Advances in Material Chemistry
Vol.06 No.03(2018), Article ID:25897,6
pages
10.12677/AMC.2018.63008
The Synthesis of New-Type Rare Earth Luminescent Material [Eu(SO4)F∙H2O]
Jiwei Liu, Shuang Shao, Xiali Yu, Wenhua Yu, Ping Liu, Hao Tang, Zhu Qiu, Wanli Zhou*
Faculty of Chemistry, Tonghua Normal University, Tonghua Jilin

Received: Jun. 22nd, 2018; accepted: Jul. 9th, 2018; published: Jul. 16th, 2018

ABSTRACT
A new 3D rare earth luminescent material [Eu(SO4)F∙H2O], has been synthesized under solvothermal conditions by using ethylenediamine (en) as the structure directing agent (SDA). The colorless block crystals were characterized by IR, TGA and ICP. The structure of compound 1 was determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction [Triclinic, P-1, a = 5.0050(5) Å, b = 7.3930(5) Å, c = 11.7210(5) Å; α = 89.981(5)˚, β = 83.593(5)˚, γ = 89.880(5)˚, V = 431.0(6) Å3]. Crystal structure analysis shows that the 3D framework of compound 1 is constructed from the left-handed and the right-handed helical channels which are connected by groups using 6-membered rings and 4-membered rings. Compound 1 represents a strong luminescence upon the excitation.
Keywords:Structure Directing Agent, Rare Earth Material, Luminescent

新型稀土发光材料[Eu(SO4)F∙H2O]的合成
刘继巍,邵爽,于夏利,余文华,刘萍,唐皓,邱竹,周万里*
通化师范学院化学学院,吉林 通化

收稿日期:2018年6月22日;录用日期:2018年7月9日;发布日期:2018年7月16日

摘 要
本论文利用溶剂热反应,以乙二胺为结构导向剂合成了一种三维稀土发光材料。结构分析表明化合物属三斜晶系,空间群均为P-1,a = 5.0050(5) Å,b = 7.3930(5) Å,c = 11.7210(5) Å;α = 89.981(5)˚,β = 83.593(5)˚,γ = 89.880(5)˚,V = 431.0(6) Å3,化合物的三维结构是由 连接左旋的L-[-Eu-O-]n链和右旋的R-[-Eu-O-]n螺旋链构筑而成的,化合物展现了强的荧光性质。
关键词 :结构导向剂,稀土材料,荧光

