Material Sciences
Vol.06 No.05(2016), Article ID:18519,8
pages
10.12677/MS.2016.65036
Effects of Solution Treatments on Microstructure and Texture of Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr Alloy Extruded Plate
Changping Tang1,2, Shengliang Cheng1,2, Guodong Li3
1School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan Hunan
2High Temperature Wear Resistant Materials and Preparation Technology of Hunan Province National Defence Science and Technology Laboratory, Xiangtan Hunan
3Equipment Management Department, Suzhou Nuclear Power Research Institute Company Limited, Shenzhen Guangdong

Received: Aug. 20th, 2016; accepted: Sep. 9th, 2016; published: Sep. 12th, 2016
Copyright © 2016 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



ABSTRACT
Effects of solution treatments on microstructure and texture of an extruded Mg-8Gd-4Y-Nd-Zr alloy plate were investigated using optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and texture testing. The results indicated that the grain growth occurred as the solution temperature increased and the solution time prolonged. The dynamic precipitates formed during extrusion dissolved into the matrix simultaneously as the solution processed. The grain growth rate was very low when the solution temperature was lower than 500˚C, while the grain growth rate increased rapidly when the sample solution treated at the temperature higher than 500˚C. The increase in grain growth rate was ascribed to the dissolution of dynamic precipitates, whose inhibiting effect on grain boundary migration decreased. The basal texture weakened while the prismatic texture strengthened as the solution processed. The strengthening in prismatic texture was attributed to the preferential growth of the prismatic texture component.
Keywords:Mg-Gd-Y Alloy, Solution Treatment, Dynamic Precipitate, Grain Growth, Texture

固溶处理对Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr合金挤压板材组织与织构的影响
唐昌平1,2,成声亮1,2,李国栋3
1湖南科技大学机电工程学院,湖南 湘潭
2高温耐磨材料及制备技术湖南省国防科技重点实验室,湖南 湘潭
3苏州热工研究院有限公司设备管理部,广东 深圳

收稿日期:2016年8月20日;录用日期:2016年9月9日;发布日期:2016年9月12日

摘 要
本文采用金相显微观察、扫描电镜观察、能谱仪及织构测试等手段,研究了固溶处理对Mg-8Gd-4Y-Nd-Zr合金挤压板材组织与织构的影响,结果表明:随着固溶温度升高和固溶时间延长,合金的晶粒发生长大,同时挤压过程中形成的动态析出相逐渐溶入基体中;合金在
关键词 :Mg-Gd-Y合金,固溶处理,动态析出相,晶粒长大,织构

