International Journal of Fluid Dynamics
Vol.05 No.02(2017), Article ID:20925,7
pages
10.12677/IJFD.2017.52008
Parallel Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Karman Vortex in Pipe Flow with Baffle
Jianying Zhang1, Guangwu Yan2
1School of Basic Sciences, Changchun University of Technology, Changchun Jilin
2College of Mathematics, Jilin University, Changchun Jilin

Received: May 23rd, 2017; accepted: Jun. 9th, 2017; published: Jun. 12th, 2017

ABSTRACT
In this paper, the lattice Boltzmann method is used to simulate the Karman vortex in the two-di- mensional pipe with baffle. The parallel scheme is used to obtain the vorticity contours in the case of different Reynolds numbers at different time steps. The calculated results reproduce the existing numerical results rather well.
Keywords:Lattice Boltzmann Method, Parallel Computing, Two-Dimensional Baffle Flow, Karman Vortex Street
具有挡板的管流中Karman涡街的并行格子Boltzmann模拟
张建影1,闫广武2
1长春工业大学基础科学学院,吉林 长春
2吉林大学数学学院,吉林 长春
收稿日期:2017年5月23日;录用日期:2017年6月9日;发布日期:2017年6月12日

摘 要
本文应用格子Boltzmann方法对具有挡板二维管道中的Karman涡街进行了数值模拟,采用并行计算模式得到了在不同雷诺数不同时间步的情况下的涡线图,计算结果较好地再现了已有的数值结果。
关键词 :格子Boltzmann方法,并行计算,二维平板绕流,Karman涡街

