Dynamical Systems and Control
Vol.3 No.03(2014), Article ID:13842,8 pages
DOI:10.12677/DSC.2014.33005
Homotopy Analysis Method for Heterclinic Orbit of Michelson System
College of Mathematics, Physics and Information Engineering, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua
Email: *qyh2004@zjnu.cn
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received: May 25th, 2014; revised: Jun. 4th, 2014; accepted: Jun. 12th, 2014
In this paper, we use the homotopy analysis method (HAM) to obtain the analytic approximation of heterclinic orbit in Michelson system. Comparisons are made between the results of the proposed method and exact solutions. The results show that the HAM is an effective and practical technique of analytic approximation for the heterclinic orbit. The proof of convergence theorems for the present method is elucidated as well.
Keywords:Homotopy Analysis Method, Heterclinic Orbit, Convergence Theorems

刘万凯,钱有华*
浙江师范大学数理信息学院,金华
Email: *qyh2004@zjnu.cn
收稿日期:2014年5月25日;修回日期:2014年6月4日;录用日期:2014年6月12日

本文用同伦分析方法给出了Michelson系统异宿轨道的解析近似,并对该方法所得到的近似解析解与精确解之间进行了比较。结果表明,对于异宿轨道的近似解析解,同伦分析方法是有效且实用的。此外,还给出了本方法中收敛定理的证明。
同伦分析方法,异宿轨道,收敛定理

同伦分析方法是研究非线性问题的重要工具[1] 。在求解非线性问题的过程中,若对系统的初值猜测,辅助参数以及辅助函数的选择合理,就可以得到系统的解析近似解。本文考虑如下的系统:
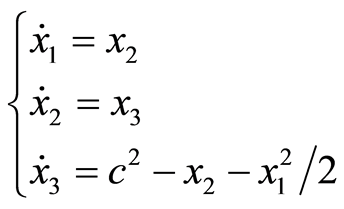 (1.1)
(1.1)
这里的点表示对 求导数。该系统是在研究Kuramoto-Sivashinsky方程的行波解中所产生的
求导数。该系统是在研究Kuramoto-Sivashinsky方程的行波解中所产生的
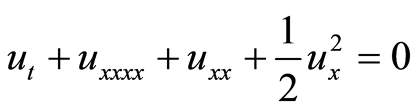 (1.2)
