Journal of Organic Chemistry Research
Vol.05 No.02(2017), Article ID:20534,7
pages
10.12677/JOCR.2017.52009
Ionic Liquid 1-Butyl-3-Carboxymethyl Benzotriazole Trifluoroacetate Catalyzed Three Component Condensation Reaction for the Synthesis of Aminonaphthols
Lei Guo, Rong Ma, Zengpeng Zhang, Chenjiang Liu*
The Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Fine Chemicals, Ministry of Education & Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Physics and Chemistry Detecting Center, Xinjiang University, Urumqi Xinjiang
*通讯作者。

Received: Apr. 25th, 2017; accepted: May 14th, 2017; published: May 17th, 2017

ABSTRACT
A green and highly efficient approach for the synthesis of aminonaphthols via ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-carboxymethyl benzotriazole trifluoroacetate catalyzed three component condensation recation of β-naphthols, aromatic aldehydes and amines under solvent-free conditions has been reported. The catalyst ionic liquid can be easily recycled and reused for at least five cycles without obvious loss of catalytic activity.
Keywords:Ionic Liquid, Aminonaphthols, Catalysis, Synthesis, Solvent-Free
离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐催化三组分缩合反应合成氨基萘酚化合物
郭磊,麻荣,张增鹏,刘晨江*
石油天然气精细化工教育部&自治区重点实验室,新疆大学理化测试中心,新疆 乌鲁木齐

收稿日期:2017年4月25日;录用日期:2017年5月14日;发布日期:2017年5月17日

摘 要
本文报道了一种离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐催化β-萘酚、芳香醛和胺在无溶剂条件下发生三组分缩合反应绿色、高效合成氨基萘酚化合物的方法。离子液体催化剂至少可以循环使用5次,并且活性没有明显降低。
关键词 :离子液体,氨基萘酚,催化,合成,无溶剂