1. 引言
Mg-Gd-Y系列合金由于具有优异的室温及高温性能而在航空航天工业中具有广阔的应用前景 [1] - [3] 。该合金是典型的时效强化型合金,时效强化是其主要的强化机制,前期研究表明 [4] - [8] ,该系合金的时效析出序列通常为:s.s.s.s→β→β'→β1→β。β相在时效初期形成,其晶体结构为DO19,晶格常数为: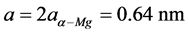 ,
,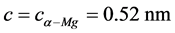 ,由于其与基体完全共格,强化效果较弱。随着时效时间的延长,将形成β'相,该相为底心正交结构(bco),其晶格常数为:
,由于其与基体完全共格,强化效果较弱。随着时效时间的延长,将形成β'相,该相为底心正交结构(bco),其晶格常数为: ,
,
 ,
,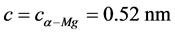 ,与基体呈半共格关系,能够有效阻碍位错的滑移,是该
,与基体呈半共格关系,能够有效阻碍位错的滑移,是该
合金的主要强化相,常常存在于峰时效状态的样品中,随着时效时间的进一步延长,β'相将逐步演变为β1相,β1相与基体不共格,对位错的阻碍作用降低,同时开始出现合金硬度和强度的下降。最后,该相演变为平衡相β,标志着合金完全进入过时效状态,强度和硬度进一步下降。近年来的研究也表明 [9] ,在一些合金中,并未观察到过渡相β1的存在,而是直接由亚稳相β'演变为平衡相β。由合金析出相演变规律及合金的强化机制可以看出,为获得高强度的Mg-Gd-Y合金材料,形成高体积分数的β'相是可能的途径。但是,研究表明 [10] [11] ,Mg-Gd-Y合金在塑性变形过程中,通常容易发生动态析出,直接形成平衡相β,降低基体中溶质原子的浓度,从而降低时效时形成的β'相的体积分数以及合金的时效强化效果。因此,在时效之前,可参考铝合金的处理方式,进行固溶处理 [12] [13] ,将析出的平衡相β重新溶入基体,但需要注意的是,镁合金晶界迁移容易,在高温固溶时容易发生晶粒长大,从而降低晶界强化效果及晶粒之间变形的协调性。针对这一难题,本文研究了固溶温度及时间对Mg-Gd-Y合金挤压板材组织与织构演变的影响规律,研究结果可为高性能镁合金制备提供参考。
2. 实验
本文所用实验材料为Mg-8Gd-4Y-Nd-Zr合金挤压板。锭坯采用差压铸造的方式进行制备,尺寸为Φ 250 × 500 mm,挤压前,铸锭预热温度为
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 挤压态显微组织
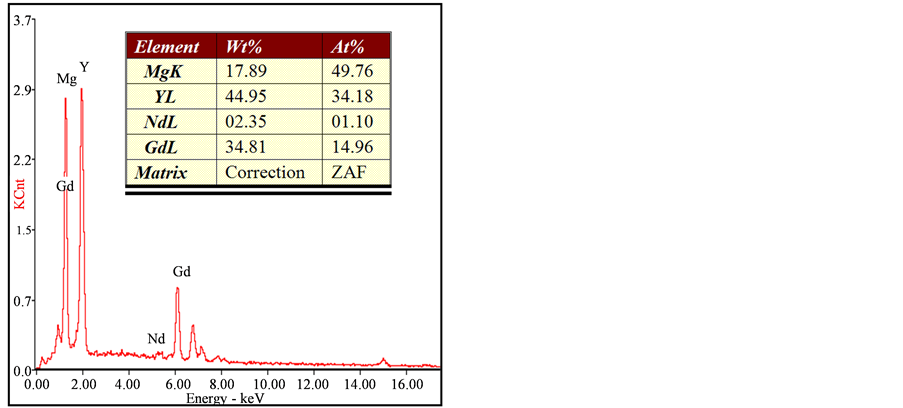
图1所示为挤压板材的金相显微组织。从图中可以看出,挤压板的晶粒组织非常细小,其平均晶粒尺寸为3.2 μm。除此之外,在合金中还可观察到大量弥散分布的细小黑色的第二相粒子,该类黑色第二相粒子在扫描电镜下为白色,如图2所示。由图可知,合金中主要有三种类型的第二相粒子:细小且形状不规则的第二相粒子(粒子A)、方块状第二相粒子(粒子B)和团聚成块状的第二相粒子(粒子C)。其中,体积分数最高的是尺寸较细小、形状不规则的第二相粒子,能谱分析表明,该粒子中Gd元素含量为13.42 wt.%,Y元素含量为6.41 wt.%,Nd元素含量为4.21 wt.%。对第二类方块状粒子的分析表明,Gd元素含量为42.83 wt.%,Y元素含量为45.32 wt.%,Nd元素含量为3.29 wt.%。此外,对团聚块状粒子的能谱分析表明,Gd元素含量为34.81 wt.%,Y元素含量为44.95 wt.%,Nd元素含量为2.35 wt.%。由上述分析结果可知,三类第二相粒子中均富含稀土元素。对比几种类型粒子的能谱分析结果,可知方块状粒子和团聚的块状粒子中Gd、Y元素的含量更高,远远超过Nd元素的含量,也超过细小不规则第二相粒子中Gd元素及Y元素的含量。结合其它研究成果可知 [11] [14] ,细小且形状不规则的第二相粒子为挤压过程中动态析出的平衡相β,方块状粒子则为铸锭均匀化处理后残留的富稀土粒子,团聚的块状粒子与此相似,可能是均匀化处理后团聚的富稀土粒子在挤压过程中被破碎,从而团聚在挤压板材中。
3.2. 固溶过程中的组织演变
上述分析表明,合金在挤压过程中形成了大量的析出相,消耗了基体中的溶质原子,降低了基体中的过饱和固溶度,将降低合金在时效过程中产生的时效析出相的体积分数,降低合金的时效强化效果。另外,合金挤压过程中形成的平衡相,由于尺寸为微米级,强化效果有限,且该相还可能引起应力集中,成为裂纹源。因此,须通过固溶处理,将动态析出的第二相溶入基体,再在时效过程中析出,增加时效强化效果,使合金具有更高的强度。