(1.2)
其中参数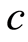 与波速度有关。Michelson研究了系统(1.1)[2] ,所以现在把它称为Michelson系统。当
与波速度有关。Michelson研究了系统(1.1)[2] ,所以现在把它称为Michelson系统。当 减小时系统(1.1)会出现“Cocoon”分叉[2] -[4] 。Kevin和John对参数
减小时系统(1.1)会出现“Cocoon”分叉[2] -[4] 。Kevin和John对参数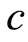 趋近零的Michelson系统进行了渐进分析,并与数值结果进行了比较[5] 。Lamb等证明了迈克尔逊系统有可数无穷多异宿环,可数无穷多个同宿环和双曲基集[6] 。当
趋近零的Michelson系统进行了渐进分析,并与数值结果进行了比较[5] 。Lamb等证明了迈克尔逊系统有可数无穷多异宿环,可数无穷多个同宿环和双曲基集[6] 。当 ,系统(1.1)在原点存在Hopf分叉[5] [7] 。在无限维系统中,偏微分方程(1.2)一般作为研究混沌现象的典型范例[8]
。
,系统(1.1)在原点存在Hopf分叉[5] [7] 。在无限维系统中,偏微分方程(1.2)一般作为研究混沌现象的典型范例[8]
。
本文用同伦分析方法讨论Michelson系统的异宿轨道,其中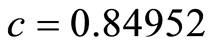 [9]
,并对42阶解析近似与精确解进行了对比。接下来,第二部分给出了求解多自由度常微分方程的同伦分析方法。第三部分的数值模拟验证了该方法的准确性和精确性。此外,在第四部分给出了该方法收敛定理的证明。最后对文章进行了总结。
[9]
,并对42阶解析近似与精确解进行了对比。接下来,第二部分给出了求解多自由度常微分方程的同伦分析方法。第三部分的数值模拟验证了该方法的准确性和精确性。此外,在第四部分给出了该方法收敛定理的证明。最后对文章进行了总结。
考虑多自由度非线性动力学系统
![]() (2.1)
(2.1)
其中, 是
是 维向量,
维向量,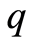 上的点表示对
上的点表示对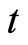 求导,
求导,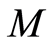 ,
, 和
和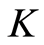 是阶实矩阵,
是阶实矩阵,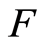 是
是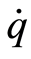 ,
, 和
和 的非线性向量函数。若
的非线性向量函数。若![]() ,则方程(2.1)是自治动力系统。
,则方程(2.1)是自治动力系统。
根据等式(2.1),构到如下非线性算子
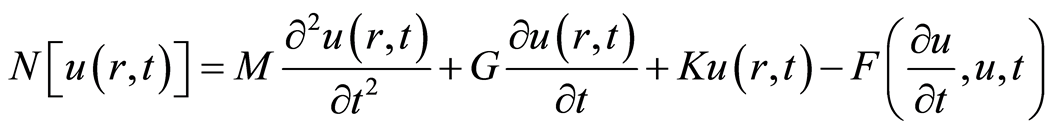 , (2.2)
, (2.2)
其中
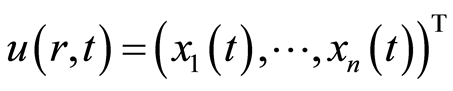 , (2.3)
