Hans Journal of Chemical Engineering and Technology
Vol.
09
No.
05
(
2019
), Article ID:
32200
,
9
pages
10.12677/HJCET.2019.95057
Study on LA-ICP-MS Determination of Trace Elements in Sulfide Minerals
Hongyu Zhang1,2*, Li Su1,2, Jing Wang1,2, Liming Yang3, Dachuan Wang4, Xiaolan Hu1,2, Yingtan Song1,2, Lu Xiong1,2
1Institute of Earth Sciences, China University of Geosciences, Beijing
2State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing
3School of Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University, Beijing
4School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing

Received: Aug. 29th, 2019; accepted: Sep. 11th, 2019; published: Sep. 18th, 2019

ABSTRACT
A method for in situ trace element analysis of sulfide minerals was established by using LA-ICP-MS, which combines the New-Wave 193ss type laser (193 nm) and the Agilent
Keywords:LA-ICP-MS, Sulfide, In-Situ, Trace Elements, The Double Internal Standard Group
LA-ICP-MS原位测定硫化物矿物微量元素的方法研究
张红雨1,2*,苏犁1,2,王静1,2,杨立明3,王大川4,胡小兰1,2,宋颖谭1,2,熊璐1,2
1中国地质大学科学研究院,北京
2中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室,北京
3北京大学地球与空间科学学院,北京
4中国地质大学地球科学与资源学院,北京

收稿日期:2019年8月29日;录用日期:2019年9月11日;发布日期:2019年9月18日

摘 要
利用New-Wave 193ss型193 nm激光器与Agilent 7500a型四级杆等离子体质谱仪联用的LA-ICP-MS系统,建立了一套原位硫化物矿物微量元素的测试方法。本实验采用单点剥蚀连续自动采集模式,采用美国国家调查局的玻璃标准物质NIST610为主标,对硫化物校准物质MASS-1进行测试,Si为外标物质的内标元素,分别选取Fe、Cu、Zn为盲样内标元素的双内标组方法进行数据处理,处理软件采用Glitter4.4.4。结果表明:综合选取两组内标Si-Fe和Si-Zn或Si-Cu和Si-Zn进行数据处理,硫化物校准物质MASS-1中已有推荐值的所有元素测试值与推荐值相对误差都在±20%以内,所有元素测试值相对标准偏差都优于10%,大部分元素优于5%。
关键词 :LA-ICP-MS,硫化物矿物,微区原位,微量元素,双内标组