Figure 1. Optical microstructure of the extruded plate
图1. 挤压板材金相显微组织

 (a)(b)
(a)(b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 2. SEM image and EDS results of the extruded plate: (a) SEM image, (b) EDS results of particle A, (c) EDS results of particle B, (d) EDS results of particle C
图2. 挤压板材的扫描电镜组织及能谱分析结果:(a) SEM照片,(b) A点能谱,(c) B点能谱,(d) C点能谱
本文研究了合金在
挤压过程中析出的第二相粒子,在固溶处理过程中对晶界迁移有显著的阻碍作用,当在


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)


 (d) (e) (f)
(d) (e) (f)

 (g) (h) (i)
(g) (h) (i)
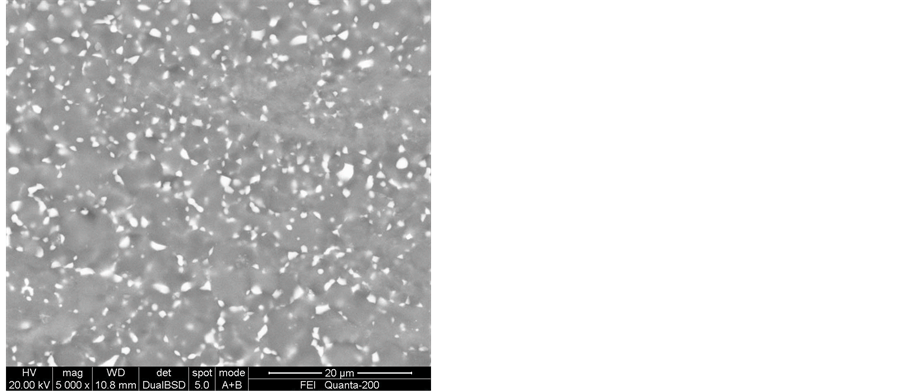
Figure 3. OM of the extruded plate after solution treatment: (a) 450˚C/1h; (b) 450˚C/3h; (c) 450˚C/4h; (d) 475˚C/0.5h; (e) 475˚C/0.75h; (f) 475˚C/1h; (g) 500˚C /0.5h; (h) 500˚C/1h; (i) 520˚C/0.5h
图3. 挤压板材固溶处理后的金相显微组织:(a) 450˚C/1h;(b) 450˚C/3h;(c) 450˚C/4h;(d) 475˚C/0.5h;(e) 475˚C/0.75h;(f) 475˚C/1h;(g) 500˚C /0.5h;(h) 500˚C/1h;(i) 520˚C/0.5h

 (a)(b)
(a)(b)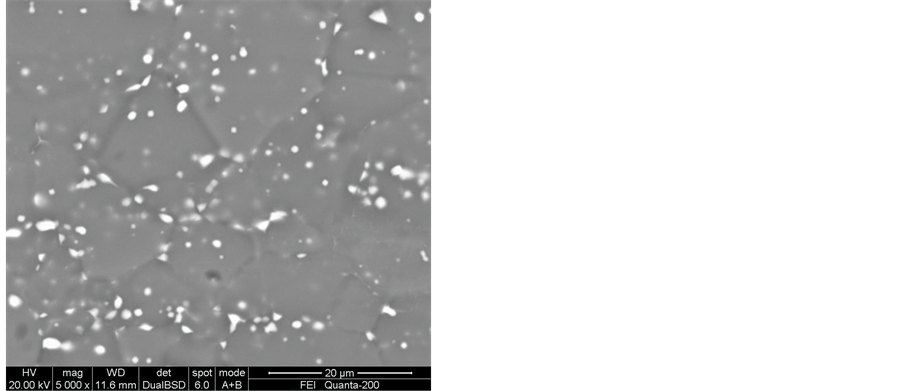
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 4. SEM images of the extruded plate after solution treatment: (a) 450˚C/0.5h; (b) 475˚C/0.5h; (c) 500˚C/ 0.5h; (d) 520˚C/0.5h
图4. 挤压板材固溶处理后的扫描电镜照片:(a) 450˚C/0.5h;(b) 475˚C/0.5h;(c) 500˚C/0.5h;(d) 520˚C/0.5h
3.3. 固溶过程中的织构演变
为进一步分析合金固溶处理过程中的组织结构演变,本文对挤压态样品及固溶处理后的样品进行了织构分析,其结果如图5所示。由图可知,合金挤压态的织构主要由两种织构组分构成,即基面平行于挤压板面的基面织构和基面垂直于板材横向的棱柱面织构组态。经过
4. 结论
通过研究挤压板材在固溶处理过程中合金微观组织与织构的演变规律,得到了如下结论:

Figure 5.  and
and  pole figures of the alloy with different states: (a) (d) as-extruded; (b) (e) 475˚C/0.5h; (c) (f) 520˚C /0.5h
pole figures of the alloy with different states: (a) (d) as-extruded; (b) (e) 475˚C/0.5h; (c) (f) 520˚C /0.5h
图5. 不同热处理状态合金的 和
和 极图:(a) (d) 挤压态;(b) (e) 475˚C/0.5h;(c) (f) 520˚C/0.5h
极图:(a) (d) 挤压态;(b) (e) 475˚C/0.5h;(c) (f) 520˚C/0.5h
1) 挤压板材固溶处理过程中,晶粒长大和动态析出相的溶解同时进行,固溶温度低于
2) 挤压板材中基面织构是主要的织构组态,经固溶处理后,基面织构强度降低,棱柱面织构增加,主要归因于该类晶粒的择优生长。
基金项目
湖南省自然科学基金(2016JJ5042)。
文章引用
唐昌平,成声亮,李国栋. 固溶处理对Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr合金挤压板材组织与织构的影响
Effects of Solution Treatments on Microstructure and Texture of Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr Alloy Extruded Plate[J]. 材料科学, 2016, 06(05): 277-284. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/MS.2016.65036
参考文献 (References)
- 1. 吴文祥, 靳丽, 董杰, 章桢彦, 丁文江. Mg-Gd-Y-Zr 高强耐热镁合金的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(11): 4-13.
- 2. 吴玉娟, 丁文江, 彭立明, 曾小勤, 林栋樑. 高性能稀土镁合金的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2011, 30(2): 1-9.
- 3. 周伟, 李全安, 亢海娟, 王耀贵. Mg-Gd-Y-Zr系耐热镁合金的研究进展[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2012, 40(5): 51-56.
- 4. He, S.M., Zeng, X.Q., Peng, L.M., Gao, X., Nie, J.F. and Ding, W.J. (2006) Precipitation in a Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.4Zr (wt.%) Alloy during Isothermal Ageing at 250˚C. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 421, 309-313.
- 5. Gao, X., He, S.M., Zeng, X.Q., Peng, L.M., Ding, W.J. and Nie, J.F. (2006) Microstructure Evolution in a Mg- 15Gd-0.5Zr (wt.%) Alloy during Isothermal Aging at 250˚C. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 431, 322-327.
- 6. Zhang, X.M., Tang, C.P., Deng, Y.L., Yang, L. and Liu, W.J. (2011) Phase Transformation in Mg-8Gd-4Y-Nd-Zr Alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 509, 6170-6174.
- 7. Zheng, J.X., Xu, X.S., Zhang, K.Y. and Chen, B. (2015) Novel Structures Observed in Mg-Gd-Y-Zr during Isothermal Ageing by Atomic-Scale HAADF-STEM. Materials Letters, 152, 287-289.
- 8. Zheng, J.X., Li, Z., Tan, L.D., Xu, X.S., Luo, R.C. and Chen, B. (2016) Precipitation in Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloy: Atomic- Scale Insights into Structures and Transformations. Materials Characterization, 117, 76-83.
- 9. Xu, C., Zheng, M.Y., Wu, K., Wang, E.D., Fan, G.H., Xu, S.W., Kamado, S., Liu, X.D., Wang, G.J. and Lv, X.Y. (2013) Effect of Ageing Treatment on the Precipitation Behaviour of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr Alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 550, 50-56.
- 10. Tang, C.P., Yang, L., Feng, D., Deng, Y.L. and Zhang, X.M. (2012) Investigation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloy Plate. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 27, 609-613.
- 11. Xiao, H.C., Tang, B., Liu, C.M., Gao, Y.H., Yu, S.L. and Jiang, S.N. (2015) Dynamic Precipitation in a Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloy during Hot Compression. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 645, 241-247.
- 12. Yang, X.B., Chen, J.H., Liu, J.Z., Liu, P., Qin, F., Cheng, Y.L. and Wu, C.L. (2013) Spherical Constituent Particles Formed by a Multistage Solution Treatment in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys. Materials Characterization, 83, 79-88.
- 13. Peng, G.S., Chen, K.H., Chen, S.Y. and Fang, H.C. (2014) Evolution of the Second Phase Particles during the Heating-Up Process of Solution Treatment of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 641, 237-241.
- 14. Gao, Y., Wang, Q.D., Gu, J.H., Zhao, Y. and Tong, Y. (2007) Behavior of Mg-15Gd-5Y-0.5Zr Alloy during Solution Heat Treatment from 500 to 540˚C. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 459, 117-123.