, (2.3)
 , (2.4)
, (2.4)
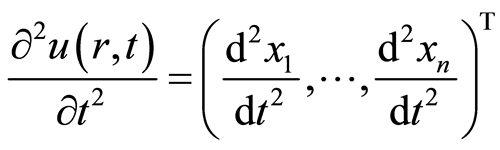 , (2.5)
, (2.5)
这里![]() 是未知的向量值函数,
是未知的向量值函数,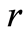 和
和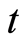 分别是空间和时间变量。
分别是空间和时间变量。
根据函数概念和同伦分析方法[10] -[13] ,零阶形变方程为
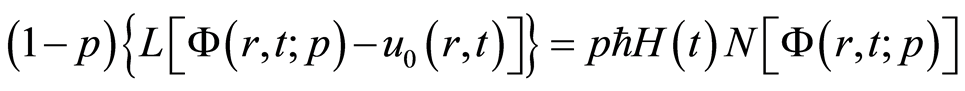 , (2.6)
, (2.6)
这里![]() 是一个嵌入变量,
是一个嵌入变量,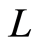 是一个辅助线性算子,
是一个辅助线性算子,![]() 是初值猜测解,
是初值猜测解,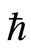 和
和![]() 分别为辅助参数和辅助函数。
分别为辅助参数和辅助函数。
当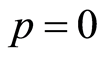 和
和 ,由零阶形变方程(2.6)易知
,由零阶形变方程(2.6)易知![]() 和
和![]() ,因此得到:当
,因此得到:当![]() 由0增大到1时,
由0增大到1时,![]() 由初值猜测
由初值猜测![]() 变化到精确解
变化到精确解![]() 。
。
设
 , (2.7)
, (2.7)
根据向量值函数的泰勒定理,把![]() 关于
关于 展成泰勒级数
展成泰勒级数
 . (2.8)
. (2.8)
合理选择辅助线性算子,初值猜测解,辅助参数 和辅助函数
和辅助函数![]() ,则当
,则当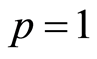 时,(2.8)中右边的级数收敛。
时,(2.8)中右边的级数收敛。
因此
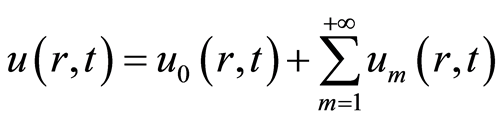 . (2.9)
. (2.9)
定义向量
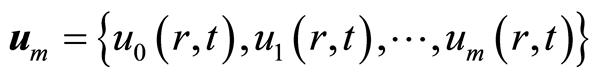 . (2.10)
. (2.10)
对零阶形变方程(2.6)关于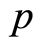 求导
求导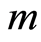 次,再除以
次,再除以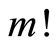 ,最后令
,最后令 得到
得到
 , (2.11)
, (2.11)
这里
 , (2.12)
, (2.12)
且
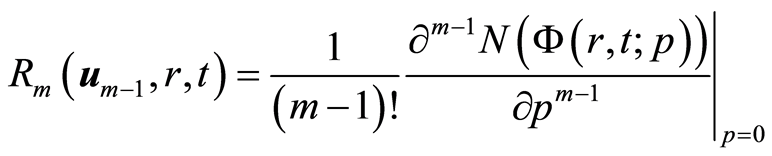 . (2.13)
. (2.13)
由等式(2.8)和(2.13)可得
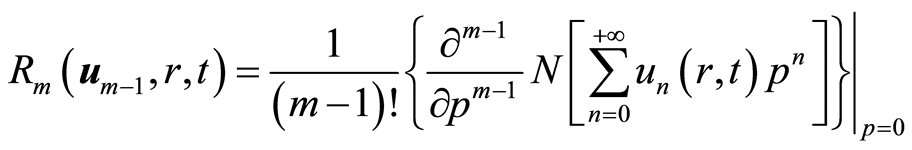 (2.14)
(2.14)
由于等式(2.11)是线性的,所以使用符号软件Mathematica或Maple可解出其解析近似解。
考虑如下Michelson的异宿轨道
