Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.03(2017), Article ID:20797,9
pages
10.12677/AAM.2017.63047
A Lattice Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann Model for the Reaction Diffusion Equation
Bo Yan1, Jianchao Wang1, Guangwu Yan2
1College of Civil Engineering, Jilin Jianzhu University, Changchun Jilin
2College of Mathematics, Jilin University, Changchun Jilin

Received: May 7th, 2017; accepted: May 24th, 2017; published: May 27th, 2017

ABSTRACT
A lattice Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann model for the reaction diffusion equations is constructed in this paper. By using the classical Runge-Kutta formula, we obtain four-order accuracy of truncation error. The Chapman-Enskog expansion and multi-scale technique are employed in order to obtain a series of equations in different time scales and modify partial differential equations of the reaction diffusion equations. Numerical tests show that the scheme can be used to simulate the reaction diffusion equations.
Keywords:Latctice Boltzmann Model, Runge-Kutta Scheme, Reaction Diffusion Equation
一种用于反应扩散方程的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型
闫铂1,王建朝1,闫广武2
1吉林建筑大学土木工程学院,吉林 长春
2吉林大学数学学院,吉林 长春
收稿日期:2017年5月7日;录用日期:2017年5月24日;发布日期:2017年5月27日

摘 要
本文构建了一个求解反应扩散方程的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型。通过使用经典的Runge-Kutta公式,得到了四阶截断误差。通过Chapmann-Enskog展开和多尺度展开技术,获得了不同时间尺度的系列偏微分方程和修正的反应扩散方程。数值结果表明,本文的模型可以用来求解反应扩散方程。
关键词 :格子Boltzmann模型,Runge-Kutta公式,反应扩散方程

