Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.07 No.05(2018), Article ID:25046,9
pages
10.12677/AAM.2018.75067
The Properties for a Kind of Time-Periodic Solutions of the Einstein’s Field Equations
Shixia Lv, Zenggui Wang
School of Mathematical Sciences, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng Shandong

Received: Apr. 30th, 2018; accepted: May 17th, 2018; published: May 24th, 2018

ABSTRACT
In general relativity theory, the solution can provide rational explanation for the final state of gravitational collapse if it with physical singularity. In this paper, we study a kind of vacuum Einstein field equations time-periodic solution and its physical properties. We computed the Riemann curvature tensor and its length. We proved it’s a time-periodic solution with physical singularity which describes a time-period universe. Through analyzing the Penrose figure of this kind of solutions, we can be found this kind of solutions have similar Physical characters. Because of the time-periodic solutions with physical singularity can provide rational explanation for the final state of gravitational collapse, this space-time can apply to modern cosmology and general relativity.
Keywords:Einstein’s Field Equations, Time-Periodic Solutions, Geometric Singularity, Physical Characters
一类真空Einstein场方程时间周期解的性质
吕士霞,王增桂
聊城大学数学科学学院,山东 聊城

收稿日期:2018年4月30日;录用日期:2018年5月17日;发布日期:2018年5月24日

摘 要
在广义相对论中,若存在有物理奇性的时间周期解,从而这个解为引力坍塌的最终状态给出了合理的解释。本文章研究了一类具有物理奇性的真空Einstein场方程的严格解,利用Maple得出该类解的Riemann曲率张量以及其模长,说明了它是一个带有物理奇性的时间周期解,这类特殊时间周期解刻画了一个带有时间周期物理奇性的时间周期宇宙。进而分析这类特殊解的Penrose图可以发现这类解都具有类似的物理性质。因为带有物理奇点的时间周期解可为引力坍缩最终状态给出合理的解释,所以这个时空可应用到现代宇宙学和广义相对论当中。
关键词 :Einstein场方程,时间周期解,几何奇性,物理性质