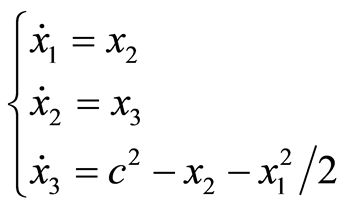 (3.1)
(3.1)
取
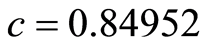 (3.2)
(3.2)
初始条件
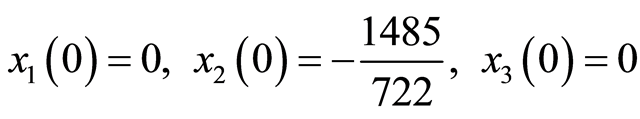 (3.3)
(3.3)
Michelson系统(3.1)满足初始条件(3.3)的精确解为
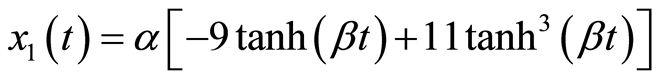 (3.4a)
(3.4a)
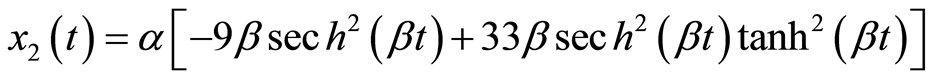 (3.4b)
(3.4b)
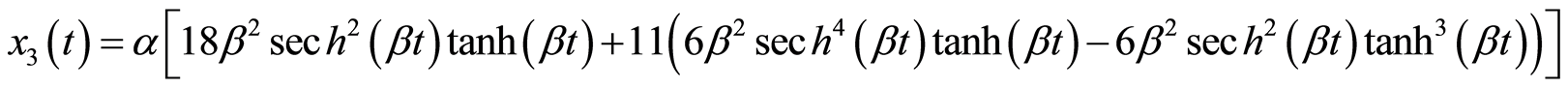 (3.4c)
(3.4c)
这里
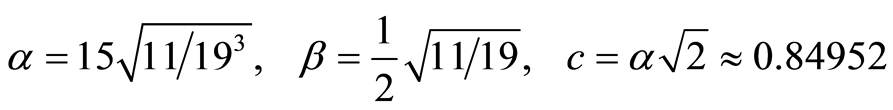 (3.5)
(3.5)
选择基函数为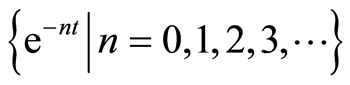 ,根据解表达原则和系数遍历原则[14] ,我们选择这样一种初值近似
,根据解表达原则和系数遍历原则[14] ,我们选择这样一种初值近似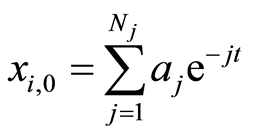 ,
,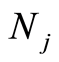 是正整数。根据初值函数的基,这里选择如下初值猜测:
是正整数。根据初值函数的基,这里选择如下初值猜测:
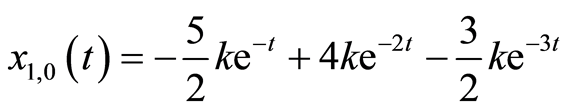 (3.6a)
(3.6a)
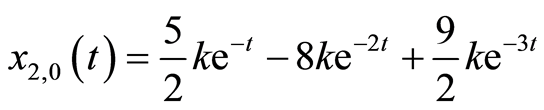 (3.6b)
(3.6b)
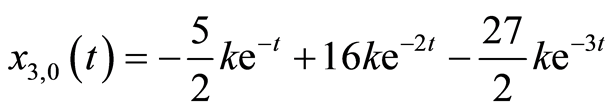 (3.6c)
(3.6c)
线性算子
 (3.7)
(3.7)
非线性算子
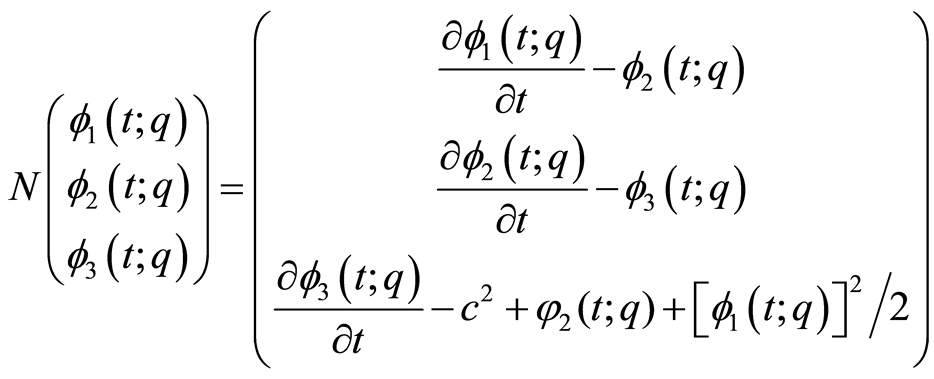 (3.8)
(3.8)
零阶形变方程
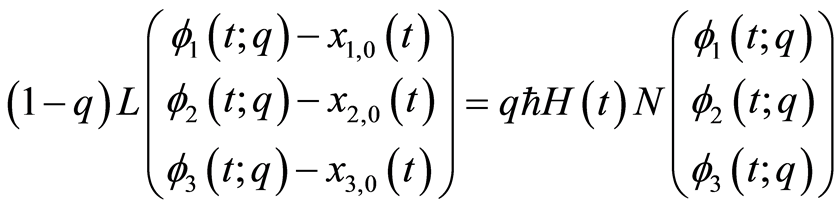 (3.9)
(3.9)
![]() 阶形变方程
阶形变方程
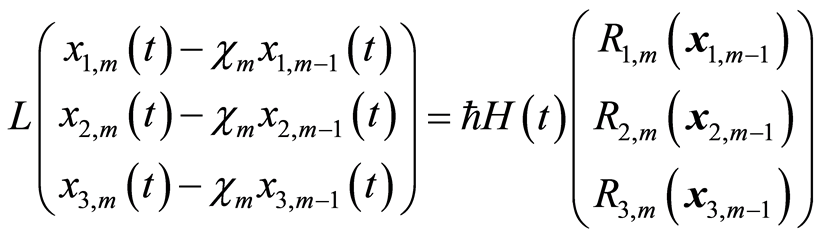 (3.10)
(3.10)
设
![]() (3.11)
(3.11)
根据初值条件和初值猜测知
![]() (3.12)
(3.12)
且
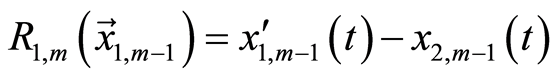 (3.13a)
(3.13a)
 (3.13b)
(3.13b)
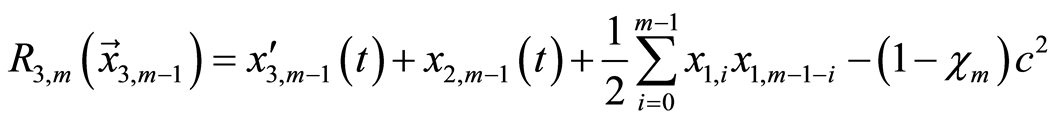 (3.13c)
(3.13c)
求解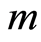 阶方程(3.10),得到
阶方程(3.10),得到
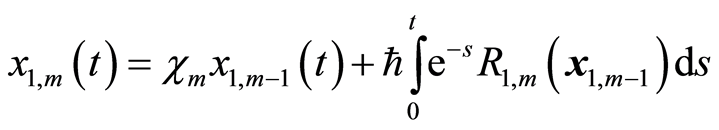 (3.14a)
(3.14a)
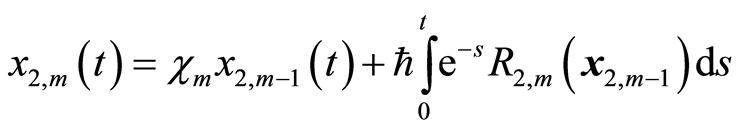 (3.14b)
(3.14b)