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
上个世纪90年代出现的格子Boltzmann方法(LBM)已经成为模拟许多复杂流动问题的有效工具 [1] - [6] 。LBM已经广泛应用于多相流 [6] 、多组分流 [7] 、多孔介质流 [8] 、悬浮流 [9] 等复杂问题。此外LBM可以用于求解诸如Burgers方程,KdV方程,Schrödinger方程,Ginzburg-Landau方程等线性和非线性偏微分物理方程 [10] - [15] 。通常的模拟计算一般使用个人计算机,工作站就可以胜任,然而我们注意到那些流动区域较大,或者需要精细流动的计算问题,计算网格数量的要求已经超出计算机的能力。在本文中采用了一种简单的并行计算模式,用格子Boltzmann方法模拟具有挡板管道的Karman涡街问题 [16] [20] [21] ,给出了这一流动的详细计算结果。
2. 格子Boltzmann算法
在标准的二维网格空间中,粒子的速度离散取决于每一个节点与相邻节点相连的方式,当一个节点与周围 个节点相邻时,该点的速度将被离散为(
个节点相邻时,该点的速度将被离散为( )个速度,其中一个是静止的零速度。
)个速度,其中一个是静止的零速度。
本文中,我们应用D2Q9网格。在正方形网格中心的每一个结点处粒子有9个速度方向,速度大小共有三种,分别为: 、
、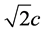 和0,速度为
和0,速度为 的粒子沿水平或者竖直方向运动,速度为
的粒子沿水平或者竖直方向运动,速度为 的粒子沿对角线方向运动,速度为0的是静止粒子。粒子速度为:
的粒子沿对角线方向运动,速度为0的是静止粒子。粒子速度为:
 (1)
(1)
函数 是时刻为
是时刻为 ,位置为
,位置为 处,方向为
处,方向为 的粒子的分布函数,
的粒子的分布函数,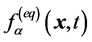 为系统达到平衡时的分布函数。流场的宏观物理量:格点处粒子的密度
为系统达到平衡时的分布函数。流场的宏观物理量:格点处粒子的密度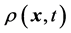 ,粒子的速度
,粒子的速度 。宏观物理量定义为:
。宏观物理量定义为:
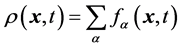 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
我们要求系统达到平衡态时,平衡态分布函数 与非平衡态分布函数
与非平衡态分布函数 有如下关系:
有如下关系:
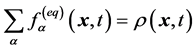 (4)
(4)
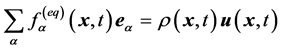 (5)
(5)
平衡态分布函数的公式为 [2] :
 (6)
(6)
其中 称为权重,
称为权重, 为声速,这里取声速
为声速,这里取声速 。
。
格子Boltzmann方程为:
 (7)
(7)
式中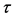 为松弛因子,取值范围为
为松弛因子,取值范围为 ,与粘性系数
,与粘性系数 满足关系式 [17] :
满足关系式 [17] :
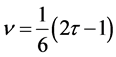 (8)
(8)
3. 具有挡板管道的并行格子Boltzmann模拟
首先我们用格子铺满整个流场(二维直管道),取水平方向为X轴,竖直方向为Y轴。格子X方向m = 512, Y方向n = 128。为了采用Message Passing Interface (MPI)并行技术,我们将计算区域分解成若干子块,每子块X方向m = 128, Y方向n = 128,一共4块。在计算中,这些子块同时计算,每块数据需要调用5部分,分别为左右两列以及该块的内部区域 [18] 。子块如图1所示。
以第一块 为例,需要调用数据为,列