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
格子Boltzmann方法(LBM)起源于格子气自动机(LGA) [1] ,并逐渐发展成为计算流体力学的重要数值模拟方法 [2] [3] [4] 。目前,LBM已广泛用于模拟单组分水动力学问题 [2] ,多相和多组分流动,包括悬浮粒子流 [5] ,磁流体 [6] ,多孔介质流 [7] 以及反应扩散系统 [8] 等。此外,LBM在求解非线性物理方程领域也有出色的表现,如波动方程 [9] 、KDV方程 [10] 、Burgers方程 [11] [12] 、非线性Schrödinger方程 [13] [14] [15] 和Poisson方程 [16] [17] 等。本文使用经典的Runge-Kutta公式 [18] 构建了具有高阶精度的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型。通过Chapmann-Enskog展开和多尺度展开技术,获得了不同时间尺度的系列偏微分方程和修正的反应扩散方程。数值结果表明,本文所提出的模型可以用来模拟反应扩散方程。
2. 格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型
2.1. 不同时间尺度的系列偏微分方程
将一个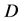 维空间离散成网格,网格中心与相邻的
维空间离散成网格,网格中心与相邻的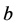 个格点连线作为速度矢量,加上网格中心的静止速度,这样就得到一个
个格点连线作为速度矢量,加上网格中心的静止速度,这样就得到一个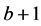 速度模型。定义
速度模型。定义 时刻,
时刻,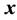 位置的分布函数为
位置的分布函数为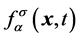 ,用来表示粒子的密度;定义该时刻该位置的速度为
,用来表示粒子的密度;定义该时刻该位置的速度为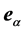 。则标准格子Boltzmann模型演化方程为
。则标准格子Boltzmann模型演化方程为
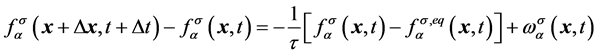 , (1)
, (1)
在方程(1)中,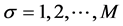 表示组分数;
表示组分数; 为附加项。为得到可以应用于稳态的宏观量,假设存在平衡态分布函数
为附加项。为得到可以应用于稳态的宏观量,假设存在平衡态分布函数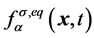 ,并且满足守恒条件
,并且满足守恒条件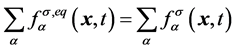 。
。
粒子状态的演化可以分为两步:流动,粒子沿速度方向运动到相邻格点;碰撞,不同速度的粒子发生碰撞并改变速度。所以,方程(1)也可以表示为
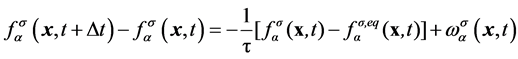 , (
, (
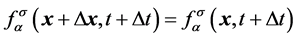 。 (2b)
。 (2b)
引入Knudsen数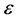 ,选择
,选择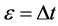 ,
,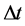 为时间步长 [9] ,将四阶Runge-Kutta公式 [18] 带入方程(
为时间步长 [9] ,将四阶Runge-Kutta公式 [18] 带入方程(
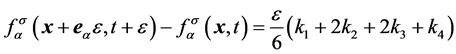 , (
, (
 ,(3b)
,(3b)
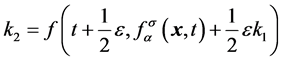 , (
, (
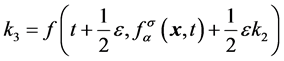 , (3d)
, (3d)
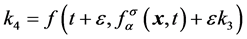 , (3e)
, (3e)
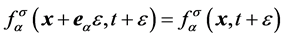 。 (
。 (
其中, 。
。
对(
 ,得
,得
 , (4)
, (4)
其中,偏微分算子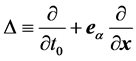 。
。
在小Knudsen数假设下,对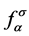 进行Chapman-Enskog展开 [19]
进行Chapman-Enskog展开 [19]
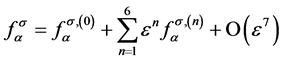 , (5)
, (5)
其中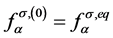 。
。
引入不同的时间尺度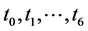 ,其中
,其中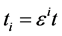 ,
,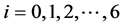 并且满足
并且满足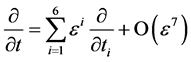 。
。
假设反应和扩散的影响为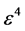 ,即
,即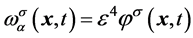 ,求得不同时间尺度的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型的系列方程为
,求得不同时间尺度的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型的系列方程为
 , (6)
, (6)
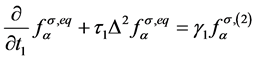 , (7)
, (7)
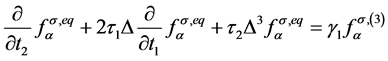 , (8)