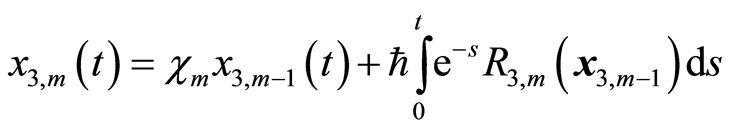 (3.14c)
(3.14c)
可解得
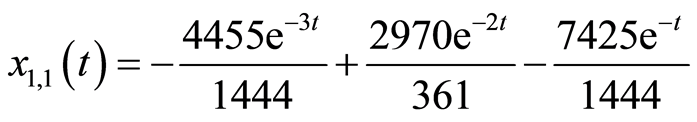 (3.15a)
(3.15a)
 (3.15b)
(3.15b)
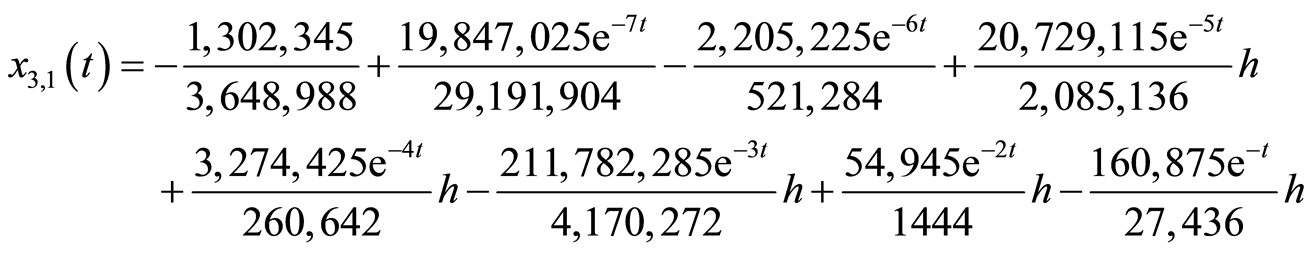 (3.15c)
(3.15c)
从而异宿轨道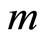 阶解析近似可表示为
阶解析近似可表示为
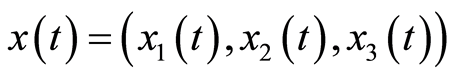 (3.16)
(3.16)
这里
![]() (3.17a)
(3.17a)
![]() (3.17b)
(3.17b)
![]() (3.17c)
(3.17c)
在同伦分析方法中,等式(2.6)中存在着非零辅助参数,辅助参数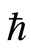 可用来控制解的级数收敛。因此当控制收敛参数
可用来控制解的级数收敛。因此当控制收敛参数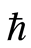 的取值范围确定之后,便可得到所研究问题的近似解。通过画
的取值范围确定之后,便可得到所研究问题的近似解。通过画 -曲线可以选择参数的有效区域,在
-曲线可以选择参数的有效区域,在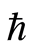 的有效区域确保近似解
的有效区域确保近似解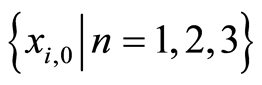 是收敛的。因此,在有效区域里可以任意选择
是收敛的。因此,在有效区域里可以任意选择 的值。
的值。
图1给出了系统十阶近似解三阶导数的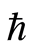 曲线,易知级数
曲线,易知级数![]() ,
,![]() 和
和![]() 在区间
在区间![]() 是收敛的。因此,在区间
是收敛的。因此,在区间![]() 可任意选取
可任意选取 的值,这里我们选择
的值,这里我们选择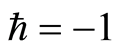 进行计算。图2对
进行计算。图2对![]() 的35阶、42阶的时间历程曲线与精确解进行了对比,显然,42阶近似解的近似程度要比35阶近似解要好。图3对42阶近似解的相图与精确解做了比较。当然为了得到更精确的解,我们可以适当的增加计算的阶数,从而增加级数解的项数。
的35阶、42阶的时间历程曲线与精确解进行了对比,显然,42阶近似解的近似程度要比35阶近似解要好。图3对42阶近似解的相图与精确解做了比较。当然为了得到更精确的解,我们可以适当的增加计算的阶数,从而增加级数解的项数。
定理1如果等式(2.9)中的级数解收敛,则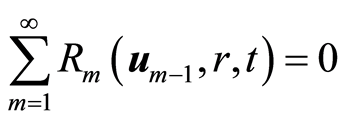 。
。

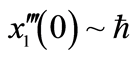 …
…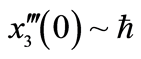
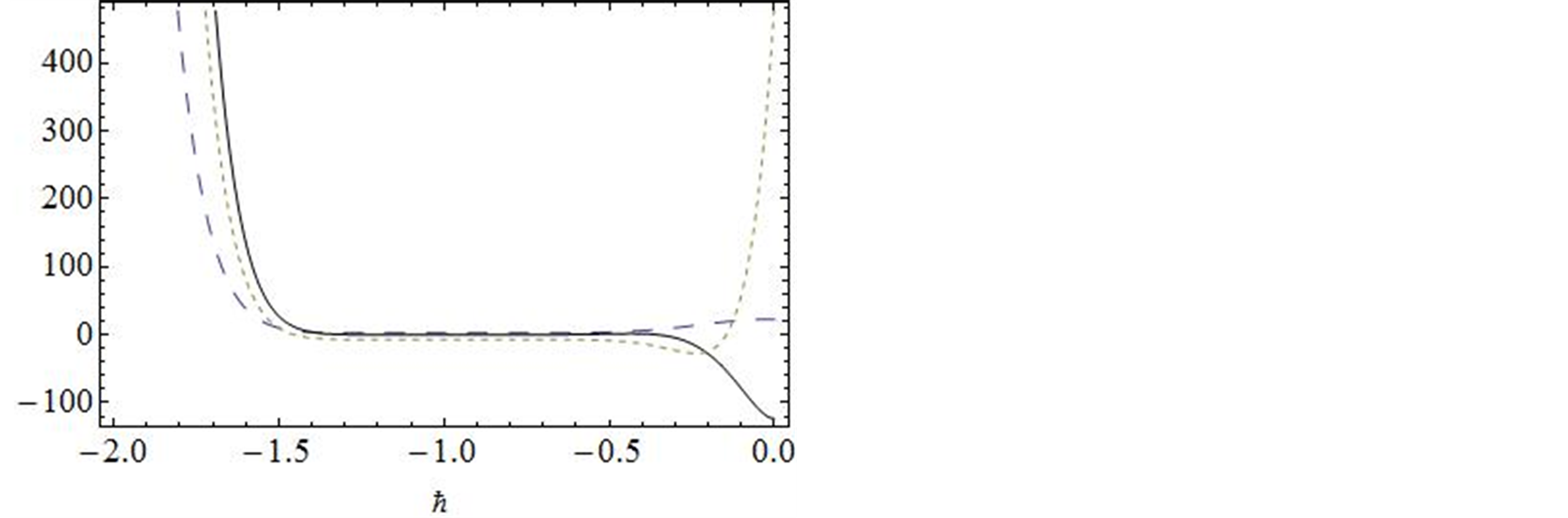
Figure 1.The