为例,需要调用数据为,列 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,和块
,和块 。时刻
。时刻 完成数据
完成数据 的计算。之所以采用双边界
的计算。之所以采用双边界 ,
, 是由于子块对接要求,就是说在计算第一子块时,
是由于子块对接要求,就是说在计算第一子块时, 是边界,但是在计算第二子块
是边界,但是在计算第二子块 时
时 为内部,此时边界为
为内部,此时边界为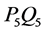 。
。
入口采用均匀速度 ,壁面处采用半步长完全反射的边界条件,出口采用Neumann边界条
,壁面处采用半步长完全反射的边界条件,出口采用Neumann边界条
件 ,密度
,密度 ,时间步长为
,时间步长为 ,驰豫时间
,驰豫时间 由给定雷诺数Re与粘性
由给定雷诺数Re与粘性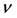 和驰豫时间的关
和驰豫时间的关
系确定 [17] [21] 。长度为36个网格的挡板放置 上,即从位置(128, 46)到(128, 82)。
上,即从位置(128, 46)到(128, 82)。
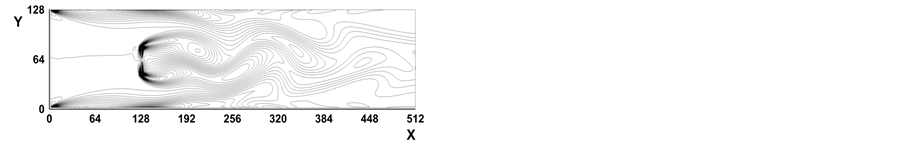
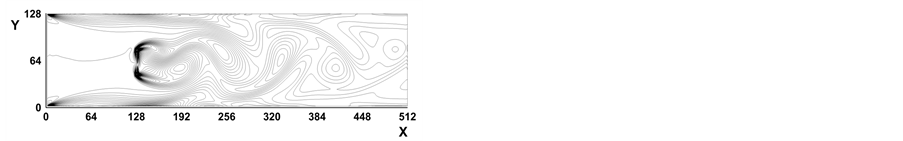
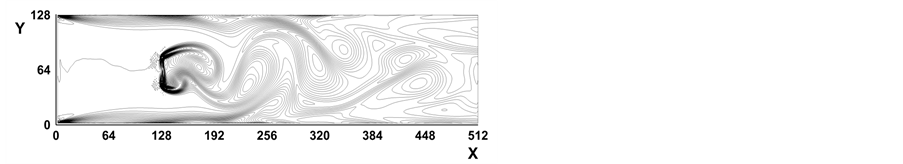
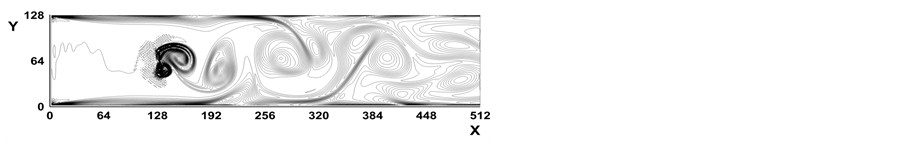
图2所示是Re = 256时,时间步分别为(a) t = 4000, (b) t = 6000, (c) t = 8000, (d) t = 10,000时涡线图。图3为Re = 512时,时间步分别为(a) t = 4000, (b) t = 6000, (c) t = 8000, (d) t = 10,000时涡线图。图4所示是Re = 1024时,时间步分别为(a) t = 4000, (b) t = 6000, (c) t = 8000, (d) t = 10,000时涡线图。从图2~图4看出,当雷诺数进一步增大,随着时间步的增大,挡板绕流已经趋于不定常流动,挡板后面出现一系列的涡旋,即Karman涡街(Karman vortex street)。这些结果再现了已有的数值结果 [16] [19] [21] 。
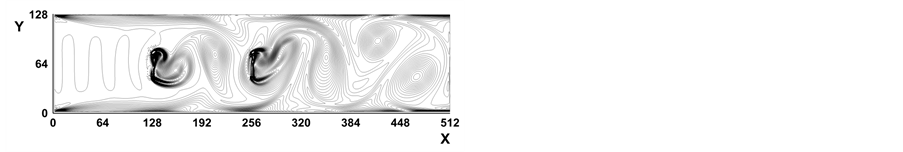
我们还模拟了两个挡板的情况,设两个挡板距离为128个网格距离。图5是Re = 256时,时间分别为(a) t = 4000, (b) t = 6000, (c) t = 8000, (d) t = 10,000涡线图,图6是Re = 512时,时间分别为(a) t = 4000, (b) t = 6000, (c) t = 8000, (d) t = 10,000涡线图,图7是Re = 1024时,时间分别为(a) t = 4000, (b) t = 6000, (c)
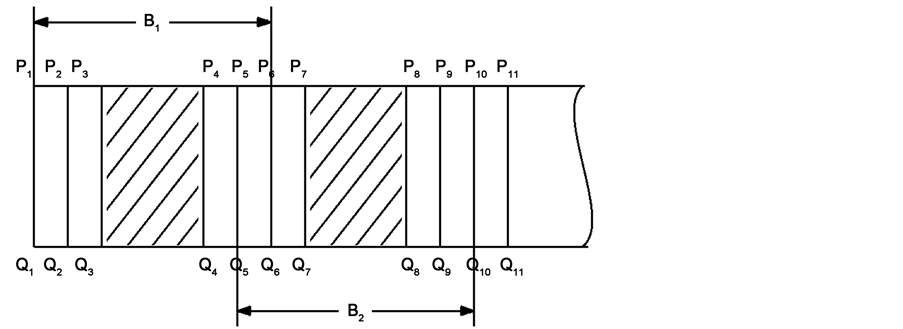
Figure 1. Sub-block division of the calculation area of two-dimensional straight pipe
图1. 二维直管道计算区域子块划分
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 2. Vorticity contours at Re = 256
图2. Re = 256时涡量等值线
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 3. Vorticity contours at Re = 512
图3. Re = 512时涡量等值线
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 4. Vorticity contours at Re = 1024
图4. Re = 1024时涡量等值线

