World Journal of Cancer Research
Vol.07 No.02(2017), Article ID:20224,8
pages
10.12677/WJCR.2017.72007
The Level of Serum MFG-E8 in Liver Cancer and Its Metastasis in Liver Cancer
Honghai Hong1, Zheng Wang1, Lei Li1, Liying Lin1, Yong Xia1, Meiling Liu1, Baocang Su2*
1Department of Clinical Laboratory, Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou Guangdong
2Department of Blood Transfusion, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou Guangdong

Received: Apr. 2nd, 2017; accepted: Apr. 16th, 2017; published: Apr. 20th, 2017

ABSTRACT
Objective: to detect the level of MFG-E8 in serum of patients with liver cancer and its role in liver cancer. Methods: ELISA was used to detect the level of MFG-E8 in serum. Molecular cloning was used to construct MFG-E8 eukaryotic expression vector. MTT assay and Migration assay were used to detect the proliferation and metastasis of HCC. Results: the level of MFG-E8 in patients’ serum with liver cancer was significantly increased, which has a good value in the diagnosis of liver cancer, and is positively correlated with the level of AFP. Overexpression of MFG-E8 can promote the metastasis of liver cancer. Conclusion: the level of serum MFG-E8 in patients with liver cancer is high, and it can promote the metastasis of liver cancer.
Keywords:Hepatocellular Carcinoma, MFG-E8, Cancer metastasis
肝癌血清中MFG-E8水平及其在肝癌 转移作用研究
洪宏海1,王征1,李磊1,林丽英1,夏勇1,刘美玲1,苏宝昌2*
1广州医科大学附属第三医院检验科,广东 广州
2暨南大学附属华侨医院血库,广东 广州

收稿日期:2017年4月2日;录用日期:2017年4月16日;发布日期:2017年4月20日

摘 要
目的:检测肝癌病人血清中MFG-E8水平及探讨其在肝癌中作用。方法:ELISA法检测血清中MFG-E8水平;分子克隆构建MFG-E8真核表达载体;MTT法和Migration assay法分别检测肝癌增殖和转移作用。结果:肝癌病人血清中MFG-E8水平明显升高,对肝癌诊断具有很好的价值,且和AFP水平呈正相关;过表达MFG-E8促进肝癌转移。结论:肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平升高,其促进肝癌转移,对肝癌诊断具有很好价值。
关键词 :肝癌,MFG-E8,肿瘤转移

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
肝癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤,其致死率在肿瘤中排第三 [1] [2] 。在过去的几十年中,肝癌诊断主要依靠影像学技术和血清标志物 [3] 。然而,大多数患者在诊断时已经处于肝癌晚期,其生存期一般小于1年 [4] [5] 。依靠血液或血清样本检测肝癌相关生物标志物对肝癌的诊断具有重要意义。血清甲胎蛋白AFP水平在肝癌检测中得到了广泛的应用 [6] 。但是,AFP诊断肝癌的灵敏性和特异性只有60% 和80%左右 [7] [8] 。因此,寻找其它更有效的血清标志物尤为重要。
乳脂肪球表皮生长因子8 (Milk fat globule–EGF factor 8,MFG-E8)是一种多功能糖蛋白,最早发现于小鼠乳房上皮细胞中,在清除凋亡细胞中起着重要作用 [9] 。MFG-E8存在于心脏、大脑、肾脏、脾脏、肺脏等中 [10] ,具有调控受精卵结合 [11] 、血管新生 [12] 、凋亡细胞清除等 [13] 作用。最近还发现其具有免疫调控和促进炎症反应作用 [14] [15] 。MFG-E8可分泌到血液中,在细胞培养液中也可检测到 [16] 。研究表明MFG-E8科促进肿瘤的上皮间质化(EMT)和肿瘤的药物抵抗 [17] [18] 。最近研究发现阻断MFG-E8可抑制乳腺癌增殖和转移 [19] 。但是,MFG-E8在肝癌病人血清中水平及其在肝癌中作用尚未清楚。
在这篇论文中,我们首先用ELISA方法检测肝癌病人血清中MFG-E8水平,同时进行ROC曲线分析研究其在肝癌诊断中价值。此外,我们也构建MFG-E8质粒,并进一步在肝癌细胞株HepG2中研究其对肝癌增殖和转移作用。
