Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.04(2017), Article ID:21532,7
pages
10.12677/AAM.2017.64074
On Numerical Solution of the Memory Dependent Partial Differential Equations
Wenwen Sun, Jinliang Wang
Research Institute for ESMD Method and Its Applications, College of science, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao Shandong

Received: Jul. 7th, 2017; accepted: Jul. 24th, 2017; published: Jul. 27th, 2017

ABSTRACT
If the rate of change respect to time in the classical string-vibration equation and heat-conduction equation is replaced by the type of memory-dependent derivative, what is the difference for the behavior of the solution? To compare with the ordinary derivative, the memory-dependent type can reflect clearly the dependence of physical process on their past states. To compare with the fractional derivative, the kernel function can be chosen freely and the interval for dependence doesn’t increase with time; so the memory-dependent partial differential equation should have strong expressive force. In this study, the case of kernel function with linear form is considered. Numerical results show that: 1) The characteristics of the solution lie between the string-vibration equation and the heat-conduction equation. It has both fluctuating and decaying properties. The amplitude of it decreases along with the increasing of time-delay and diffusion-coefficient. 2) To compare with the Caputo type of fractional partial differential equation, the fluctuation of the solution is stronger and the decay of amplitude is slower.
Keywords:Memory-Dependent Derivative, Memory-Dependent Partial Differential Equation, Caputo Fractional Derivative, String Vibration Equation, Heat Conduction Equation
记忆依赖型偏微分方程数值解研究
孙雯雯,王金良
青岛理工大学理学院,ESMD方法及其应用研究所,山东 青岛
收稿日期:2017年7月7日;录用日期:2017年7月24日;发布日期:2017年7月27日

摘 要
若将经典的弦振动方程与热传导方程中关于时间的变化率替换成记忆依赖型导数形式,其解的性态会发生怎样的变化呢?相对于普通导数而言,记忆依赖型导数可反映物理过程对过去状态的依赖性。与分数阶导数相比,其核函数的选取更自由,依赖区间也不会随时间的增长而增大,故而记忆依赖型偏微分方程也应具有更强表现力。本文针对核函数为线性函数的情况进行探讨。数值结果显示:1) 其解的性态介于弦振动方程和热传导方程之间,既有波动性又有衰减性,振幅随时滞和扩散系数的增大而减小。2) 与Caputo型分数阶偏微分方程相比,其波动性更强,振幅衰减更慢。
关键词 :记忆依赖型导数,记忆依赖型偏微分方程,Caputo型分数阶导数,波动方程,热传导方程

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
分数阶微积分是数学领域的一个重要分支,最初的分数阶微分算子主要有三种形式:Grumwald- Letnikov定义、Riemann-Liouville定义和Caputo定义。Caputo型分数阶导数在解决实际问题时应用更为方便。于2011年,Wang & Li [1] 参照Caputo型分数阶导数提出了一种新的导数——记忆依赖型导数。与分数阶导数相比,其核函数可以根据实际选择,且记忆依赖区间不会随时间t增长而增大,始终将依赖区间集中在与过去状态有关的某个有限的时间段 ,其中τ为时滞。记忆依赖型导数概念的提出引起了不少学者的关注,Ezzat等人在 [2] [3] [4] 中将记忆依赖型导数用于广义热粘弹性等问题。此外,Wang & Li还提出了记忆依赖型微分方程,并在 [5] 中对其做了深入研究。若将其引入偏微分方程结果会如何呢?
,其中τ为时滞。记忆依赖型导数概念的提出引起了不少学者的关注,Ezzat等人在 [2] [3] [4] 中将记忆依赖型导数用于广义热粘弹性等问题。此外,Wang & Li还提出了记忆依赖型微分方程,并在 [5] 中对其做了深入研究。若将其引入偏微分方程结果会如何呢?
经典的弦振动方程和热传导方程的解都有明显的特性,前者解的振幅具有随时间不减的波动性,后者解的振幅具有衰减性。当将关于时间的变化率换成记忆依赖型导数形式时其解的性态到底会发生怎样的变化?本文采用数值方法进行探索。先分析扩散系数及时滞对其数值解的影响;后将其与经典的弦振动方程、一维热传导方程及Caputo型分数阶偏微分方程进行了比较。
2. 记忆依赖型偏微分方程
2.1. 记忆依赖型导数(MD)
基于Caputo型分数阶微分算子,即:
 (1)
(1)
其中核函数 ,
, 表示通常的m阶导数,Wang & Li给出了记忆依赖型导数的定义。
表示通常的m阶导数,Wang & Li给出了记忆依赖型导数的定义。
定义1 [1] [6] :设m是一个自然数( ),对m-次可微函数
),对m-次可微函数 ,
,
 (2)
(2)
被称为m阶记忆依赖型导数, 是时滞,它代表记忆依赖时段的长短。权重函数K是一个m阶连续函数。
是时滞,它代表记忆依赖时段的长短。权重函数K是一个m阶连续函数。
与(1)式中导数相比,(2)式中导数的核函数可根据实际情况选择,在 [1] [6] 中通过计算发现,Caputo型导数在大的时间t下将导致长时间变化过程的失效,这是此类导数的固有缺陷,故而记忆依赖型导数较之更为合理。
此处取