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
众所周知,氨基萘酚化合物广泛存在于天然产物和药物中,可以用作HIV蛋白酶抑制、抗生素以及抗肿瘤和抗抑郁等药物 [1] [2] [3] 。因此,该类化合物的合成受到化学家们的广泛关注。
β-萘酚、芳香醛和胺的三组分缩合反应是合成氨基萘酚化合物的有效途径之一。p-TSA [4] 、FeCl3∙SiO2 [5] 和I2 [6] 等作为催化剂已被应用于该反应,遗憾的是这些方法有的存在底物普适性不好、反应时间长和腐蚀性强的缺点。离子液体(ILs)具有蒸汽压低、毒性低、可循环利用、热稳定性好和溶解性好等优点,在有机合成领域已得到广泛应用 [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] 。Ruoho课题组 [12] 报道了离子液体[TEBSA][HSO4]催化β-萘酚、芳香醛和胺的三组分缩合反应,产物产率为73%~90%。为了丰富氨基萘酚化合物的合成方法,我们课题组在前期合成该类化合物的研究基础上 [13] ,开展了无溶剂条件下离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐催化β-萘酚、芳香醛和胺的三组分反应研究,合成了一系列氨基萘酚化合物,产物产率为87%~99%。同时考察了离子液体催化剂的循环使用效果。
2. 实验部分
2.1. 实验仪器及试剂
薄层层析硅胶用GF254硅胶和300-400目柱层析硅胶(青岛海洋化工厂)。ZF-2型三用紫外仪,Varian inova-400型核磁共振仪(400 MHz),瑞士BüchiB-560型熔点仪,德国Bruker Equinox 55红外光谱仪(KBr压片)。所用药品及试剂均为市售分析纯,用前未经处理。
2.2. 离子液体的合成
离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐的合成如式1所示。将0.20 mol的1-丁基苯并三唑和0.24 mol的1-氯乙酸在90℃搅拌反应36 h,冷却至室温,用乙醚和丙酮(V:V = 2:1,3 × 20 mL)混合溶剂浸泡洗涤所得的棕色固体,抽滤,所得固体在90℃下真空干燥10 h,即得氯化1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑,白色固体,熔点:148℃~149℃。
在室温下,将0.012 mol三氟乙酸缓慢滴加到0.01 mol氯化1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑中,滴毕升温至80℃回流反应48 h,得到褐色液体,减压旋除过量的三氟乙酸,残余物在90℃下真空干燥10 h,即得
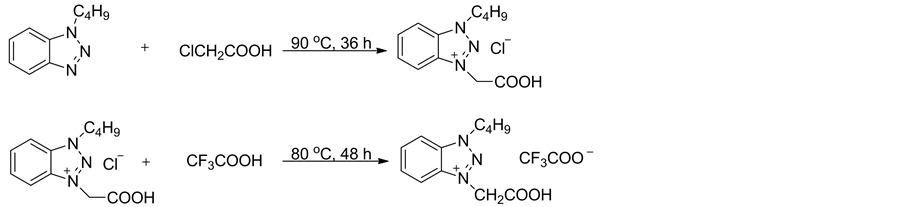
Scheme 1. The synthesis of ionic liquid[C2O2BBTA][TFA]
式1. 离子液体[C2O2BBTA][TFA]的合成
离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐[C2O2BBTA][TFA]。
2.3. 目标化合物的合成及结构分析
化合物4a-4s的合成如式2所示。将β-萘酚(1 mmol)、芳香醛(1 mmol)、胺(1.2 mmol)和离子液体催化剂1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐(15 mol%)的混合物在无溶剂条件下125℃搅拌反应10 min。反应结束后冷却至室温,加入乙酸乙酯和水(V:V =1:2,3 × 15 mL)萃取分离,所得有机相用无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤除去硫酸钠,旋除乙酸乙酯,残余物经柱层析分离即得目标产物的纯品。化合物结构经1H NMR,13C NMR,IR和MS确征。
未知化合物的表征如下:
离子液体[C2O2BBTA][TFA]:褐色液体;[C2O2BBTA][TFA]:1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ:8.79-8.24 (m, 3H), 8.06-7.96 (m, 2H), 5.93 (s, 2H), 5.08 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 2.06-1.99 (m, 2H), 1.39-1.31 (m, 2H), 0.93 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ:166.26 134.99, 134.22, 131.13, 130.80, 120.96, 117.76, 114.22, 113.85, 52.66, 51.09, 30.27, 18.81, 13.09. IR (KBr, ν/cm-1): 3106, 2967, 2940, 2879, 2511, 1738, 1505, 1471, 1364, 1190, 1141, 1029, 754, 718, 643, 599. ESI-MS: m/z (%) = 234.1 (100%) [M + H] +.
4f:白色固体;1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ: 10.29 (s, 1H), 8.98 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 8.07 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.87-7.78 (m, 4H), 7.55-7.45 (m, 4H), 7.28 (dt, J = 8.6, 6.1 Hz, 3H), 7.08 (s, 1H), 7.01 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 2.13 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 6H).13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ: 165.43, 139.23, 135.65, 152.96,134.29, 132.19,131.28, 129.10, 128.48, 128.41, 128.24, 127.50, 126.97, 126.58, 123.86, 122.64, 122.54, 118.61, 118.40, 48.97, 19.50, 18.83. IR (KBr, ν/cm-1): 3422, 3066, 1627, 1569, 1535, 1344, 1270, 820. ESI-MS: m/z (%) = 382.1 (100%) [M + H] +.
4h:白色固体;1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ: 10.32 (s, 1H), 9.01 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 8.09 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.89-7.79 (m, 4H), 7.55-7.45 (m, 4H), 7.32-7.24 (m, 3H), 7.18-7.13 (m, 2H), 7.04 (dd, J = 19.9, 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (s, 3H).13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO)δ: 165.52, 153.02, 141.85, 137.07, 134.22, 132.20, 131.30, 129.20, 128.50, 128.41, 128.25, 128.01, 127.16, 127.02, 126.88, 126.63, 123.55, 122.56, 118.59, 118.31, 49.08,21.07. IR (KBr, ν/cm-1): 3411, 3059, 1628, 1571, 1539, 1351, 1275, 821. ESI-MS: m/z (%) = 368.1 (100%) [M + H] +.
3. 结果讨论
3.1. 反应条件优化
以β-萘酚,苯甲醛和苯甲酰胺的反应为模型,考察了反应温度、催化剂用量、反应时间等因素对反应的影响,结果如表1所示。温度对反应影响的研究发现,产物产率随着温度的升高而增加,温度为125℃
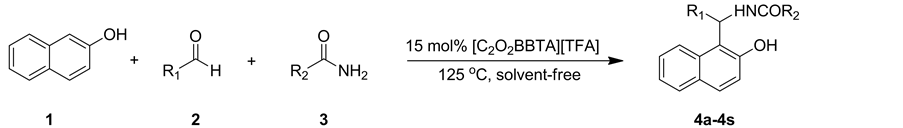
Scheme 2. The synthesis of amino naphthol compounds
式2. 氨基萘酚化合物的合成
Table 1. Optimization of reaction conditionsa
表1. 反应条件的优化a