, (8)
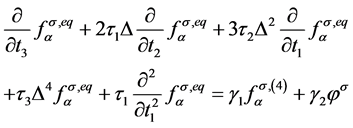 , (9)
, (9)
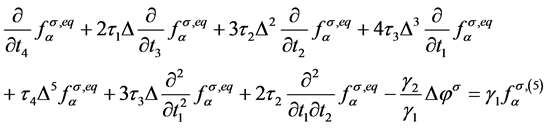 , (10)
, (10)
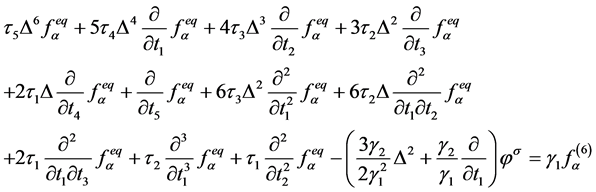 。(11)
。(11)
方程(6)~(11)中,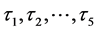 是Chapmann多项式,用来表示修正的反应扩散方程中耗散项和色散项系数,
是Chapmann多项式,用来表示修正的反应扩散方程中耗散项和色散项系数,
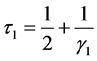 , (12)
, (12)
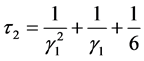 , (13)
, (13)
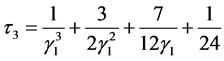 , (14)
, (14)
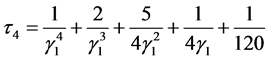 , (15)
, (15)
 , (16)
, (16)
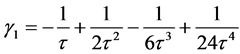 , (17)
, (17)
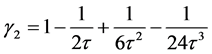 。 (18)
。 (18)
2.2. 反应扩散方程
含源项的一维反应扩散方程为
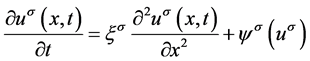 , (19)
, (19)
定义宏观量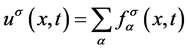 。根据守恒条件有
。根据守恒条件有 。对于反应扩散方程,选取平衡态分布函数的矩为
。对于反应扩散方程,选取平衡态分布函数的矩为
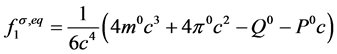 ,(20)
,(20)
 , (21)
, (21)
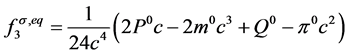 , (22)
, (22)
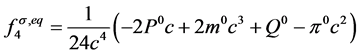 , (23)
, (23)
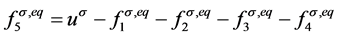 。 (24)
。 (24)
其中 为扩散系数,且
为扩散系数,且 ,
,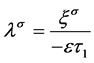 。
。
2.3. 误差分析
将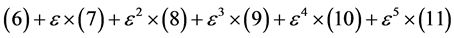 式两端对
式两端对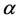 求和,得
求和,得
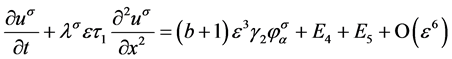 。 (25)
。 (25)
如取方程(19)的源项为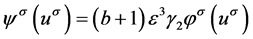 ,则修正后的一维反应扩散方程为
,则修正后的一维反应扩散方程为
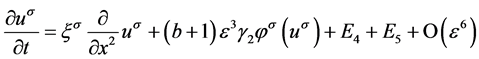 , (26)
, (26)
其中,
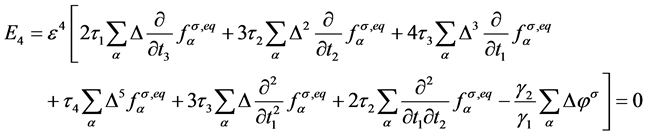 , (27)
, (27)
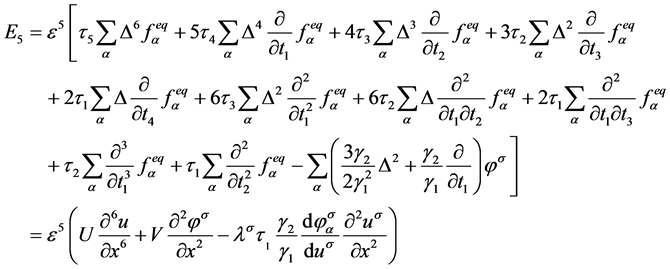 , (28)
, (28)
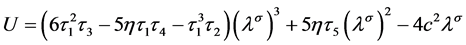 , (29)
, (29)
 。 (30)
。 (30)
方程(28)的主要项为 。根据Hirt启发式稳定性理论,格子Boltzmann模型正耗散条件为
。根据Hirt启发式稳定性理论,格子Boltzmann模型正耗散条件为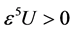 。
。
3. 数值算例
下面应用本文所提出的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型求解反应扩散方程。
例1:考虑方程
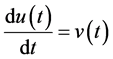 ,
,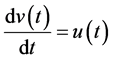 ,
,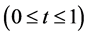 。 (31)
。 (31)
边界条件为
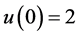 ,
,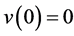 。 (32)
。 (32)
该方程的解析解为
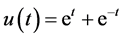 ,
,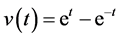 。 (33)
。 (33)
图1和图2给出了数值计算结果。其中图1(a)和图1(b)分别为u-t和v-t的Runge-Kutta算法计算结果、本文的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型(在图中表示为LRKB模型)计算结果与解析解的比较;图2(a)和图2(b)分别为u和v的绝对误差曲线,图2(c)为绝对误差E对Knudsen数 的无穷范数曲线。其中
的无穷范数曲线。其中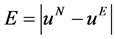 ,
, 为本文的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型计算结果,
为本文的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型计算结果,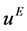 为解析解。其它参数为:
为解析解。其它参数为: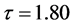 、
、 、
、 、
、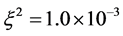 、格子数为51、时间步长为
、格子数为51、时间步长为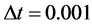 。从图1和图2
。从图1和图2