对(2)应用积分的平均值公式得:

其中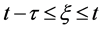 。由此可见原记忆依赖型导数大约等于
。由此可见原记忆依赖型导数大约等于 的一半。将上式中的
的一半。将上式中的 用
用 代替后量值基本保持不变。由此可得改进后的定义。
代替后量值基本保持不变。由此可得改进后的定义。
定义2:设m是一个自然数( ),对m-次可微函数
),对m-次可微函数 ,
,
 (3)
(3)
被称为m阶记忆依赖型导数, 是时滞,它代表记忆依赖时段的长短。权重函数K是一个m阶连续函数。
是时滞,它代表记忆依赖时段的长短。权重函数K是一个m阶连续函数。
2.2. 记忆依赖型偏微分方程
在 [1] [6] 中已指出记忆依赖型导数相比于分数阶导数在刻画记忆效应方面更具表现力,相应的记忆依赖型微分方程也具有更强的表现力,由其构成的偏微分方程也应具有较强的表现力,而经典的弦振动方程和热传导方程数值解有明显的特性,由此,启发我们利用(3)式中的记忆依赖型导数代替原来的时间导数,探讨其解的性态变化。
探讨如下初边值问题:
 (4)
(4)
其中 为二阶的(3)式中的记忆依赖型导数,
为二阶的(3)式中的记忆依赖型导数,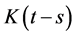 取的是一次函数形式,即:
取的是一次函数形式,即:

通过计算得, 。易发现,除扩散系数
。易发现,除扩散系数 外,时滞
外,时滞 是影响问题(4)数值解的主要因素。
是影响问题(4)数值解的主要因素。
利用有限差分法将问题(4)进行离散化,取∆t为时间步长,∆x为空间步长,令 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,得下式:
,得下式:

其中一式中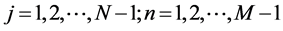 。
。
固定 时,选取时滞为15个步长不变,分别选取扩散系数
时,选取时滞为15个步长不变,分别选取扩散系数 时,得图1。
时,得图1。
由图1可见,记忆依赖型偏微方程的数值解具有波动性,且随着时间增加其振幅逐渐减小,时滞为15个步长不变时,其振幅随 的增加而减小。
的增加而减小。
进一步,固定 及
及 时,分别选取
时,分别选取 (其中
(其中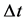 为时间步长)时,由MATLAB软件实现得图2。
为时间步长)时,由MATLAB软件实现得图2。
由图2可见,在 时,随着时滞的增加,解的振度随之降低,趋于稳定所需的时间也随之减少。由图1和图2可见,记忆依赖型偏微分方程的解既有波动性又有衰减性,其振幅随扩散系数和时滞的增大而减少,趋于稳定的时间也随之缩短。
时,随着时滞的增加,解的振度随之降低,趋于稳定所需的时间也随之减少。由图1和图2可见,记忆依赖型偏微分方程的解既有波动性又有衰减性,其振幅随扩散系数和时滞的增大而减少,趋于稳定的时间也随之缩短。
3. 与经典的热传导方程及波动方程的比较
将问题(4)与经典的热传导方程:
 (5)
(5)

Figure 1. The influence of different diffusion coefficients on the solutions
图1. 不同扩散系数对解的影响情况

Figure 2. Influence of different time delay on solution
图2. 不同时滞对解的影响情况
及弦振动方程:
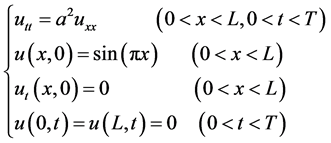 (6)
(6)
进行比较。利用有限差分法将上述问题进行离散化,并由MATLAB软件实现得到图3。
由图3可见,波动方程随时间以波的形式传播,同时能量不衰减;热传导方程随时间为能量衰减型,并且衰减速度很快;记忆依赖型偏微分方程介于波动方程及热传导方程之间,既有波动性又有衰减性(见图3(d),这种变化符合“加权周期”函数 [7] 的特性。这种现象的产生应与记忆依赖型导数依赖于时滞有关。通过比较分析,发现记忆依赖型导数对于描述现实中与时滞相关的能量逐步衰减的波(如击鼓时产生的波)更有表现力。
4. 与分数阶偏微分方程的对比
记忆依赖型导数在Caputo型分数阶微分算子的基础上提出,两者依赖区间及核函数都有所不同,故而两者分别构成的偏微分方程数值解也应有所差异。将问题(4)与以下Caputo型分数阶微分算子构成的分数阶偏微分方程进行比较:
 (7)
(7)
Figure 3. When a, k = 1, string vibration equation (a), the heat conduction equation (b), memory dependent partial differential equations (c) and the numerical solution of memory-dependent partial differential equations in  (d)
(d)
图3. a, k = 1的弦振动方程(a)、热传导方程(b)、记忆依赖型偏微分方程(c)及记忆依赖型偏微分方程于 的数值解图像(d)
的数值解图像(d)
利用以下引理及有限差分法对问题(7)进行离散 [8] :
引理 [9] 设 ,则
,则