2. 材料与方法
标本收集
健康人血清来自广州医科大学附属第三医院体检中心。肝癌病人血清来自暨南大学附属华侨医院检验科。所有病人资料和标本收集都严格按照广州医科大学和暨南大学伦理委员会相关规定。伦理批准时间为2016年5月。
试剂和耗材
MFG-E8 ELISA检测试剂盒购自上海星科生物科技公司。AFPELISA检测试剂盒购自安图生物公司。DNA maker购自Bio-Rad公司。引物由Invitrogen公司合成。MFG-E8一抗购自CST公司。MTT购自北京鼎国公司。Transwell小室购自BD公司。
MFG-E8过表达质粒构建
在Pubmed上面调出MFG-E8基因CDS序列,根据MFG-E8基因CDS序列设计克隆引物(引物1F:5'-CCCAAGCTTATGCCGCGCCCCC-3';引物1R:5'-CCGGAATTCCTAACAGCCCAGC-3';引物2F:5'-CCCAAGCTTATGCCGCGCCCCCGCCTGCTGGCC-3';引物2R: 5'-CCGGAATTCCTAACAGCCCAGCAGCTCCAGGCG-3'),以HepG2细胞cDNA为模板,进行PCR钓取MFG-E8基因,酶切、连接到pcDNA3.1+载体上,经公司测序确定MFG-E8过表达质粒构建成功。
MTT法检测肝癌细胞增殖能力
MTT法,即噻唑兰颜色反应法,是反映细胞增殖活力的测定方法 [19] 。活细胞里面线粒体琥珀酸脱氢酶能使MTT还原为不溶于水的蓝紫色晶体——甲缵,并沉淀在细胞里面,而死细胞则并不能使细胞里面的甲缵沉淀。取对数生长期肝癌细胞,接种到48孔细胞培养板中,每孔加入500 ml细胞悬液,置于37℃、5% CO2 cell incubator中培养;细胞贴壁后其融合度达到80%左右,瞬时转染MFG-E8过表达质粒,不同时间点(24 h, 48 h, 72 h)加入200 µl的MTT工作液(浓度为5 mg/ml),继续培养4小时;去掉上清后每孔加入2 ml dimethyl sulfoxide(二甲基亚砜,DMSO),用摇床震荡摇匀,以使蓝色结晶颗粒甲缵完全溶解,用酶标仪测定OD570的光密度值。实验中每个实验组设置3个重复的培养孔,重复进行3次。
Migration assay检测肝癌转移能力
Migration assay是用Boyden transwell小室来进行实验的。将细胞消化后种植到6孔板中,等细胞融合度到达80%至90%时,瞬时转入MFG-E8质粒,在不同时间点消化细胞;将消化的细胞置于15 ml离心管中,用无血清的培养液配制成一定浓度细胞悬液。于24孔板中先加入500 μl含有10%血清的培养液,把transwell小室放到24孔板中,使transwell小室底端刚好接触到下面的培养液。以每孔加入1 × 105个细胞加入transwell小室的上室。在不同时间点取出transwell小室,用4%的多聚甲醛固定15 min。然后进行结晶紫染色30 min,用清水轻轻洗去多余结晶紫染液,用棉签小心擦去transwell小室里面的细胞,然后室温晾干,使用显微镜观察transwell小室外面细胞和拍照。统计迁移过去的细胞数目。
统计学分析
采用SPSS17.0软件进行统计学处理。计量资料以均数±标准差表示。血清中MFG-E8水平和AFP水平采用t检验。ROC曲线分析用来判断血清MFG-E8对肝癌诊断价值。P < 0.05表示具有统计学意义。
3. 实验结果
肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平升高且具有诊断价值
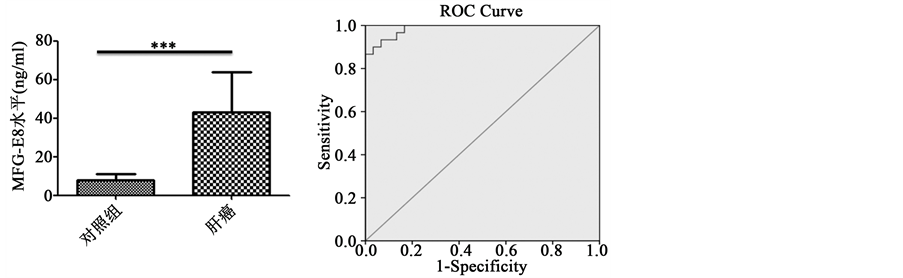
为了检测MFG-E8在肝癌病人血清中水平,我们收集了30例健康人和肝癌病人的血清,用ELISA试剂盒检测血清中MFG-E8水平。结果显示,与对照组相比,肝癌病人血清中MFG-E8水平明显高于健康人(图1(a))。此外,为了验证血清MFG-E8对肝癌病人的诊断价值,我们也进行了ROC曲线分析。结果显示,AUC面积为0.987,表明血清MFG-E8对肝癌的诊断具有很好的价值(图1(b))。同时ROC曲线分析表明血清MFG-E8对肝癌诊断敏感性和特异性分别为93.3%和90%;其诊断的cutoff值为11.95,95%置信区间为0.967~1.006 (图1(c))。
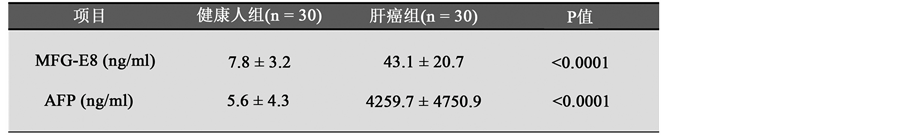
肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平呈正相关
甲胎蛋白AFP是肝癌诊断重要指标之一。为了进一步研究血清MFG-E8对肝癌诊断的价值,我们用肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平进行相关性分析。我们首先检测30例肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平(图2(a)),然后进行相关性分析。结果显示肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平呈
 (a) (b)
(a) (b) (c)
(c)
Figure 1. The level of MFG-E8 in HCC patients’ serum and ROC curve analysis. (a) ELISA detection of serum MFG-E8 levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 30). *** < 0.0001; (b) ROC curve analysis of the value of MFG-E8 in the diagnosis of liver cancer; (c) ROC curve analysis of the value of MFG-E8 diagnosis of liver cancer related indicators