 (a)(b)
(a)(b)
Figure 1. Comparison between the Runge-Kutta solution, lattice Runge-Kut- ta-Boltzmann solution and the analytical result: (a) u versus t; (b) v versus t
图1. Runge-Kutta模拟结果、格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模拟结果与解析解的比较:(a) u对t图;(b) v对t图


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 2. (a) The absolute error of u; (b) The absolute error of v; (c) Curves of the infinite norm of the absolute error E versus the Knudsen number e
图2. (a) u的绝对误差曲线;(b) v的绝对误差曲线;(c) 绝对误差E对Knudsen数e的无穷范数曲线
中可以看出,格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型模拟结果与解析解有较好的一致性。
例2:考虑反应扩散方程
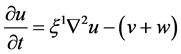 , (34)
, (34)
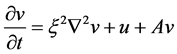 , (35)
, (35)
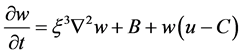 。 (36)
。 (36)
其中,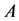 、
、 、
、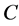 为参数。当
为参数。当 ,
,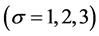 ,方程(34)~(36)简化为Rössler方程 [20]
,方程(34)~(36)简化为Rössler方程 [20]
 , (37)
, (37)
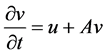 , (38)
, (38)
 。 (39)
。 (39)
在数值模拟中,令方程(26)中附加项为
 。 (40)
。 (40)
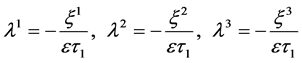 。 (41)
。 (41)
取计算域为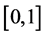 ;初始条件为
;初始条件为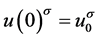 ,
,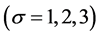 ;边界条件为
;边界条件为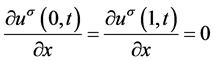 。
。
图3至图5给出了 ,
, 时通过Runge-Kutta算法、文献 [20] 中的格子Boltzmann模型和本文的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型绘制的相图。其中图3(a)、图4(a)和图5(a)为使用Runge-Kutta算法得到的v-u、w-u、w-v相图;图3(b)、图4(b)和图5(b)是通过文献 [20] 中的模型计算的v-u、w-u、w-v相图;图3(c)、图4(c)和图5(c)给出了使用本文格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型绘制的v-u、w-u、w-v相图。其它参数为:
时通过Runge-Kutta算法、文献 [20] 中的格子Boltzmann模型和本文的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型绘制的相图。其中图3(a)、图4(a)和图5(a)为使用Runge-Kutta算法得到的v-u、w-u、w-v相图;图3(b)、图4(b)和图5(b)是通过文献 [20] 中的模型计算的v-u、w-u、w-v相图;图3(c)、图4(c)和图5(c)给出了使用本文格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型绘制的v-u、w-u、w-v相图。其它参数为: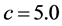 ,
,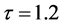 ,
,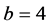 ,
, ,
,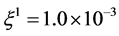 ,
,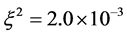 ,
,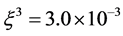 ,格子数为
,格子数为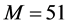 。从图中可以得出,本文模型所得结果与经典四阶Runge-Kutta算法吻合较好,并且比文献 [20] 的结果更精细。
。从图中可以得出,本文模型所得结果与经典四阶Runge-Kutta算法吻合较好,并且比文献 [20] 的结果更精细。


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 3. The phase figures of v versus u: (a) the Runge-Kutta formula; (b) the lattice Boltzmann result in Ref. [20] ; (c) the result of the lattice Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann scheme
图3. v对u的相图:(a) Runge-Kutta计算结果;(b) 文献 [20] 模拟结果;(c) 本文格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模拟结果


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 4. The phase figures of w versus u: (a) the Runge-Kutta formula; (b) the lattice Boltzmann result in Ref. [20] ; (c) the result of the lattice Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann scheme
图4. w对u的相图:(a) Runge-Kutta计算结果;(b) 文献 [20] 模拟结果;(c) 本文格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模拟结果