其中

在此我们选取 ,将离散化后的问题(7)利用MATLAB实现得图4。
,将离散化后的问题(7)利用MATLAB实现得图4。
对比图3(c),图3(d)与图4,从整体形态上发现,记忆依赖型导数与Caputo型微分算子虽都为分数阶的,但所构成的偏微分方程数值解明显有所不同,两者都具有波动性,以波的形式向前传播,并且在传播过程中能量都在衰减,在扩散系数相同时,相对于分数阶偏微分方程数值解的快速衰减,记忆依赖型偏微分方程数值解的衰减速度明显慢很多。
5. 结论
在记忆依赖型导数基础上提出记忆依赖型偏微分方程,通过数值方法与弦振动方程、一维热传导方程及分数阶偏微分方程相比,其解介于两者之间,既具有波动性又具有衰减性,且振幅衰减速度慢于热传导方程。其振幅及趋于稳定的时间随时滞和扩散系数的增大而减少,这更近似于现实生活中声音的传播等现象。另外,此处实验结果显示,其振幅远大于弦振动方程和热传导方程的振幅,这一现象应与记
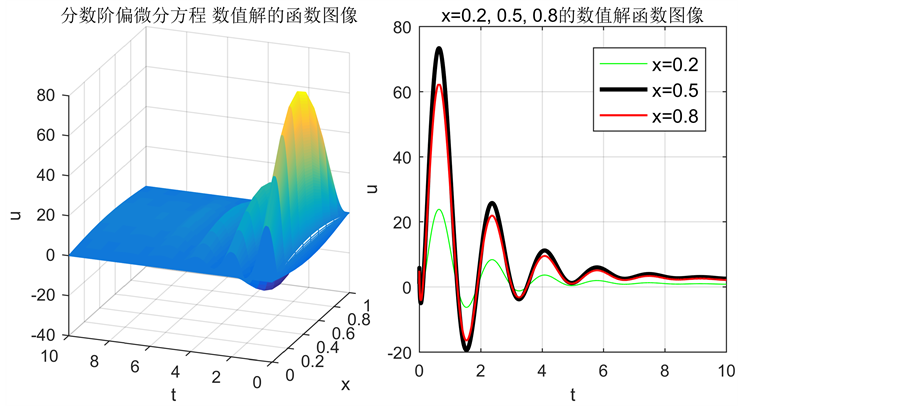
Figure 4. Numerical solutions of FPDE composed of Caputo type differential operators when  and
and 
图4. 时,Caputo型微分算子构成的分数阶偏微方程数值解
时,Caputo型微分算子构成的分数阶偏微方程数值解
忆依赖型导数的时滞及核函数有关,值得进一步探讨。与分数阶偏微分方程数值解相比,其解的衰减速度更缓慢,且波动性更明显。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(No.41376030)。
文章引用
孙雯雯,王金良. 记忆依赖型偏微分方程数值解研究
On Numerical Solution of the Memory Dependent Partial Differential Equations[J]. 应用数学进展, 2017, 06(04): 637-643. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/AAM.2017.64074
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Wang, J.L. and Li, H.F. (2011) Surpassing the Fractional Derivative: Concept of the Memory-Dependent Derivative. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 62, 1562-1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2011.04.028
- 2. Ezzat, M.A., El-Karamany, A.S. and El-Bary, A.A. (2016) Generalized Thermos-Viscoelasticity with Memory-Dependent Derivatives Involving Two Tempera-tures. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 23, 545-553. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2015.1007189
- 3. Ezzat, M.A. and El-Bary, A.A. (2016) Thermoelectric MHD with Memory-Dependent Derivative Heat Transfer. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 75, 270-281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.04.026
- 4. Ezzat, M.A. and El-Bary. A.A. (2015) Memory-Dependent De-rivatives Theory of Thermo-Viscoelasticity Involving Two-Temperature. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 29, 4273-4279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-0924-1
- 5. Li, H.F. and Wang, J.L. (2012) Molding the Dynamic System with Memo-ry-Dependent Derivative. 24th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Taiyuan, 23-25 May 2012, 1032-1036. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCDC.2012.6244162
- 6. 王金良, 李宗军. 极点对称模态分解方法: 数据分析与科学探索的新途径[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015.
- 7. Wang, J.L. and Li, H.F. (2006) The Weighted Periodic Function and its Properties. Dynamics of Continuous Discrete and Impulsive Systems (Series A-Mathematical Analysis), 13, 1179-1183.
- 8. 胡秀玲. 几类时间分数阶偏微分方程的有限差分方法研究[D]: [博士学位论文]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2012.
- 9. Sun, Z.Z. and Wu, X. (2006) A Fully Discrete Difference Scheme for a Diffusion-Wave System. Applied Numerical Mathematics, 56, 193-209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnum.2005.03.003