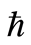 -curve of
-curve of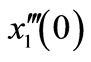 ,
,
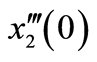 and
and
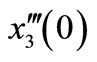 obtained from the tenth-order approximation of Equation (3.1)
obtained from the tenth-order approximation of Equation (3.1)
图1. 系统十阶近似解三阶导数的 曲线
曲线
30-order approximate solution … 42-order approximate solution exact solution
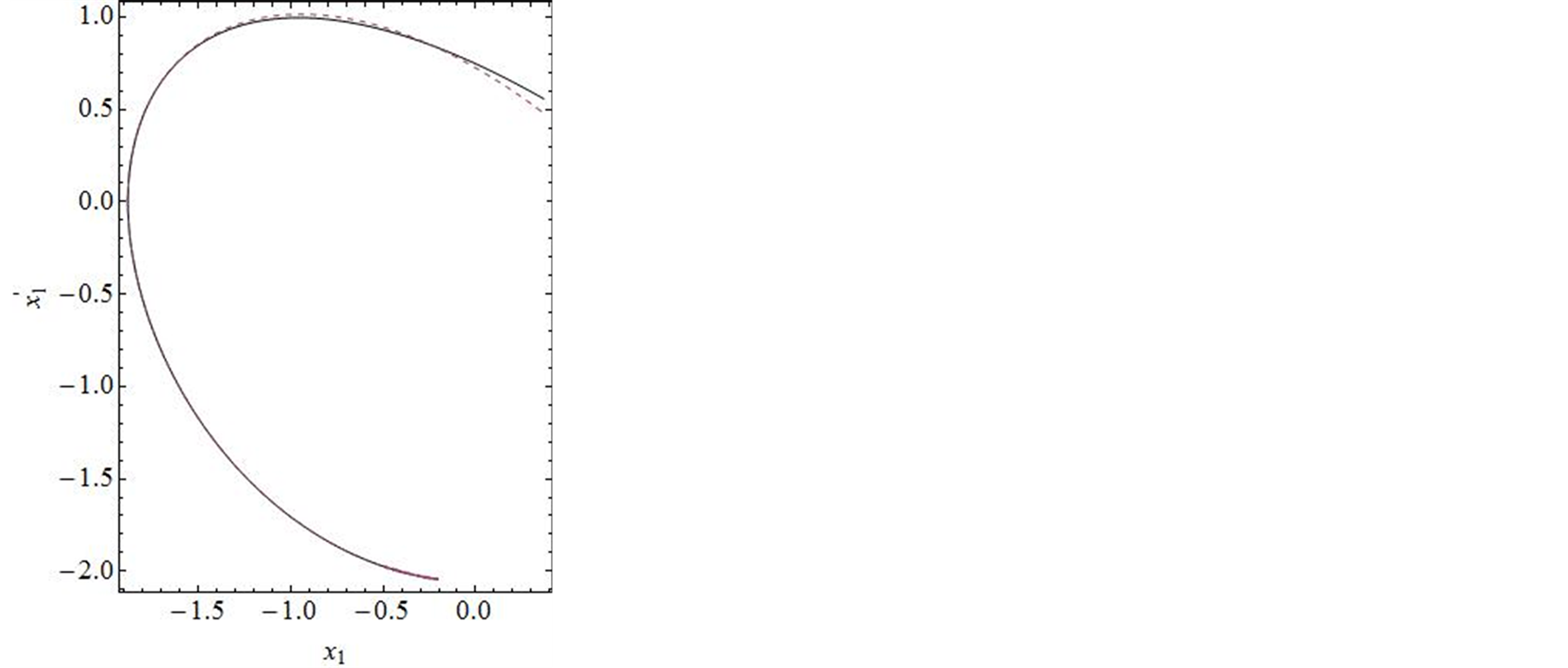
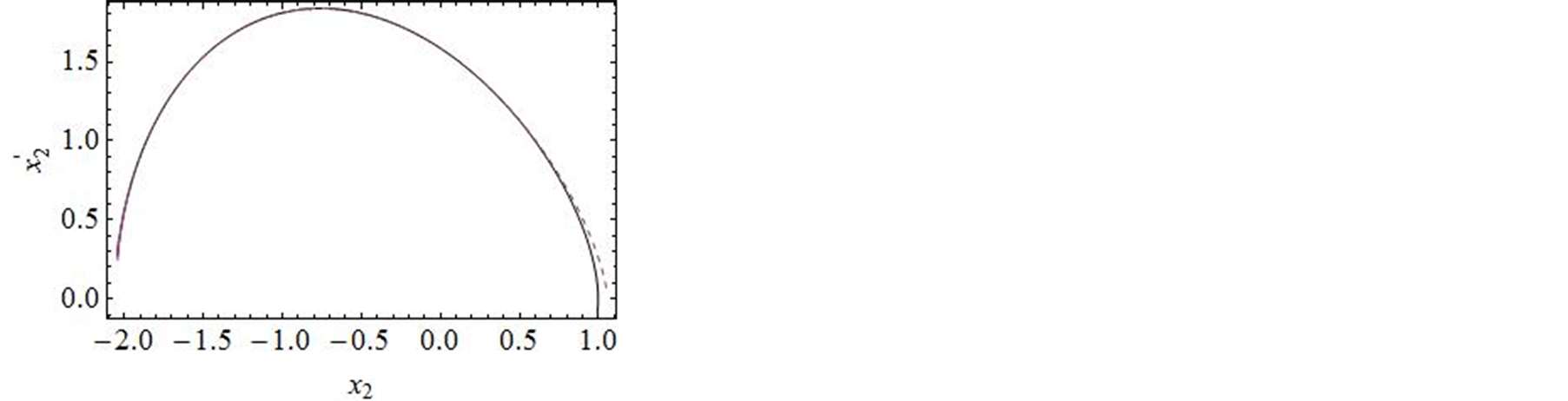

Figure 2. Comparison of the phase portrait curves of the 30 and 42-order approximate solution with the exact solution
图2. 系统解析近似解的30阶,42阶近似的时间历程曲线与精确解的比较
Approximatesolution exactsolution
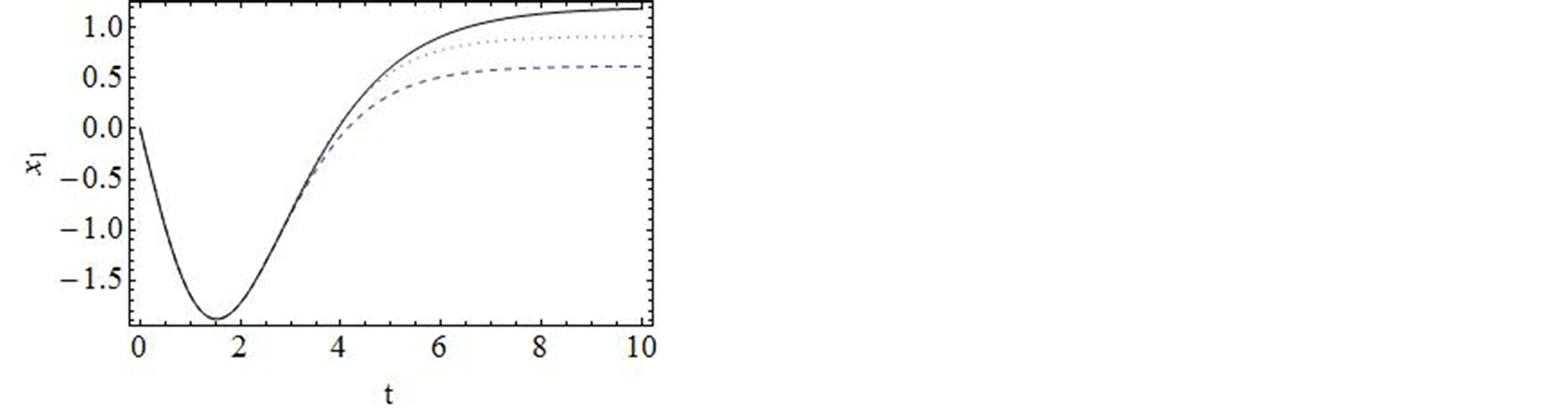
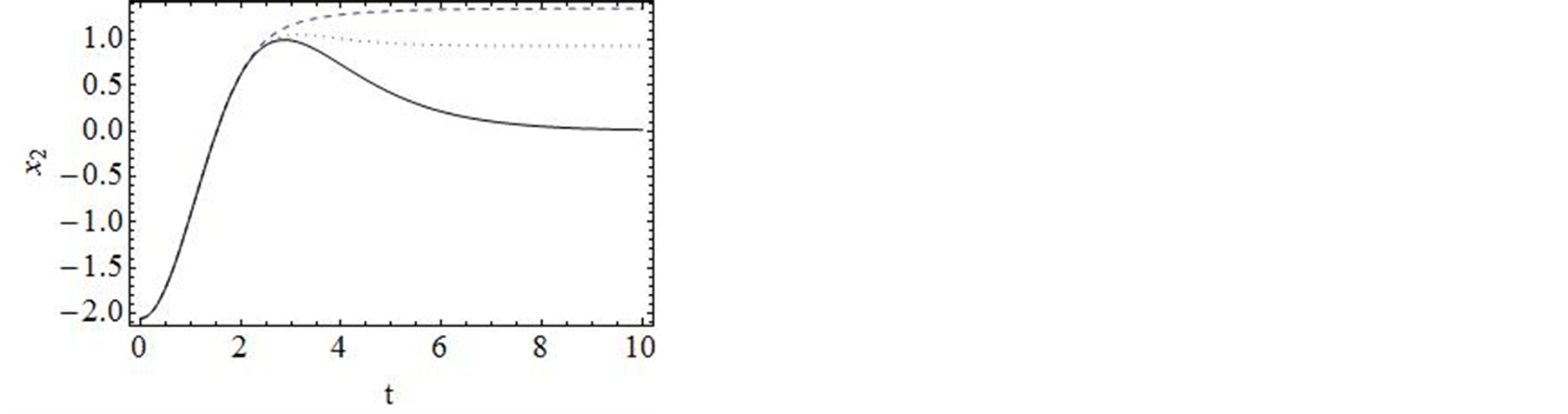
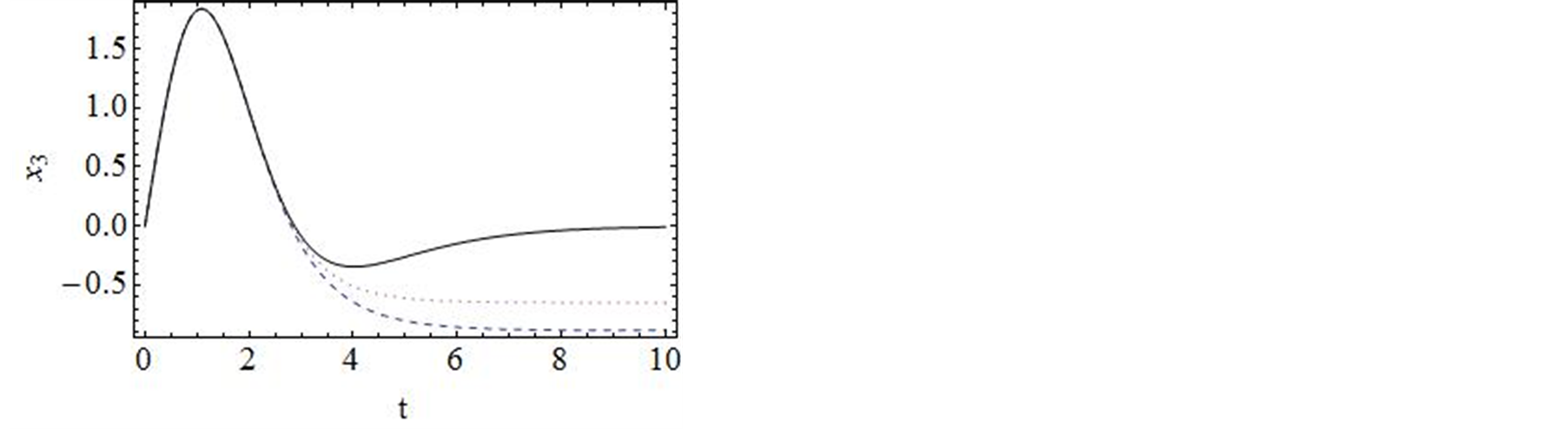
Figure 3.Comparison of the phase portrait curves of the 42-order approximate solution with the exact solution
图3. 系统解析近似解的42阶近似与精确解的比较
证明:由于级数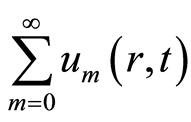 收敛,设
收敛,设
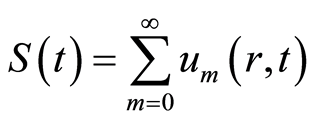 , (4.1)
, (4.1)
且
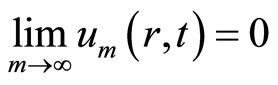 . (4.2)
. (4.2)
根据等式(2.12),知等式(2.11)满足
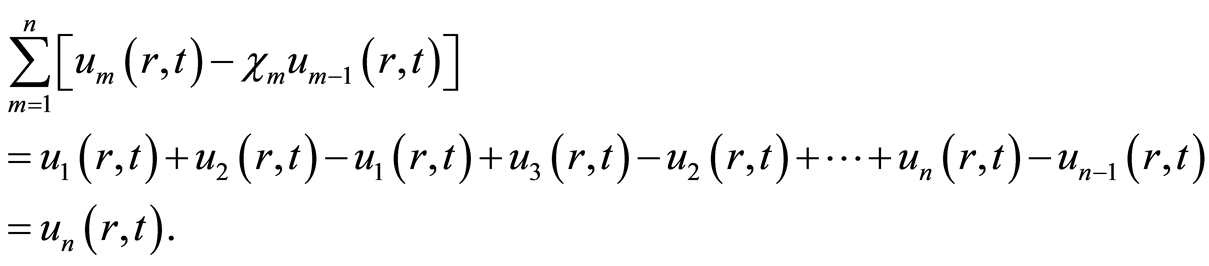 (4.3)
(4.3)
由等式(4.2),可得
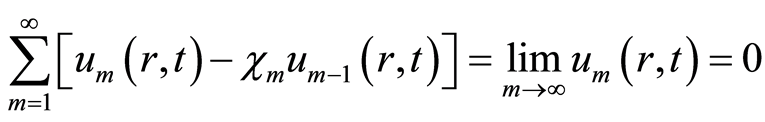 . (4.4)
. (4.4)
由于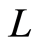 是线性算子,因此有
是线性算子,因此有
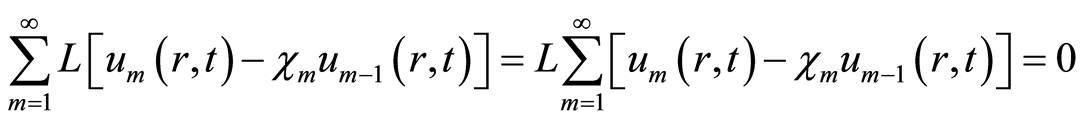 . (4.5)
. (4.5)
根据等式(2.11)和(4.5),可知
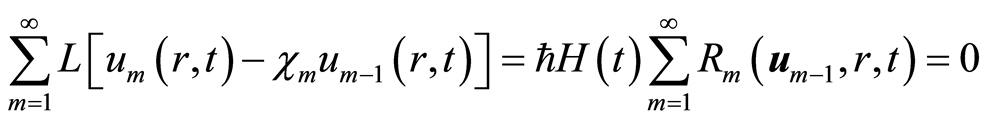 . (4.6)