Copyright © 2018 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
有机模板金属化合物展现了良好的光学、磁性、催化和手性材料等性质而备受关注。调研文献发现,早期对于有机模板化合物的报道集中于铁、钴、镍、锌和钒等过渡金属有机模板硫酸盐 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] 。区别于过渡金属,稀土金属具有灵活的配位数(7-12)和多种配位模式,开发有机模板稀土化合物吸引了科研工作者的关注。该化合物的特点是以有机胺为模板剂形成稀土硫酸盐,通过改变有机胺、稀土离子、反应条件等因素合成以硫酸根作为配体连接稀土金属形成一维链状、二维层状、三维孔道结构的有机模板稀土硫酸盐 [6] [7] [8] [9] 。在该类化合物中有机胺有两种作用:一、有机胺为模板剂,以氢键的形式与稀土硫酸盐骨架相连,不同的有机胺为模板剂诱导生成不同新颖结构的稀土硫酸盐。二、有机胺没有出现在分子结构单元中,起到结构导向剂的作用 [10] [11] 。由于铕具有出色的荧光性质,关于铕的荧光材料备受关注。
本文选择了乙二胺为结构导向剂,以 , 为混合配体,利用高温溶剂热方法合成了具有良好荧光性质的三维硫酸铕氟化物。
2. 新型稀土发光材料[Eu(SO4)F·H2O]的合成过程
2.1. 试剂与仪器
合成材料实验所需试剂和仪器如表1。
2.2. Eu(SO4)F·H2O (1)的合成
Eu2O3 0.1020 g (0.02 mmol),乙二胺(0.0245 g, 0.27 mmol),HF (0.1 mL)和异丙醇5 mL放入100 mL烧杯中,用硫酸(3 mol/L)调节pH为1.5,搅拌2小时后将混合液装入25 mL反应釜中,调节烘箱温度为170℃,加热5天,以10℃/h的速度缓慢冷却至室温,得到无色块状晶体。产率约为0.65% (以Eu2O3计算)。
3. Eu(SO4)F·H2O的表征
3.1. 晶体学数据的收集
X-射线衍射数据是在Bruker D8 QUEST ECO单晶衍射仪上进行,Mo-Kα射线, -scan方式扫描。晶体结构均利用SHELXTL-2014程序,采用直接法解析,并且用最小二乘法F2精致修改。化合物1中的所有非氢原子(Eu, S, O, F)均采用各项异性修正。化合物1的晶体学数据见表2,选择性的键长键角数据见表3。
Table 1. Reagent and instrument
表1. 试剂与仪器
Table 2. Crystal data and structure refinement for compound 1
表2. 化合物1的晶体学数据
Table 3. Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (˚)
表3. 选择性键长[Å]和键角[˚]
Symmetry transformations used to generate equivalent atoms: #1 −x + 1/2, y − 1/2, −z + 1/2 #2 −x + 1/2, y + 1/2, −z + 1/2 #3 x + 1/2, −y + 3/2, z − 1/2 #4 x + 1, y, z #5 –x − 1/2, y + 1/2, −z + 1/2 #6 x − 1, y, z #7 x − 1/2, −y + 3/2, z + 1/2 #8 –x − 1/2, y−1/2, −z + 1/2。
3.2. 化合物1的晶体结构
单晶X-射线研究表明该化合物具有三维孔道结构的稀土硫酸铕氟化物。在化合物的结构单元中(图1),包含1个Eu原子,1个
,1个
和1个配位H2O分子。Eu1与6个氧原子和两个F原子配位,构成EuO6F2多面体构型,6个配位的O原子5个来源于3个硫酸根离子,1个来自配位水分子(O1W)。Eu1-O键长在2.349~2.419 Å之间,S1原子核4个O原子(O1,O2,O3,O4)配位,S-O的键长在1.456~1.493 Å之间,S-O的键角在108.9~110.3之间,符合 四面体构型。
四面体构型。
如图2所示,化合物1的实验和模拟粉末衍射特征峰拟合较好,表明化合物1是纯相的。
从空间堆积方式来看,如图3,每个 连接相邻的Eu原子形成[-Eu-F-]n“之”字型链,相邻的[-Eu-F-]n链被硫酸根连接形成2D层状结构,层与层之间通过对称的硫酸根连接形成三维孔道结构。由u3-O(O1)连接Eu1和晶体学上对称的Eu1分别形成左旋的L-[-Eu-O-]n链和右旋的R-[-Eu-O-]n螺旋链。三维化合物结构也可描述为由{Eu2S2}四元环和{Eu4S2}六元环建筑单元通过u3-O(O1)连接构筑而成。
连接相邻的Eu原子形成[-Eu-F-]n“之”字型链,相邻的[-Eu-F-]n链被硫酸根连接形成2D层状结构,层与层之间通过对称的硫酸根连接形成三维孔道结构。由u3-O(O1)连接Eu1和晶体学上对称的Eu1分别形成左旋的L-[-Eu-O-]n链和右旋的R-[-Eu-O-]n螺旋链。三维化合物结构也可描述为由{Eu2S2}四元环和{Eu4S2}六元环建筑单元通过u3-O(O1)连接构筑而成。
3.3. 化合物的荧光光谱
由于Eu3+能发出很强的红光,在395 nm激发波长下测定了化合物1的荧光性质,如图4所示,化合物1的发射光谱是由于5D0→7FJ (J = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4)的跃迁。580和586 nm归于5D0 →7F0的跃迁;593 nm为D0→7F1跃迁;614和619 nm为5D0→7F2跃迁;652 nm为5D0→7F3跃迁;687.5和696.5 nm归于D0→7F4跃迁。这与报道的铕的化合物荧光性质是一致的 [12] 。
4. 论文小结
我们利用异丙醇作为溶剂,乙二胺为结构导向剂,在强酸性条件下利用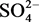 和
和 为混合配体合成了硫酸铕氟化物。结构分析表明化合物1是由{Eu2S2}四元环和{Eu4S2}六元环为建筑单元构筑的三维孔道结构。化合物的荧光光谱表明了化合物1具有强的荧光,可以作为新型的荧光材料。
为混合配体合成了硫酸铕氟化物。结构分析表明化合物1是由{Eu2S2}四元环和{Eu4S2}六元环为建筑单元构筑的三维孔道结构。化合物的荧光光谱表明了化合物1具有强的荧光,可以作为新型的荧光材料。

Figure 1. The asymmetric unit of compound 1. Hydrogen atoms water molecule are omitted for clarity
图1. 化合物1的基本结构单元(水中氢原子省略)