图1. MFG-E8在肝癌病人血清中水平及其ROC曲线分析。(a) ELISA法检测肝癌病人血清中MFG-E8水平(n = 30)。*** < 0.0001;(b) ROC曲线分析MFG-E8对肝癌诊断的价值;(c) ROC曲线分析MFG-E8对肝癌诊断的价值相关指标
 (a)
(a)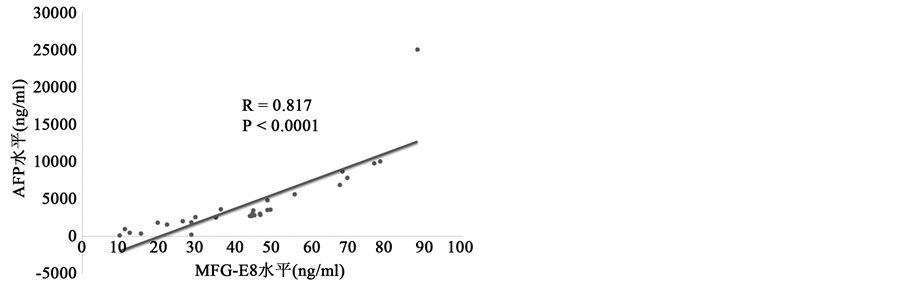 (b)
(b)
Figure 2. The correlation of MFG-E8 and AFP in HCC patients’ serum. (a) Serum MFG-E8 and AFP levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Detection of serum MFG-E8 and AFP levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by ELISA method; (b) correlation analysis of serum MFG-E8 and AFP levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
图2. 肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平呈正相关。(a)肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平。ELISA法检测肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平;(b)肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平和AFP水平相关性分析
正相关(图2(b)),具有明显的统计学意义,表明血清MFG-E8水平可以联合AFP水平来诊断肝癌,可能成为肝癌诊断指标之一。
MFG-E8真核质粒构建及其在肝癌细胞株HepG2中表达
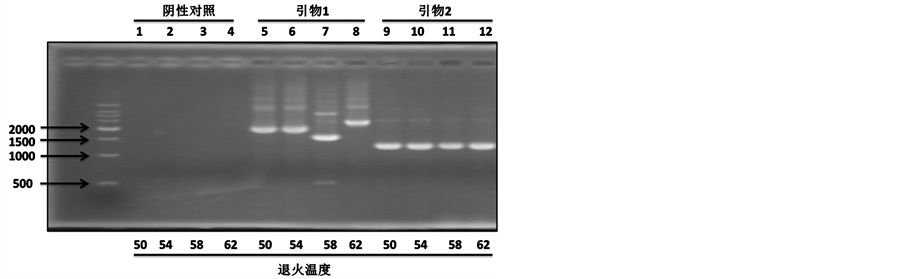
上面结果提示了血清中MFG-E8在肝癌中诊断意义。为了进一步研究MFG-E8在肝癌中作用,我们首先构建MFG-E8真核质粒。首先,我们设计特异性引物,进行PCR试验,在肝癌细胞株HepG2中钓取MFG-E8基因。结果显示,在不同的退火温度,引物2都可以有效地钓取MFG-E8基因,而引物1钓取其它基因片段(图3(a))。因此,我们选用引物2进行PCR钓取的MFG-E8基因进行酶切、连接到pcDNA3.1+载体上,最后送公司测序。为了研究MFG-E8在肝癌中作用,我们用构建成功的MFG-E8质粒转染肝癌细胞株HepG2,验证其表达水平。Real-time PCR和Western blot结果显示MFG-E8在肝癌细胞株HepG2成功表达(图3(b)和图3(c)),为下一步功能研究提供了基础。
MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2生长作用
肿瘤异常增殖是肿瘤恶性特征之一。为了研究MFG-E8在肝癌中作用,我们首先检测MFG-E8对肝癌增殖作用。转染MFG-E8后在不同时间点(24h、48h、72h)进行MTT实验。结果显示,MFG-E8对肝癌生长并没有影响(图4(a))。为了进一步确认MFG-E8对肝癌增殖作用,我们也进行了平板克隆形成实验。与MTT实验结果一致,平板克隆形成实验结果也表明MFG-E8对肝癌生长作用没有影响(图4(b))。
 (a)
(a)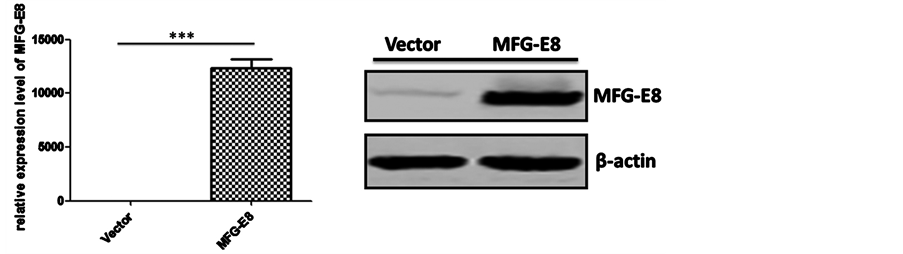 (b) (c)
(b) (c)
Figure 3. The construction of MFG-E8 eukaryotic expression vector and expression in HepG2. (a) MFG-E8 target segment fishing. Two pairs of primers and different annealing temperatures were used to obtain the target gene; (b) Real-time PCR was used to detect the transcription level of MFG-E8 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. *** < 0.0001; (c) Western blot detection of MFG-E8 protein in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2
图3. MFG-E8真核质粒构建及其在肝癌细胞株HepG2中表达。(a) MFG-E8目的片段钓取。用两对引物和不同退火温度来钓取目的基因;(b) Real-time PCR检测肝癌细胞株HepG2中MFG-E8转录水平。*** < 0.0001;(c) Western blot检测肝癌细胞株HepG2中MFG-E8蛋白水平
MFG-E8促进肝癌细胞株HepG2转移作用
肿瘤转移也是肿瘤恶性特征之一。接下来我们研究MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2转移作用。划痕实验表明MFG-E8促进肝癌细胞株HepG2转移(图5(a))。为了进一步确认MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2转移作用,我们也进行了Migration assay。结果同样表明MFG-E8促进肝癌细胞株HepG2转移(图5(b))。