. (4.6)
因此假设![]() 和
和![]() ,从而有
,从而有
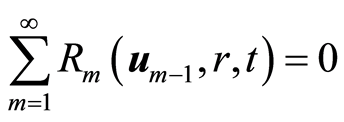 . (4.7)
. (4.7)
定理2 如果等式(2.9)中的级数收敛。那么,它一定是系统(2.1)的解。
证明 把等式(2.14)带入等式(4.7),得到
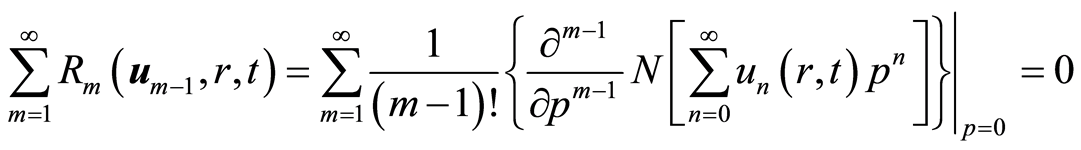 . (4.8)
. (4.8)
设
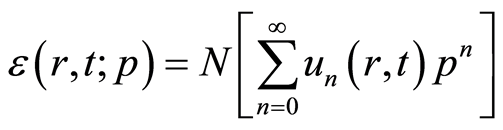 (4.9)
(4.9)
是等式(2.1)的残差,在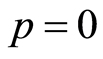 处可以把它展成如下泰勒级数
处可以把它展成如下泰勒级数
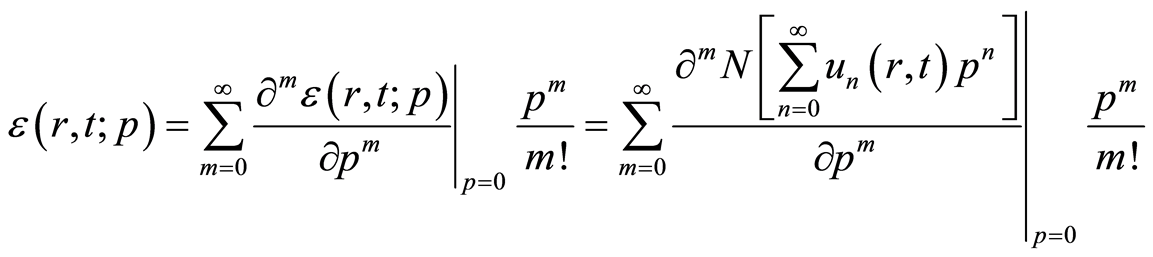 . (4.10)
. (4.10)
设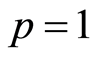 有
有
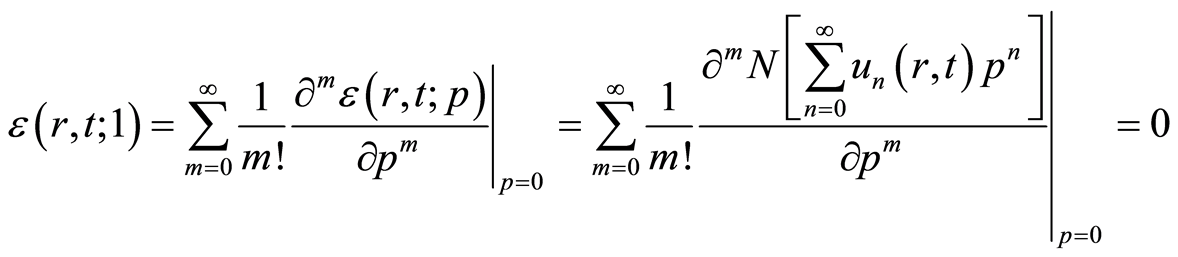 . (4.11)
. (4.11)
因此,等式(2.9)的级数是系统(2.1)的一个解。
本文用同伦分析方法得到了非线性动力学系统异宿轨道的近似解析解。考虑了自治系统(1.1),由此给出了同伦分析方法的求解过程。该方法通过一种巧妙的途径控制近似级数的收敛,并给出了其收敛定理的证明过程。该方法通过一种巧妙的途径控制近似级数的收敛,并给出了其收敛定理的证明过程。同伦分析方法的基本思想与其他分析方法不同,数值对比也说明了该方法的有效性和实用性。
国家自然科学基金项目(11202189)和浙江省自然科学基金项目(LY12A02002)资助。
- [1] Liao, S.J. (2003) Beyond perturbation: Introduction to the homotopy analysis method. CRC Press/Chapman and Hall, Boca Raton.
- [2] Michelson, D. (1986) Steady solution of the Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equation. Phisica D, 19, 89-111.
- [3] Lau, Y.T. (1992) The “cocoon” bifurcations in three-dimensional systems with two fixed points. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2, 543-558.
- [4] Kokubu, H., Wilczak, D. and Zgliczyński, P. (2007) Rigorous verification of cocoon bifurcations in the Michelson system. Nonlinearity, 20, 2147-2174.
- [5] Kevin, N.W. and John, N.E. (2003) Asymptotic analysis of the Michelson system. Nonlinearity, 16, 2149.
