Ultrathin Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes. Advanced Materials, 30, Article ID: 1703279. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201703279
- 6. Kim, J., Shim, H.J., Yang, J., Choi, M.K., Kim, D.C., Kim, J., Hyeon, T. and Kim, D.H. (2017) Ultrathin Quantum Dot Display Integrated with Wearable Electronics. Advanced Mate-rials, 29, Article ID: 1700217. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201700217
- 7. Aulin, C., Karabulut, E., Tran, A., Lars, W. and Tom, L. (2013) Transparent Nanocellulosic Multilayer Thin Films on Polylactic Acid with Tunable Gas Barrier Properties. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5, 7352-7359. https://doi.org/10.1021/am401700n
- 8. 王禹, 邹帅, 徐思晨, 等. 生长在类单晶硅片上的Ni81Fe19薄膜的微结构和磁性能研究[J]. 应用物理, 2019, 9(6): 300.
- 9. Zhang, Y., Shen, L., Li, M., Li, X., Lu, X., Lu, L., Chunrui, M., You, C., Che, A. and Huang, C. (2017) Flexible Quasi-Two-Dimensional CoFe2O4 Epitaxial Thin Films for Continuous Strain Tuning of Magnetic Properties. ACS Nano, 11, 8002-8009. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b02637
NOTES
*相同贡献。
#通讯作者。