Copyright © 2019 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
硫化物矿物的微量元素含量及比值能有效指示成矿流体来源、演化(如岩浆、变质、天水等)和成矿作用过程 [1] [2] [3] ,在岩浆–热液矿床的成矿作用研究中受到高度关注。硫化物微量元素的微区精确测定可为深入认识矿床成因、提高成矿预测及找矿勘探提供重要科学依据 [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] 。利用LA-ICP-MS进行硫化物矿物微量元素丰度的原位微区检测,具有低检出限、高精度等优点 [9] [10] [11] ,而且可依据待检矿物的结构特征(如环带结构),选择不同大小激光束斑的精准取样,进而可以精确测定硫化物矿物不同生长环带等特定部位的微量元素丰度,反演不同阶段矿物结晶过程的成矿流体成分特征和演化规律,实现对成矿过程的精细刻画。
然而,制约LA-ICP-MS准确测定矿物微量元素含量的首要因素就是外标物质的选择和制备,目前测试硅酸盐、氧化物和碳酸盐矿物时使用人工合成的硅酸盐和氧化物玻璃,例如NIST600系列,而且实验证明人工合成的硅酸盐和氧化物玻璃是测试硅酸盐、氧化物和碳酸盐矿物很好的校正标样 [12] 。鉴于硫化物矿物原位分析标准物质较稀少,目前国内外常用的有美国地质调查局合成的标准物质MASS-1 [12] ,Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser等人合成的PGE sulfide standards [13] ,澳大利亚塔斯马尼亚大学合成的STDGL2b2 [14] 和华东理工大学合成的标准物质IMER-1 [15] 等少数几个校准物质,缺少完全基质匹配的标准物质。用基体不匹配的标准物质进行标定样品时会产生基体效应,进而影响LA-ICP-MS分析的准确度。经前人研究MASS-1和IMER-1与天然硫化物矿物也并非完全基体匹配 [16] 。综上,本文尝试使用国内外通用且含量稳定的美国国家调查局的NIST系列玻璃标准物质校准硫化物矿物,后期采用一种特殊的数据处理方法,进行硫化物矿物原位分析,以期有效降低基体效应对数据准确度的影响,提高测试精确度。
2. 实验部分
2.1. 仪器及主要工作参数
采用美国New-Wave 193ss型193 nm激光器与美国安捷伦公司
Table 1. Operating conditions of the LA-ICP-MS system
表1. LA-ICP-MS主要工作参数
2.2. 标准及样品
各类标准物质:美国标准技术研究院NIST合成玻璃标准物质NIST SRM 610 (主标),NIST SRM 612 (盲标);美国地质调查局硫化物校准物质MASS-1 (盲样)。
标准物质靶制备:将所用标准物质同等条件下粘在一个样品靶上,抛光处理,上机前用酒精擦拭干净。
2.3. 仪器优化
激光采用线扫模式,束斑直径120 um,纯He为载气,氩气为辅助气,NIST610作为校准物质,调试ICP-MS条件,其调谐工作参数应满足背景值、灵敏度、氧化物、双电荷、稳定性要求等各项指标。使轻中重质量数代表元素信号强度分别大于1.0 × 106 cps、6.0 × 105 cps、1.0 × 106 cps,氧化物产率(238U16O/238U)小于0.6%,双电荷:Ce2+/Ce+ < 2%,降低氧化物干扰,得到较高灵敏度,长期稳定性RSD < 5%。
2.4. 同位素干扰校正
正确的选择待测元素的同位素是实验进行的关键,本次实验采用仪器内设的标准干扰校正方程作为本实验的干扰校正方法。干扰校正方程如下:
2.5. 数据采集
样品采集采用激光单点剥蚀连续自动采集模式,各类标准物质按顺序依次测试18次。每个剥蚀点总分析时间为100 s,其中预剥蚀时间5 s,气体空白收集时间20 s,激光剥蚀45 s,两次预热时间各15 s。待测元素选择及对应积分时间见表2,测试中MASS-1的2号测试点各元素的质谱响应信号如图1。
Table 2. Integration time for element measuring
表2. 待测元素积分时间
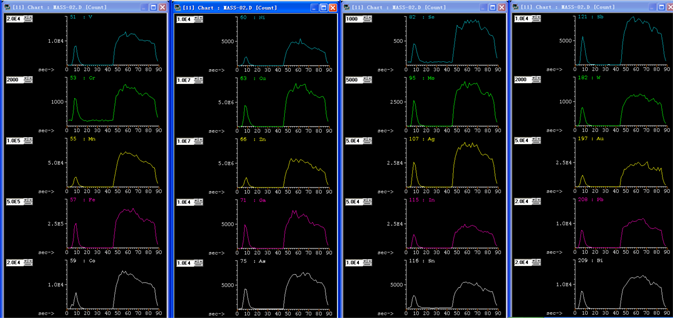
Figure 1. Counts per second of each element in MASS-02
图1. MASS-02各元素计数值
2.6. 数据处理
采用Glitter
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 测试结果与推荐值
标准物质MASS-1中Fe、Cu、Zn含量很高且稳定适于作内标元素,而且MASS-1中无Si推荐值,故最终采用Si为外标物质的内标元素,分别对应Fe、Cu、Zn为盲样内标元素的双内标方法进行数据处理。美国地质调查局硫化物校准物质MASS-1推荐值与三组不同内标组处理结果平均值见表3。
Table 3. Recommended value and the average of test results of MASS-1
表3. MASS-1推荐值与测试结果平均值
注:* is the recommended value for the input (*为输入的推荐值)。
3.2. 标准物质分析结果的相对标准偏差
按照上述实验条件及测试方法进行实验测试,采用三种不同内标元素组数据处理结果的相对标准偏差如图2所示:1) 分别采用Si-Fe和Si-Cu (图2(a)和图2(b))为内标时除Au外其他元素都优于10%,其中除Zn,Ga,As和Sb外其元素优于5%;2) 采用Si-Zn (图2(c))为内标时除Ga外其他元素都优于10%,其中As,Mo,Sn,Sb和Bi优于5%。