 (a)Vector MFG-E8
(a)Vector MFG-E8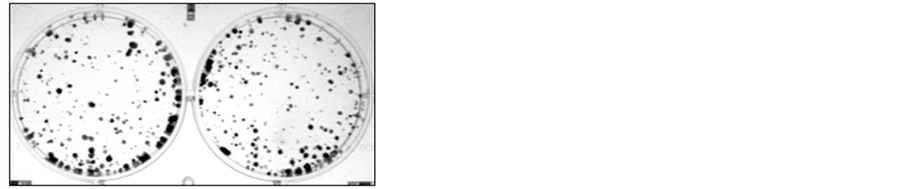 (b)
(b)
Figure 4. The role of MFG-E8 on growth of HepG2 cells. (a) MTT assay was used to detect the effect of MFG-E8 on the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2; (b) and the effect of MFG-E8 on the growth of hepatoma cell line HepG2
图4. MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2生长作用。(a) MTT法检测MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2生长作用;(b)平板克隆形成实验检测MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2生长作用
 (a)Vector MFG-E8
(a)Vector MFG-E8 (b)
(b)
Figure 5. The role of MFG-E8 on HepG2 cells metastasis. (a) The effect of MFG-E8 on the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 was detected by scratch test; (b) and Migration (assay) MFG-E8 was used to detect the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2
图5. MFG-E8促进肝癌细胞株HepG2转移作用。(a)划痕实验检测MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2转移作用;(b) Migration assay检测MFG-E8对肝癌细胞株HepG2转移作用
4. 讨论
肝癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤,其死亡率在恶性肿瘤中排名前列 [1] 。许多研究表明肝癌的早期诊断和治疗可明显改善患者预后和生存期 [2] 。迄今为止,还没有理想的检查手段来筛查早期肝癌。甲胎蛋白是诊断肝癌的重要指标之一,但是,其灵敏性和特异性低 [7] 。因此,寻找新的高灵敏性和特异性的血清标志物对肝癌诊断尤为重要。乳脂球表皮生长因子8 (milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor-factor 8,MFG-E8)是包裹着蛋白质和甘油三酯的脂肪球膜组成部分 [9] 。新生的MFG-E8蛋白N-末端含有信号肽序列,介导MFG-E8分泌到细胞外 [13] 。MFG-E8广泛存在于人体各个组织和器官中,涉及到许多生理功能,如调控受精卵结合、血管新生、凋亡细胞清除、免疫调控和促进炎症反应作用 [10] [11] [12] [13] 。研究表明MFG-E8可促进乳腺癌和黑色素瘤的发展 [17] 。最近研究表明MFG-E8促进卵巢癌和乳腺癌的增殖和转移 [19] 。但是,MFG-E8在肝癌病人血清中水平、其能否成为诊断肝癌的指标以及MFG-E8在肝癌中作用尚未清楚。在这篇文章中,我们研究发现肝癌病人血清MFG-E8表达增高,且ROC曲线表明血清MFG-E8对肝癌具有很好的诊断价值(AUC = 0.987;敏感性为93.3%;特异性为90%;cutoff值为11.95)。此外,我们构建MFG-E8过表达质粒并在肝癌细胞HepG2成功表达。功能实验表明MFG-E8促进肝癌的转移。
越来越多研究表明,肝癌的早期诊断和手术明显改善肝癌病人疾病状态和存活期。AFP是肝癌诊断的重要指标之一 [13] 。但是,在许多疾病中AFP水平也升高 [8] ,AFP在肝癌诊断中特异性仅为80% [7] [8] 。因此,寻找更加敏感性和特异性的诊断标志物尤为重要。我们发现肝癌病人血清MFG-E8水平明显升高,进一步的ROC曲线分析表明其具有良好的诊断价值,其特异性优于AFP,表明血清MFG-E8可能成为诊断肝癌指标之一。
为了研究MFG-E8对肝癌功能影响,我们首先构建MFG-E8过表达质粒,并且成功转染肝癌细胞HepG2,表达高水平的MFG-E8 (图3)。MTT实验和平板克隆形成实验都表明MFG-E8对肝癌增殖能力并没有影响,这和MFG-E8促进乳腺癌增殖结果不一致 [19] ,可能是因为MFG-E8在不同的肿瘤中其功能不一样。进一步的功能实验表明,MFG-E8具有促进肝癌转移作用,结果类似于MFG-E8促进乳腺癌转移 [19] ,证明MFG-E8促进肿瘤转移具有广泛性。但是,MFG-E8促进肝癌转移的信号通路及详细分子机制尚未清楚,是我们本论文的局限地方,还值得我们进一步研究。
总之,在这篇论文中,我们实验结果证明MFG-E8在肝癌病人血清中高表达,且对肝癌具有良好的诊断意义;进一步研究表明MFG-E8促进肝癌转移,而不影响肝癌的增殖能力。
文章引用
洪宏海,王征,李磊,林丽英,夏勇,刘美玲,苏宝昌. 肝癌血清中MFG-E8水平及其在肝癌转移作用研究