- [6] Lamb, J.S.W., Teixeira, M.A. and Webster, K.N. (2005) Heteroclinic bifurcations near Hopf-zero bifurcation in reversible vector fields in R3. Journal of Differential Equations, 219, 78-115.
- [7] Jaume, L. and Zhang, X. (2014) On the Hopf-zero bifurcation of the Michelson system. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 12, 1650-1653.
- [8] Hyman, J.M. and Nicolaenko, B. (1988) The Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equation: A bridge between PDEs and dynamical system. Phisica D, 18, 113-126.
- [9] Kuramoto, Y. and Tsuzuki, T. (1976) Persistent propagation of concentration waves in dissipative media far from thermal equilibrium. Progress of Theoretical Physics, 55, 356-369.
- [10] Qian, L.H., Qian, Y.H. and Chen, S.M. (2013) Homotopy analysis method for homoclinic orbit of a buckled thin plate system. Acta Mechanica, 225, 373-381.
- [11] Qian, Y.H., Chen, S.M. and Shen, L. (2014) Application of extended homotopy analysis method to the two-degree-offreedom coupled Van Der Pol-Duffing oscillator. Abstract and Applied Analysis, 2014, Article ID: 729184.
- [12] Wiggins, G. (1992) Orbits homoclinic to resonances with an application to chaos in a model of the forced and damped sine-Gordon equation. Physica D, 57, 185-225.
- [13] Wiggins, G. and Global, S. (1988) Bifurcation and chaos: Analytical methods. Springer, New York.

*通讯作者。