Figure 2. The relative standard deviation of treatment results of different internal standard groups
图2. 不同内标组处理结果相对标准偏差
3.3. 标准物质分析结果与推荐值相对误差
将三种不同内标元素数据处理结果与推荐值比较,其各自相对误差见图3,如图所示:1) 分别采用Si-Fe和Si-Cu (图3(a)和图3(b))为内标时,除Co、Zn、Ag、In和Au五个元素的部分测试点数据与推荐值相对误差超过±20%,其他14个元素测试值均在误差范围内;2) 采用Si-Zn (图3(c))为内标时,Mn、Co、As、Ag、In、Sb、Sn、Pb、Bi和Au十个元素与推荐值相对误差在误差范围内,其他9个元素的部分测试点数据与推荐值相对误差超过±20%。

Figure 3. The relative errors between the processing results and the recommended values of different internal standard groups
图3. 不同内标组处理结果与推荐值相对误差
3.4. 待测元素优选内标组分析
通过综合对比三次不同内标组数据处理结果,并非一组内标即可得到所有选测元素理想值,选定不同内标组能得到某些元素理想值。不同待测元素的优选内标如图4所示,Mn、As、Sb、Sn、Pb和Bi6个元素可选择三组内标中任一组得到理想值,Co、Ag、In、和Au4个元素只能选择Si-Zn为内标得到理想值,其它元素可以选择Si-Fe或Si-Cu为内标获得理想值。