The Level of Serum MFG-E8 in Liver Cancer and Its Metastasis in Liver Cancer[J]. 世界肿瘤研究, 2017, 07(02): 40-47. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/WJCR.2017.72007
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Ferlay, J., Shin, H.-R., Bray, F., Forman, D., Mathers, C. and Parkin, D.M. (2010) Estimates of Worldwide Burden of Cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. International Journal of Cancer, 127, 2893-2917. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25516
- 2. Venook, A.P., Papandreou, C., Furuse, J. and Ladrón de Guevara, L. (2010) The Incidence and Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Global and Regional Perspective. Oncologist, 15, 5-13. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2010-S4-05
- 3. Forner, A., et al. (2009) [Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma]. Medicina Clínica, 132, 272-287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2008.11.024
- 4. Altekruse, S.F., McGlynn, K.A. and Reichman, M.E. (2009) Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence, Mortality, and Survival Trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27, 1485-1491. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7753
- 5. Llovet, J.M., et al. (1999) Natural History of Untreated Nonsurgical Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Rationale for the Design and Evaluation of Therapeutic Trials. Hepatology, 29, 62-67. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.510290145
- 6. El-Serag, H.B., et al. (2013) Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening Practices in the Department of Veterans Affairs: Findings from a National Facility Survey. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 58, 3117-3126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2794-7
- 7. Farinati, F., et al. (2006) Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Both or Neither? The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 101, 524-532. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00443.x
- 8. Lok, A.S., et al. (2010) Des-Gamma-Carboxy Prothrombin and Alpha-Fetoprotein as Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology, 138, 493-502. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.10.031
- 9. Oshima, K., Aoki, N., Kato, T., Kitajima, K. and Matsuda, T. (2002) Secretion of a Peripheral Membrane Protein, MFG-E8, as a Complex with Membrane Vesicles. The FEBS Journal, 269, 1209-1218. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02758.x