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 5. Vorticity contours at Re = 256 with 2 baffles
图5. 两个挡板,Re = 256时的涡量等值线

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
Figure 6. Vorticity contours at Re = 512 with 2 baffles
图6. 两个挡板,Re = 512时的涡量等值线

 (a) (b)
(a) (b)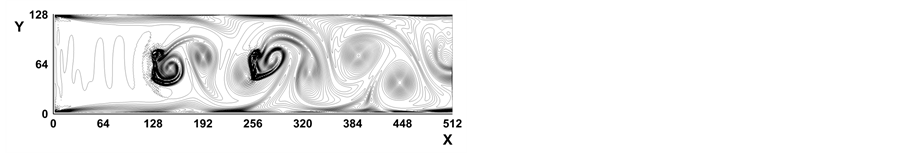
 (c) (d)
(c) (d)
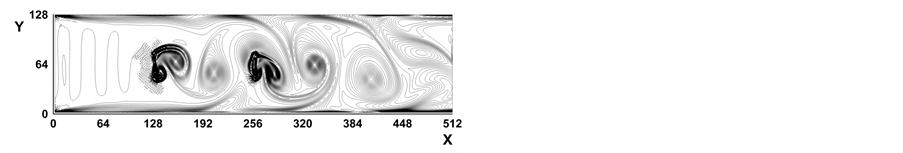
Figure 7. Vorticity contours at Re = 1024 with 2 baffles
图7. 两个挡板,Re = 1024时的涡量等值线
t = 8000, (d) t = 10,000涡线图。可以看出当Re数比较大时将在挡板之间出现Karman涡街。这个结果再现了文献 [21] 中的数值结果。我们发现随着Re数的增大,在流动区域内将出现更多的涡旋,使得涡旋变得拥挤,究其原因是因为流动发生在管内所致。
利用现有的个人计算机,通过使用本文提出的并行计算模式可以增加计算网格数量,从而进一步得到大尺度流场详细的流动细节。
4. 结论
综上,本文应用格子Boltzmann模型模拟了二维平板绕流,给出不同雷诺数下不同时间的涡线图。通过这些图我们可以看出在一定的雷诺数范围内挡板后会形成一系列涡即卡门涡街。而且在同时存在两个挡板的情况下,只要达到适当的Re数就依然会形成Karman涡街。这些结果很好地再现了经典的数值和实验结果。应用LBM对上述不同Re数的数值模拟均得到了较好的结果,显示了此方法的有效性。依然有很多问题需要注意,例如精细的三维流动的模拟是需要完成的,有效地利用MPI平台和分块并行算法是可以得到相当一部分值得期待的结果的,当然我们更期待于计算机速度的提高和算法的改进。
致 谢
国家自然科学基金(No. 11602033, No. 11272133)资助。
文章引用
张建影,闫广武. 具有挡板的管流中Karman涡街的并行格子Boltzmann模拟
Parallel Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Karman Vortex in Pipe Flow with Baffle[J]. 流体动力学, 2017, 05(02): 69-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/IJFD.2017.52008
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Chen, S.Y. and Doolen, G.D. (1998) Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Flows. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 30, 329-364. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fluid.30.1.329
- 2. Qian, Y.H., d’Humieres, D. and Lallemand, P. (1992) Lattice BGK Model for Navier-Stokes Equations. Europhysics Letters, 17, 479-484. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/17/6/001
- 3. Chen, H.D., Chen, S.Y. and Matthaeus, M.H. (1992) Recovery of the Navier-Stokes Equations Using a Lattice Boltz- mann Gas Method. Physical Review A, 45, 5339-5342. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.45.R5339
- 4. Benzi, R., Succi, S. and Vergassola, M. (1992) The Lattice Boltzmann Equations: Theory and Applications. Physics Reports, 222, 147-197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0370-1573(92)90090-M
- 5. Shim, J.W. (2017) Parametric Lattice Boltzmann Method. Journal of Computational Physics, 338, 240-251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2017.02.057
- 6. Shan, X.W. and Chen, H.D. (1994) Simulation of Non-Ideal Gases Liquid Gas Phase Transitions by the Lattice Boltz- mann Equation. Physical Review E, 49, 2941. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.49.2941
- 7. Filippova, O. and Hanel, D. (1997) Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Gas Particle Flow in Filters. Computer & Fluids, 26, 697-712. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7930(97)00009-1
- 8. Succi, S., Foti, E. and Higuera, F.J. (1989) 3-Dimensional Flows in Complex Geometries with the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Europhysics Letters, 10, 433. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/10/5/008
- 9. Ladd, A. (1994) Numerical Simulations of Particle Suspensions via a Discretized Boltzmann Equation. Part 2. Numerical Results. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 271, 311. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112094001783
- 10. Zhang, J.Y. and Yan, G.W. (2008) Lattice Boltzmann Methods for One and Two-Dimensional Burger’s Equation. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 387, 4771-4786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2008.04.002
- 11. Yan, G.W. and Zhang, J.Y. (2009) A Higher-Order Moment Method of the Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Korteweg-Devries Equation. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 79, 1554-1565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2008.07.006
- 12. Palpacelli, S. and Succi, S. (2007) Numerical Validation of the Quantum Lattice Boltzmann Scheme in Two and Three Dimension. Physical Review E, 75, Article ID: 066704. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.75.066704
- 13. Zhang, J.Y. and Yan, G.W. (2015) Spatiotemporal Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Three-Dimensional Cubic-Quintic Complex Ginzburg-Landau Equation. Physica A, 440, 19-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2015.08.004
- 14. An, B. and Bergadà, J.M. (2017) A 8-Neighbor Model Lattice Boltzmann Method Applied to Mathematical-Physical Equations. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 42, 363-381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2016.10.016
- 15. Hu, W.Q., Gao, Y.T., Lan, Z.Z., et al. (2017) Lattice Boltzmann Model for a Generalized Gardner Equation with Time-Dependent Variable Coefficients. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 46, 126-140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.01.061
- 16. Taneda, S. and Honi, H., (1971) Unsteady Flow past a Flat Plate Normal to the Direction of Motion. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 30, 262-272. https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.30.262
- 17. 闫广武. 二维剪切流的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2003, 9(5): 521-525.
- 18. 闫广武. 二维直角弯道粘性流动的格子气体仿真[D]: [硕士学位论文]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1988.
- 19. 胡守信. 直管道中绕平板平面流动的格子气仿真[J]. 计算物理, 1989, 6(4): 457-464.
- 20. Lee, J.S., Shin, J.H. and Lee, S.H. (2012) Fluid-Structure Interaction of a Flapping Flexible Plate in Quiescent Fluid. Computers & Fluids, 57, 124-137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2011.12.015
- 21. 孙福振. 用格子Boltzmann方法研究平板绕流[D]: [硕士学位论文]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2007.