a反应条件:β-萘酚(1 mmol),苯甲醛(1 mmol),苯甲酰胺(1.2 mmol),催化剂[C2O2BBTA][TFA],无溶剂。b分离产率。
时的反应效果最好(表1, entry 5),此后继续升高温度产物产率保持不变。其次,考察了催化剂的用量对反应体系的影响(表1, entries 5, 7-11),发现催化剂的用量为15 mol%时产物产率最高为87%。当反应体系中不加催化剂时,反应无法进行。最后,我们对反应时间进行了筛选(表1, entries 5, 12-17),结果表明最优反应时间为10 min。因此,反应的最优条件为:催化剂[C2O2BBTA][TFA]用量为15 mol%,无溶剂条件下125℃反应10 min。
3.2. 底物普适性研究
在最优条件下,我们对该反应的底物普适性进行了研究,结果见表2。从表可以看出,苯甲醛的苯环上不管是带有供电子基团还是吸电子基团,都能顺利的参与反应,以87%~99%的收率得到相应的氨基萘酚产物(表2, entries 4a-4s)。乙酰胺、丙烯酰胺和脲代替苯甲酰胺参与反应也能得到令人满意的结果,相应产物的产率为86%~99% (表2, entries 4n-4s)。因此,离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐催化合成氨基萘酚化合物具有很好的底物普适性。
3.3. 离子液体循环使用性
由于离子液体的特性之一是可循环使用,因此本文以β-萘酚、苯甲醛和苯甲酰胺的三组分反应为模型,在最优条件下考察了离子液体催化剂1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐的循环使用效果。具体方法是:将反应结束萃取分离的水相减压旋除水,残余物经真空干燥至恒重,即得回收的离子液体,可直接用于下一次催化循环。从图1可知,离子液体催化剂1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐循环使用5次后仍能保持较好的催化活性,表明该离子液体具有较好的循环使用效果。
Table 2. Research of substrate scopea
表2. 底物的普适性研究a