Figure 4. Preferred interior plot of different elements
图4. 不同元素的优选内标图
4. 结论
通过本实验建立了一种使用激光等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS)原位测定硫化物矿物微量元素的测试方法。该方法使用国内外通用且含量稳定的美国国家调查局NIST系列玻璃标准物质校准硫化物矿物,采用标样和盲样不同内标元素对的数据处理方法,进而抵消部分基体效应对测试结果准确性的影响。实验分析结果表明LA-ICP-MS可进行原位、微区测试未知硫化物矿物。采用美国国家调查局的NIST系列玻璃标准物质为主标,以硫化物校准物质MASS-1为盲标进行硫化物矿物盲样测试,可测试前述所有待测元素,通过选取两组内标(Si-Fe或Si-Cu和Si-Zn)进行数据处理,最后综合分析两组处理结果,若MASS-1中元素测试值与推荐值相对误差未超过±20%,则硫化物盲样中元素含量可用。
基金项目
中国地质大学(北京)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室自主课题(MSFGPMR201806)项目资助。
文章引用
张红雨,苏犁,杨立明,王大川,胡小兰,宋颖谭,熊璐. LA-ICP-MS原位测定硫化物矿物微量元素的方法研究
Study on LA-ICP-MS Determination of Trace Elements in Sulfide Minerals[J]. 化学工程与技术, 2019, 09(05): 401-409. https://doi.org/10.12677/HJCET.2019.95057
参考文献
- 1. Cook, N.J., Ciobanu, C.L., Pring, A., Skinner, W., Shimizu, M., Danyushevsky, L., Saini-Eidukat, B. and Melcher, F. (2009) Trace and Minor Elements in Sphalerite: A LA-ICPMS Study. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73, 4761-4791.
- 2. Makoundi, C., Zaw, K., Large, R.R., et al. (2014) Geology, Geochemistry and Metallogenesis of the Selinsing Gold Deposit, Central Malaysia. Gondwana Research, 26, 241-261.
- 3. Gourcerol, B., Kontak, D.J., Thurston, P.C. and Petrus, J.A. (2018) Results of LA-ICP-MS Sulfide Mapping from Algoma-Type BIF Gold Systems with Implications for the Nature of Mineralizing Fluids, Metal Sources, and Deposit Models. Mineralium Deposita, 53, 871-894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-017-0788-7
- 4. Zhao, H.X., Frimmel, H.E., Jiang, S.Y. and Dai, B.Z. (2011) LA-ICP-MS Trace Element Analysis of Pyrite from the Xiaoqinling Gold District, China: Implications for Ore Genesis. Ore Geology Reviews, 43, 142-153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.07.006
- 5. Thomas, H.V., Large, R.R., Bull, S.W., Maslennikov, V., Berry, R.F., Fraser, R., Froud, S. and Moye, R. (2011) Pyrite and Pyrrhotite Textures and Composition in Sediments, Laminated Quartz Veins, and Reefs at Bendigo Gold Mine, Australia: Insights for Ore Genesis. Economic Geology, 106, 1-31. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.106.1.1
- 6. 周涛发, 张乐骏, 袁峰, 范裕, Cooke D.R. 安徽铜陵新桥Cu-Au-S矿床黄铁矿微量元素LA-ICP-MS原位测定及其对矿床成因的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2): 306-319.
- 7. Winderbaum, L., Ciobanu, C.L., Cook, N.J., Paul, M., Metcalfe, A. and Gilbert, S. (2012) Multivariate Analysis of an LA-ICP-MS Trace Element Dataset for Pyrite. Mathematical Geosciences, 44, 823-842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-012-9418-1
- 8. Peterson, E.C. and Mavrogenes, J.A. (2014) Linking High-Grade Gold Mineralization to Earthquake-Induced Fault-Valve Processes in the Porgera Gold Deposit, Papua New Guinea. Geology, 42, 383-386. https://doi.org/10.1130/G35286.1
- 9. Norman, M.D., Pearson, N.J., Sharma, A. and Griffin, W.L. (1996) Quantitative Analysis of Trace Elements in Geological Materials by Laser Ablation Icpms: Instrumental Operating Conditions and Calibration Values of Nist Glasses. Geostandards Newsletter, 20, 247-261. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-908X.1996.tb00186.x
- 10. Flem, B., Larsen, R.B., Grimstvedt, A. and Mansfeld, J. (2002) In Situ Analysis of Trace Elements in Quartz by Using Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Chemical Geology, 182, 237-247. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00292-3
- 11. Günther, D. and Hattendorf, B. (2005) Solid Sample Analysis Using Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 24, 255-265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2004.11.017
- 12. Wilson, S.A., Ridley, W.I. and Koenig, A.E. (2002) Development of Sulfide Calibration Standards for the Laser Ablation Inductively-Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Technique. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17, 406-409. https://doi.org/10.1039/B108787H
- 13. Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.C., Ballhaus, C., Bernd, J., Paliulionyte, V.S. and Meisel, T. (2007) Synthesis of PGE Sulfide Standards for Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 154, 607-617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0212-x
- 14. Danyushevsky, L., Robinson, P., Gilbert, S., Norman, M., Large, R., McGoldrick, P. and Shelley, M. (2011) Routine Quantitative Multi-Element Analysis of Sulphide Minerals by Laser Ablation ICP-MS: Standard Development and Consideration of Matrix Effects. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 11, 51-60. https://doi.org/10.1144/1467-7873/09-244
- 15. Ding, L.H., Yang, G., Xia, F., Lenehan, C.E., Qian, G.J., McFadden, A., Brugge, J., Zhang, X.H., Chen, G.R. and Pring, A. (2011) A LA-ICP-MS Sulphide Calibration Standard Based on a Chalcogenide Glass. Mineralogical Magazine, 75, 279-287. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.2011.075.2.279
- 16. 袁继海, 詹秀春, 胡明月, 赵令浩, 孙冬阳. 基于元素对研究激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱分析硫化物矿物的基体效应[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(2): 512-518.
NOTES
*通讯作者。