Figure 2. The experimental (red line) and simulated (black line) PXRD patterns obtained from compound 1
图2. 化合物1的实验(红线)和(黑线)模拟粉末衍射图

Figure 3. View of the 3D framework of compound 1 along a axis
图3. 化合物1沿a轴的三维框架结构

Figure 4. Photoluminescence spectrum obtained from compound 1
图4. 化合物1的荧光光谱
致谢
本论文得到大学生创新创业训练项目《新型稀土发光材料的合成》(项目编号:201710202005)的资助。
文章引用
刘继巍,邵爽,于夏利,余文华,刘萍,唐皓,邱竹,周万里. 新型稀土发光材料[Eu(SO4)F·H2O]的合成
The Synthesis of New-Type Rare Earth Luminescent Material [Eu(SO4)F·H2O][J]. 材料化学前沿, 2018, 06(03): 66-71. https://doi.org/10.12677/AMC.2018.63008
参考文献
- 1. Paul, G., Choudhury, A., Nagarajan, R., et al. (2003) Amine-Templated Linear Vanadium Sulfates with Different Chain Structures. Inorganic Chemistry, 42, 2004-2013. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic020645v
- 2. Paul, G., Choudhury, A., Sampathkumaran, E.V., et al. (2002) Organically Templated Mixed-Valent Iron Sulfates Possessing Kagom and Other Types of Layered Networks. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 41, 4297-4300. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3773(20021115)41:22<4297::AID-ANIE4297>3.0.CO;2-E
- 3. Paul, G., Choudhury, A. and Rao, C.N.R. (2002) An Organically Templated Iron Sulfate with a Distorted Kagome Lattice Exhibiting Unusual Magnetic Properties. Chemical Communications, 1904-1095. https://doi.org/10.1039/b204615f
- 4. Behera, J.N., Paul, G., Choudhury, A., et al. (2004) An Organically Templated Co(II) Sulfate with the Kagome Lattice. Chemical Communications, 456-457. https://doi.org/10.1039/b313594b
- 5. Behera, J.N., Gopalkrishnan, K.V., et al. (2004) Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetic Properties of Amine-Templated Open-Framework Nickel(II) Sulfates. Inorganic Chemistry, 43, 2636-2642. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic035488u
- 6. Rao, C.N.R., Behera, J.N. and Dan, M. (2006) Organically-Templated Metal Sulfates, Selenites and Selenates. Chemical Society Reviews, 35, 375-387. https://doi.org/10.1039/b510396g
- 7. Bataille, T. and Louer, D. (2002) Two New Diamine Templated Lanthanum Sulfates, La2(H2O)2(C4H12N2)(SO4)4 and La2(H2O)2(C2H10N2)3(SO4)6•4H2O, with 3D and 2D Crystal Structures. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 12, 3487-3493. https://doi.org/10.1039/B207212M
- 8. Dan, M., Beheraa, J.N. and Rao, C.N.R. (2004) Organically Templated Rare Earth Sulfates with Three-Dimensional and Layered Structures. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 14, 1257-1265. https://doi.org/10.1039/B314663D
- 9. Zhang, D., Lu, Y., Zhu, D.R., et al. (2013) (C4N2H12)3[Ln3(OH)(SO4)7] (Ln = Sm, Eu, and Tb): A Series of Honeycomb-Like Open-Framework Lanthanide Sulfates with Extra-Large Channels Containing 24-Membered Rings. Inorganic Chemistry, 52, 3253-3258. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic3027682
- 10. Zhou, W.L., Xu, Y., Han, L.J., et al. (2010) Solvothermal Syntheses, Crystal Structures and Luminescence Properties of Three New Lanthanide Sulfate Fluorides. Dalton Transactions, 39, 3681-3686. https://doi.org/10.1039/b926131a
- 11. Ju, W.W., Zhang, D., Zhu, D.R., et al. (2012) l- and d-[Ln(HCO2)(SO4)(H2O)]n (Ln = La, Ce, Pr, Nd, and Eu): Chiral Enantiomerically 3D Architectures Constructed by Double -[Ln-O]n-Helices. Inorganic Chemistry, 51, 13373-13379. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic302134m
- 12. Zhu, Y.L., Sun, X.C., Zhu, D.R., et al. (2009) Solvothermal Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Luminescence of the First Organic Amine Templated Europium Sulfate. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 362, 2565-2568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2008.11.015
NOTES
*通讯作者。