Figure 1. Recycling research of ionic liquid [C2O2BBTA][TFA]
图1. 离子液体[C2O2BBTA][TFA]的循环性研究
a反应条件:β-萘酚(1 mmol),苯甲醛(1 mmol),苯甲酰胺(1.2 mmol),催化剂[C2O2BBTA][TFA] (15 mol%),无溶剂条件下,125℃,10 min。b分离产率。
4. 总结
我们发展了一种离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐催化β-萘酚、芳香醛和胺绿色、高效合成氨基萘酚化合物的方法。该方法具有对环境友好、反应时间短、产率高等优点,离子液体催化剂可循环使用5次并且活性没有明显降低。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(No.21572195, 21262035, 21162025)。
文章引用
郭 磊,麻 荣,张增鹏,刘晨江. 离子液体1-丁基-3-羧甲基苯并三唑三氟乙酸盐催化三组分缩合反应合成氨基萘酚化合物
Ionic Liquid 1-Butyl-3-Carboxymethyl Benzotriazole Trifluoroacetate Catalyzed Three Component Condensation Reaction for the Synthesis of Aminonaphthols[J]. 有机化学研究, 2017, 05(02): 71-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/JOCR.2017.52009
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Tayebee, M., Amini, M., Akbaria, M. and Aliakbari, A. (2015) A Novel Inorganic-Organic Nanohybrid Material H4SiW12O40/pyridino-MCM-41 as Efficient Catalyst for the Preparation of 1-Amidoalkyl-2-Naphthols under Solvent-Free Conditions. Dalton Transaction, 44, 9596-9609.
- 2. Nasresfahani, Z., Kassaee, M.Z. and Eidi, E. (2016) Homopiperazine Sulfamic Acid Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNs-HPZ-SO3H) as an Efficient Catalyst for One-Pot Synthesis of 1-Amidoalkyl-2-Naphthols. New Journal Chemistry, 40, 4720-4726. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02974K
- 3. Mulla, S.A.R., Salama, T.A., Pathan, M.Y., Inamdar, S.M. and Chavan, S.S. (2013) Solvent-Free, Highly Efficient One-Pot Multi-Component Synthesis of 1-Amido-And1-Carbamato-Alkyl Naphthols/Phenols Catalyzed by Ethylammonium Nitrate as Reusable Ionic Liquid under Neat Reaction Condition at Ambient Temperature. Tetrahedron Letters, 54, 672-675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.12.004.
- 4. Shaterian, H.R. and Yarahmadi, H. (2008) A Modified Reaction for the Preparation of Amidoalkylnaphthols. Tetrahedron Letters, 49, 1297-1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.12.093
- 5. Khodaei, M.M., Khosropour, A.R. and Moghanian, H. (2006) A Simple and Efficient Procedure for the Synthesis of Amidoalkylnaphthols by P-TSA in Solution or under Solvent-Free Conditions. Synlett, 6, 916-920. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-939034
- 6. Das, B., Laxminarayana, K., Ravikanth, B. and Rao, B.R. (2007) Iodine Catalyzed Preparation of Amidoalkylnaphthols in Solution and under Solvent-Free Conditions. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 261, 180-183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2006.07.077
- 7. Colin, D.H., Peter, I. and Rudi, E. (2011) Understanding Chemical Reaction Mechanisms in Ionic Liquids: Successes and Challenges. Chemical Society Reviews, 40, 272-290.
- 8. Jason, P.H. and Tom, W. (2011) Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chemical Reviews, 111, 3508-3565. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1003248
- 9. Małgorzata, E.Z., Ewa, B.Ł. and Rafał, B.Ł. (2011) Ionic Liquid-Mediated Formation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfurals a Promising Biomass-Derived Building Block. Chemical Reviews, 111, 397-417. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr100171a
- 10. Zhang, Q. and Jean’ne, M.S. (2014) Energetic Ionic Liquids as Explosives and Propellant Fuels: A New Journey of Ionic Liquid Chemistry. Chemical Reviews, 114, 10527-10572.
- 11. Maxim, V.F. and Alexei, A.K. (2014) Ionic Liquids at Electrified Interfaces. Chemical Reviews, 114, 2978-3025.
- 12. Hajipour, A.R., Ghayeb, Y., Sheikhan, N. and Ruoho, A.E. (2009) Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid as an Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for One-Pot Synthesis of 1-Amidoalkyl 2-Naphthols under Solvent-Free Conditions. Tetrahedron Letters, 50, 5649-5651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.07.116
- 13. Lei, Z.K., Xiao, L., Lu, X.Q., Huang, H. and Liu, C.J. (2013) Graphite-Supported Perchloric Acid (HClO4-C): An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst for the One-Pot Synthesis of Amidoalkylnaphthols. Molecules, 18, 1653-1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18021653
- 14. Nandi, G.C., Samai, S., Kumar, R. and Singh, M. S. (2009) Atom-Efficient and Environment-Friendly Multicomponent Synthesis of Amidoalkylnaphthols Catalyzed by P2O5. Tetrahedron Letters, 50, 7220-7222.
- 15. Patil, S.B., Singh, P.R., Surpur, M.P. and Samant, S.D. (2007) Ultrasound-Promoted Synthesis of 1-Amidoalkyl- 2-Naphthols via a Three-Component Condensation of 2-Naphthol, Ureas/Amides, and Aldehydes, Catalyzed by Sulfamic Acid under Ambient Conditions. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 14, 515-518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2006.09.006
- 16. Zhang, Q., Luo, J. and Wei, Y. (2010) A Silica Gel Supported Dual Acidic Ionic Liquid: An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst for the One-Pot Synthesis of Amidoalkylnaphthol. Green Chemistry, 12, 2246-2254.
- 17. Hajipour, A.R., Ghayeb, Y., Sheikhan, N. and Ruoho, A.E. (2009)Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid as an Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for One-Pot Synthesis of 1-Amidoalkyl 2-Naphthols under Solvent-Free Conditions. Tetrahedron Letters, 50, 5649-5651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.07.116
- 18. Shaterian, H.R., Yarahmadi, H. and Ghashang, M. (2008) Silica Supported Perchloric Acid (HClO4-SiO2): An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst for the One-Pot Synthesis of Amidoalkylnaphthols. Tetrahedron, 64, 1263- 1269.
- 19. Zhang, P. and Zhang, Z.H. (2009) Preparation of Amidoalkylnaphthols by a Three-Component Reaction Catalyzed by 2,4,6-Trichloro-1,3,5-Triazine under Solvent-Free Conditions. Monatshefte Fur Chemie, 140, 199-203.
- 20. Shaterian, H.R. and Yarahmadi, H. (2008) A Modified Reaction for the Preparation of Amidoalkylnaphthols. Tetrahedron Letters, 49, 1297-1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.12.093
- 21. Luo, J. and Zhang, Q.A (2011) One-Pot Multicomponent Reaction for Synthesis of 1-Amidoalkyl-2-Naphthols Catalyzed by Peg-Based Dicationic Acidic Ionic Liquids under Solvent-Free Conditions. Monatshefte Fur Chemie, 142, 923-930.
- 22. Chavan, N.L., Naik, P.N., Nayak, S.K. and Kusurkar, R.S. (2010) Indium(III) Chloride: An Efficient Catalyst for the Synthesis of Amidoalkylnaphthols. Synthetic Communications, 40, 2941-2947. https://doi.org/10.1080/00397910903340702
- 23. Jiang, W.Q., An, L.T. and Zou, J.P. (2008) Molybdophosphoric Acid: An Efficient Keggin-Type Heteropolyacid Catalyst for the One-Pot Three-Component Synthesis of 1-Amidoalkyl-2-Naphthols. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 26, 1697-1701. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.200890307