 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 5. The phase figures of w versus v: (a) the Runge-Kutta formula; (b) the lattice Boltzmann result in Ref. [20] ; (c) the result of the lattice Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann scheme
图5. w对v的相图:(a) Runge-Kutta计算结果;(b) 文献 [20] 模拟结果;(c) 本文格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模拟结果
4. 结论
本文使用经典Runge-Kutta算法构建了用于反应扩散方程的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型,获得了具有高阶精度的截断误差。数值结果表明,该模型的计算结果与经典Runge-Kutta模型吻合的较好。本文的主要思路,包括不同时间尺度的系列偏微分方程以及平衡态分布函数的形式,可以用来求解其它非线性偏微分方程。
致谢
国家自然科学基金(NO. 51406067,NO. 11272133),吉林省教育厅科研项目(吉教科合字[2016]第141号)资助。
文章引用
闫铂,王建朝,闫广武. 一种用于反应扩散方程的格子Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann模型
A Lattice Runge-Kutta-Boltzmann Model for the Reaction Diffusion Equation[J]. 应用数学进展, 2017, 06(03): 408-416. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/AAM.2017.63047
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Frisch, U., Hasslacher, B. and Pomeau, Y. (1986) Lattice Gas Automata for the Navier-Stokes Equations. Physical Review Letters, 56, 1505-1508. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.1505
- 2. Chen, S.Y. and Doolen, G.D. (1998) Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Flows. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 30, 329-364.
- 3. Succi, S. (2001) The Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond. Oxford University Press, New York.
- 4. Benzi, R., Succi, S. and Vergassola, M. (1992) The Lattice Boltzmann Equations: Theory and Applications. Physics Reports, 222, 147-197.
- 5. Ladd, A. (1994) Numerical Simulations of Particulate Suspensions via a Discretized Boltzmann Equation. Part II. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 271, 311-339. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112094001783
- 6. Chen, S.Y., Chen, H.D., Martíınez, D. and Matthaeus, W. (1991) Lattice Boltzmann Model for Simulation of Magneto-Hydrodynamics. Physical Review Letters, 67, 3776-3779. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.3776
- 7. Gunstensen, A.K. (1992) Lattice-Boltzmann Studies of Multiphase Flow through Porous Media. MIT, Boston.
- 8. Chen, S.Y., Dawson, S.P., Doolen, G., Jenecky, D. and Lawniczak, A. (1995) Lattice Methods for Chemically Reacting Systems. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 19, 617-646.
- 9. Yan, G.W. (2000) A Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Waves. Journal of Computational Physics, 161, 61-69. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.2000.6486
- 10. Yan, G.W. and Zhang, J.Y. (2009) A Higher-Order Moment Method of the Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Korteweg-de Vries Equation. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 79, 1554-1565.
- 11. Velivelli, A.C. and Bryden, K.M. (2006) Parallel Performance and Accuracy of Lattice Boltzmann and Traditional Finite Difference Methods for Solving the Unsteady Two Dimensional Burger’s Equation. Physica A, 362, 139-145.
- 12. Zhang, J.Y. and Yan, G.W. (2008) Lattice Boltzmann Methods for One and Two-Dimensional Burger’s Equation. Physica A, 387, 4771-4786.
- 13. Succi, S. (1993) Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Quantum Mechanics. Physica D, 69, 327-332.
- 14. Palpacelli, S. and Succi, S. (2007) Numerical Validation of the Quantum Lattice Boltzmann Scheme in Two and Three Dimension. Physical Review E, 75, Article ID: 066704. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.75.066704
- 15. Zhong, L.H., Feng, S.D., Dong, P. and Gao, S.T. (2006) Lattice Boltzmann Schemes for the Nonlinear Schrodinger Equation. Physical Review E, 74, Article ID: 036704. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.74.036704
- 16. Chai, Z.H. and Shi, B.C. (2007) A Novel Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Poisson Equation. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 32, 2050-2058.
- 17. Wang, M.R., Wang, J.K. and Chen, S.Y. (2007) Roughness and Cavitations Effect on Electro-Osmotic Flows in Rough Microchannels Using the Lattice Poisson-Boltzmann Methods. Journal of Computational Physics, 226, 836-851.
- 18. King, J.T. (1984) Introduction to Numerical Computation. McGraw-Hill Inc., New York.
- 19. Chapman, S. and Cowling, T.G. (1970) The Mathematical Theory of Non-Uniform Gas. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- 20. Yan, G.W. and Yuan, L. (2000) Lattice Boltzmann Solver of Rössler Equation. Communications in Nonlinear Science & Numerical Simulation, 5, 64-68.