Copyright © 2018 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
爱因斯坦场方程的精确解在广义相对论和宇宙学中具有举足轻重的作用。在数学上对Einstein场方程的探索大致上可分为两个方面:一方面是探索解的适定性理论,另一方面是构造有物理背景的严格解。至今,对Einstein场方程适定性理论的研究结果稀少。关于寻找严格解,目前已经取得了许多有意义的结果。最经典的例子是Schwarzschild解、Reissner Nordstrom解和Kerr解 [1] [2] [3] [4] 。虽然在Einstein场方程精确解方面已得到许多重大的研究结果,但是依旧有一些重要而基本的问题没有解决。例如“真空Einstein场方程是否存在包含物理奇性(黑洞)的一个时间周期解”。
最近,Dafermos [5] 证明了视界外具有时间周期性的球对称黑洞时空不存在性,这个结果将“无毛”定理从静态推广到时间周期情况。受Gauss坐标系,Schwarzschild坐标和Kerr坐标的启发,孔德兴、刘克峰 [6] 构建了一个刻画了一个正则时空的Einstein场方程的时间周期解,并且它的Riemann曲率张量为零,却不是渐近平坦的。此后,孔德兴、刘克峰与沈明 [7] 根据之前的研究成果 [6] 中Type I的度规形式构建了三种不同类型的新的Einstein场方程的时间周期解。第一类是Riemann曲率张量为零,第二类是Riemann曲率张量为有限数,第三类是具有几何奇性的时间周期解。此外孔德兴、刘克峰与沈明 [8] 还构建了具有物理奇性的真空Einstein场方程的时间周期解以及其方程Jacobi椭圆函数形式的严格解,计算了解的Weyl张量并且分析了解的奇性,由此并发现了新的物理现象。
本文我们构造了一类普通的时间周期解,这类时间周期解可以用来描述具有时间周期物理奇性的一个时间周期宇宙。通过这类解中一个特殊解的Penrose图,研究了这类解的物理性质。
本文组织如下:第二部分构造出时间周期解,第三部分介绍几何奇性和物理奇性的概念并分析了解的奇性,第四部分研究一类特殊时间周期解的物理性质。
2. 时间周期解
本文关注于真空Einstein场方程
(1)
的时间周期解,相当于
(2)
其中 是度规张量, 是Ricci张量,R是标量曲率, 是Einstein张量。
取 作为求坐标系, 考虑如下度量形式:
其中 是t的光滑函数。由参考文献 [8] 得到定理1:
定理1. 在坐标系 下,真空Einstein场方程(2)有下面的解:
(3)
其中,
(4)
而 和 是依赖于t的函数, 。
定理2. 在坐标系 下,真空Einstein场方程(2)有下面的时间周期解:
(5)
其中 是关于t的周期函数,T为一个周期,且存在 使得 。
(6)
其中, 。
证明:由定理1可得(5)是方程(2)的解,由此只需证明(5)是时间周期的。即证明变量t是时间坐标。
计算可得 的行列式为
(7)
并且,满足
和
因此可得t为时间坐标。即(5)是真空Einstein场方程(2)的时间周期解。 □
3. 奇性分析
本节利用Maple求出(5)这个时间周期解的Riemann曲率张量及其模长,并对时空(5)的奇性进行了分析。通过Maple计算可得(5)的Riemann曲率张量为
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
而其他的 。此外求得
(15)
因此,当 ,并且 时,成立
(16)
当取不同的 函数值,Riemann曲率张量不一样,但是其模长相同。
为了分析时空的奇性,引入下面的定义:
定义1. 如果存在指标 使得在P点 但 点P即被称为时空的几何奇点;若在P点 点P就被称为时空的物理奇点。若每一点 ( 是一个低维流形)是一个几何(物理)奇点,则 被称为几何(物理)奇性。
定义1中的“几何奇性”经常被物理学者称为坐标奇性,而“物理奇性”称为本质奇性。
性质1. 是时空(5)的物理奇点,在本文中把它定义为“时间周期物理奇性”。所以(5)表述了一个具有时间周期物理奇性的时间周期时空。
特别地,当 及 时, 在不同的方向极限R的取值是不相同的,这说明在这些点“黑洞”存在不确定性。
依据视界面 [9] 的定义,超曲面 是时空(5)的视界面。所以有
性质2. 超曲面 是时空(5)的视界面,依据定义1可知它们是几何奇性的。
4. 一类特殊时间周期解的物理性质
本节我们主要研究一类特殊的时间周期解的物理性质。 时,在球极坐标 中,度规形式为
(17)
表明这个度规表述了一个时间周期时空,我们把它命名为LW时间周期宇宙。根据文献 [9] Riemann曲率范数为
(18)
除了 这个物理奇性之外它是非奇异的。在当 (即 )时, 取值为零。并且这个解具有一些非本性奇点,而这些奇点是由超曲面 构成的。
将 与 取定值,可得度规
考虑 -平面的类光曲线:
则由上式得
把常微分方程
(10)
的解记为 。由此可知
(20)
令 ,可得
(21)
给出了在点 (实际上,所有的点 )附近类光曲线的奇性行为。 的幂次与Friedman方程得到的FRW宇宙的加速度之一是一致的。
对t-截面的几何行为分析如下:
当 取为定值,t-截面的诱导度规由(5)可得:
(22)
如上所述超曲面 是时空(5)的奇性,且当 时,t-截面是一个以 为中心的三维锥状的流形。
不妨我们只研究一个周期范围内的宇宙模型 。
定义
(23)
即
则
(24)
也就是 。在 坐标下,度规相应的变为
(25)
继续定义
则
(26)
定义为超前零坐标,且
(27)
定义为延迟零坐标。在 坐标下,类似于Eddington-Finkelstein形式 [3] 度规可定义为:
(28)
这种表示的时间周期解依然具有奇异特征,即它是非时间对称的。这点从Finkelstein图 [10] 中可得。由Finkelstein图可得 是类光本性奇点。Finkelstein图是当 为常数的时空的截面,任一点表明拓
扑结构为 的二维曲面。
若我们用坐标w代替v,则度规形式为
(29)
根据(26)和(27)定义的超前和延迟零坐标 ,可得另一个坐标系,度规相应的形式为
(30)
其中 分别由下式给出
(31)
由于度规为 时的空间是平直的,所以它表示零共形平直坐标下的二维空间( 为常数)。维持这个二维空间共形平直的两个类光坐标最一般的坐标变换是 ( 与 是任意的 维函数),相应的度规为
(32)
定义
(33)
则度规的形式为
(34)
度规的具体形式由函数 的选取决定。选取 ,因此r由方程
(35)
确定。且t由方程
(36)
确定。进而 与 分别由下式给出
(37)
对坐标 在 条件下定义的流形 ,函数r和 是正的并且解析。由(34)定义度规 ,则 定义的 的区域I等距于 。通过图1我们可知存在另一个由 定义的区域I',也等距于 。我们把它命名为LW“喉”另一端的另一个渐进平直宇宙。
为研究时间周期时空无穷远处的布局,可联系(17)定义新的超前和延迟零坐标来构建Penrose图
(38)
其中 ,且
在Penrose图中,用共形坐标(34) (类光曲面总是斜率为 的直线)来表示时空布局,并且整个时空映射为一个有限图。所以用一种简单的方式来表示类光曲面,在图中可直观的给出其因果关系。远处观测者在 (或t)时刻看到的一个拓扑结构为
的二维曲面由Penrose图的每一点 来表示。图2中的Penrose图整体的阐述了带有“黑洞”时间周期解的整体布局。