- 10. Aoki, N., et al. (1997) Stage Specific Expression of Milk Fat Globule Membrane Glycoproteins in Mouse Mammary Gland: Comparison of MFG-E8, Butyrophilin, and CD36 with a Major Milk Protein, Beta-Casein. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 1334, 182-190.
- 11. Ensslin, M.A. and Shur, B.D. (2003) Identification of Mouse Sperm SED1, a Bimotif EGF Repeat and Discoidin-Domain Protein Involved in Sperm-Egg Binding. Cell, 114, 405-417. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00643-3
- 12. Silvestre, J.S., Théry, C., Lévy, B., Tedgui, A., Amigorena, S. and Mallat, Z. (2005) Lactadherin Promotes VEGF- Dependent Neovascularization. Medecine Sciences (Paris), 21, 683-685. https://doi.org/10.1051/medsci/2005218-9683
- 13. Hanayama, R., Tanaka, M., Miwa, K., Shinohara, A., Iwamatsu, A. and Nagata, S. (2002) Identification of a Factor That Links Apoptotic Cells to Phagocytes. Nature, 417, 182-187. https://doi.org/10.1038/417182a
- 14. Aziz, M.M., et al. (2009) MFG-E8 Attenuates Intestinal Inflammation in Murine Experimental Colitis by Modulating Osteopontin-Dependent αvβ3 Integrin Signaling. The Journal of Immunology, 182, 7222-7232. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0803711
- 15. Huang, W., et al. (2017) Milk Fat Globule-EGF Factor 8 Suppresses the Aberrant Immune Response of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Derived Neutrophils and Associated Tissue Damage. Cell Death and Differentiation, 24, 263-275. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.115
- 16. Thery, C., et al. (1999) Molecular Characterization of Dendritic Cell-Derived Exosomes. Selective Accumulation of the Heat Shock Protein HSC73. The Journal of Cell Biology, 147, 599-610. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.147.3.599
- 17. Jinushi, M., et al. (2008) Milk Fat Globule EGF-8 Promotes Melanoma Progression through Coordinated Akt and Twist Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Research, 68, 8889-8898. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2147
- 18. Jinushi, M., et al. (2011) Tumor-Associated Macrophages Regulate Tumorigenicity and Anticancer Drug Responses of Cancer Stem/Initiating Cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108, 12425-12430. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1106645108
- 19. Tibaldi, L., et al. (2013) New Blocking Antibodies Impede Adhesion, Migration and Survival of Ovarian Cancer Cells, Highlighting MFGE8 as a Potential Therapeutic Target of Human Ovarian Carcinoma. PLoS ONE, 8, e72708. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072708
NOTES
*通讯作者。