Figure 1. Kruskal diagram, you can see the time period space region I and I prime, and area of
图1. Kruskal图,可看出时间周期宇宙空间区域I和I',以及 的区域
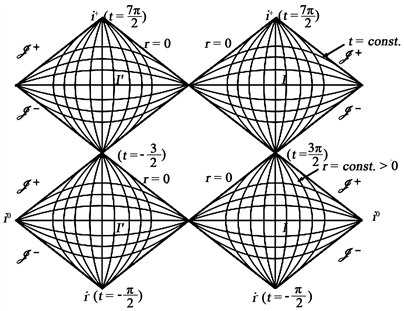
Figure 2. The Penrose diagram of the LW time period universe
图2. LW时间周期宇宙的Penrose图
注记1. 对任意固定的 度规(22)描述只含两个参量r和 的流形。这和Schwarzschild度规在Eddington-Finkelstein坐标下的形式是类似的,即,
其中v为外时空的时间坐标(即 )。在这种情况下对任意固定的 ,v-截面的诱导度规为
上面的度规同样仅依赖 和 两个参量。
注记2. 在 时, 或 时的解也具有类似的物理性质。
5. 结论
本文章研究了具有物理奇性的真空Einstein场方程的严格解,利用Maple得出解的Riemann曲率张量以及其模长,说明它是一个具有物理奇性的时间周期解。因为具有物理奇点的时间周期解可为引力坍缩最终状态给出合理的解释,所以这个时空可应用到现代宇宙学和广义相对论中。本文构造的一类特殊解相比之前的研究有所推广但是还不够广泛,期待有更进一步的开展,解释更多的物理现象。
致谢
作者感谢审稿人提出的宝贵意见。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(批准号:11001115, 1120473)和山东省自然科学基金(批准号:ZR2015AL008)资助的课题。
文章引用
吕士霞,王增桂. 一类真空Einstein场方程时间周期解的性质
The Properties for a Kind of Time-Periodic Solutions of the Einstein’s Field Equations[J]. 应用数学进展, 2018, 07(05): 565-573. https://doi.org/10.12677/AAM.2018.75067
参考文献
- 1. Bicak, J. (2000) Selected Solutions of Einstein’s Field Equations: Their Role in General Relativity and Astrophysics. Einstein’s Field Equations and Their Physical Implications, Lecture Notes in Phys. Springer, Berlin, 1-126.
- 2. Schwarzschild, K. (1916) Über das Gravitationsfeld eines Massenpunktes nach der Einsteins chen theorie. Sitz. Preuss. Akad. Wiss, 189, 688-696.
- 3. Hawking, S. and Ellis, G. (1973) The Large Scale Structure of Space-Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- 4. Stephani, H., Kramer, D., MacCallum, M., et al. (2003) Exact Solutions of Einstein’s Field Equations. 2nd Edition. Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- 5. Dafermos, M. (2003) Stability and Instability of the Cauchy Horizon for the Spherically Symmetric Einstein-Max- well-Scalar Field Equations. Annals of Mathematics, 158, 875-928.
https://doi.org/10.4007/annals.2003.158.875 - 6. Kong, D.X. and Liu, K.F. (2010) Time-Periodic Solutions of the Einstein’s Field Equations I: General Framework. Science in China Series A, 5, 66-83.
- 7. Kong, D.X, Liu, K.F. and Shen, M. (2010) Time-Periodic Solutions of the Einstein’s Field Equations II: Geometric Singularities. Science China Mathematics, 53, 1507-1520.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-009-3164-y - 8. Kong, D.X., Liu, K.F. and Shen, M. (2011) Time-Periodic Solutions of the Einstein’s Field Equations III: Physical Singularities. Science China Mathematics, 54, 23-33.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-010-4003-x - 9. Wald, R.M. (1984) Gencral Rtlativity. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago and London.
https://doi.org/10.7208/chicago/9780226870373.001.0001 - 10. Wang, Z.G. (2009) Physical Characters of KLS Time-Periodic Universe. Science in China Series A, 39, 1039-1044