Pure Mathematics
Vol.06 No.06(2016), Article ID:19037,6
pages
10.12677/PM.2016.66066
Nonexistence of Positive Nonconstant Stationary Solutions for Generalized Gray-Scott Model
Ling Yang, Ying Li
School of Science, Dalian Minzu University, Dalian Liaoning

Received: Nov. 3rd, 2016; accepted: Nov. 18th, 2016; published: Nov. 25th, 2016
Copyright © 2016 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



ABSTRACT
In his paper, some sufficient conditions for nonexistence of positive nonconstant stationary solutions for generalized Gray-Scott model are given.
Keywords:Generalized Gray-Scott Model, Stationary Solution, Nonexistence

广义Gray-Scott模型非常值正稳态解的不存在性
杨 玲,李 莹
大连民族大学理学院,辽宁 大连

收稿日期:2016年11月3日;录用日期:2016年11月18日;发布日期:2016年11月25日

摘 要
本文给出了广义Gray-Scott模型不存在非常值正稳态解的若干充分条件。
关键词 :广义Gray-Scott模型,稳态解,不存在性

1. 引言
广义Gray-Scott模型的化学反应机制如下 [1] :

其中 ,
, 和
和 是正常数。对于一维情形,反应物
是正常数。对于一维情形,反应物 和
和 的浓度
的浓度 ,
, 满足如下反应扩散方程:
满足如下反应扩散方程:

其中 和
和 是化学反应物
是化学反应物 和
和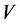 的扩散系数。当
的扩散系数。当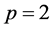 时,通常称上述模型为Gray-Scott模型 [2] [3] 。通过变换,其相应的高维广义Gray-Scott模型为:
时,通常称上述模型为Gray-Scott模型 [2] [3] 。通过变换,其相应的高维广义Gray-Scott模型为:
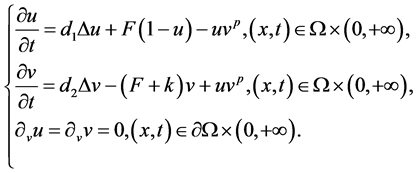 (1.1)
(1.1)
此处, 是Laplace算子;
是Laplace算子; 为
为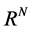 中的有界区域,且其边界充分光滑;
中的有界区域,且其边界充分光滑; 是
是 上的单位外法向量
上的单位外法向量 ;
; 是正常数。上述模型的正稳态解满足下面的椭圆型方程组:
是正常数。上述模型的正稳态解满足下面的椭圆型方程组:

称 是(1.1)的一个正解,如果,
是(1.1)的一个正解,如果,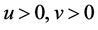 ,且其满足(1.1)。
,且其满足(1.1)。
目前,关于广义Gray-Scott模型的研究主要集中在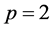 的情形 [4] - [9] ,对于
的情形 [4] - [9] ,对于 的情形的研究很少,文献 [1] 也仅仅讨论了一维情形。对其它类似模型如Sel’kov模型、 Brusselator模型、Schnakenberg模型等的研究参见 [10] [11] [12] [13] 。
的情形的研究很少,文献 [1] 也仅仅讨论了一维情形。对其它类似模型如Sel’kov模型、 Brusselator模型、Schnakenberg模型等的研究参见 [10] [11] [12] [13] 。
本文研究问题(1.1)非常值正解的不存在性。主要结果如下:
引理1.1:设 ,如果下列条件之一成立:
,如果下列条件之一成立:
(i) ,
,
(ii) 且
且 ,则问题(1.1)不存在非常值正解。
,则问题(1.1)不存在非常值正解。
定理1.2:设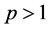 ,如果下列条件之一成立:
,如果下列条件之一成立:
(i) 且
且 ,
,
(ii) 且
且 ,
,
则问题(1.1)不存在非常值正解。
在第二节给出定理1.1的证明;在第三节,给出定理1.2的证明。
2. 定理1.1的证明
引理2.1:设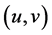 为问题(1.1)的一个正解,则
为问题(1.1)的一个正解,则
 ,
,  ,
,
其中, 。
。
证明:设 ,
, 。依文献 [14] 中命题2.2,得
。依文献 [14] 中命题2.2,得
 ,
,
由此得到第一个结论。
令
 ,
,
得
 .
.
令 ,依文献 [14] 中命题2.2,得
,依文献 [14] 中命题2.2,得
 ,
,
即
 ,
,
进而
 .
.
这表明,第二个结论成立,这样,引理2.1得证。
定理1.1的证明:对任意 ,记
,记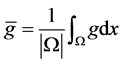 。假设
。假设 是(1.1)的正解。用
是(1.1)的正解。用 乘以(1.1)中的第一个方程两边,然后在
乘以(1.1)中的第一个方程两边,然后在 上积分,得
上积分,得
 (2.1)
(2.1)
由中值定理知:对任意 ,存在介于
,存在介于 之间的
之间的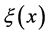 ,使得
,使得 ,由于
,由于 ,所以
,所以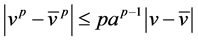 。注意到:
。注意到: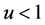 ,得
,得
 。
。
同理,用 乘以(1.1)中的第二个方程两边,然后在
乘以(1.1)中的第二个方程两边,然后在 上积分,得
上积分,得
 .
.
由Poincaré不等式
 ,
,
得
 .
.
利用Young不等式,得

进而
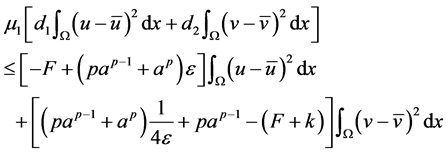 .
.
取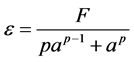 得
得
 ,
,
所以当 时,有
时,有 ,这证明了第一个结论。类似地,可得到第二个结论。这样,定理1.1得证。
,这证明了第一个结论。类似地,可得到第二个结论。这样,定理1.1得证。
3. 定理1.2的证明
引理3.1:设 是(1.1)的一个正解,则
是(1.1)的一个正解,则 满足如下积分恒等式
满足如下积分恒等式
 (3.1)
(3.1)
其中 ,
, ,
, ,
, 。
。
证明:将模型(1.1)的两个方程在 上积分,得
上积分,得
 (3.2)
(3.2)
令
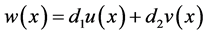 ,
,
得

在上式两边乘以 ,在
,在 上积分,并注意到:
上积分,并注意到: ,得
,得

由此得

另一方面
 (3.3)
(3.3)
在(3.2)的两边乘以 ,然后在
,然后在 上积分,得
上积分,得
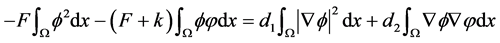 (3.4)
(3.4)
联合(3.3)和(3.4),引理3.1得证。
定理1.2证明 由引理3.1的证明可知 ,再根据引理3.1知:如果
,再根据引理3.1知:如果 ,则有
,则有

由Poincaré不等式
 (3.5)
(3.5)
接下来在(1.1)中的第一个方程两边同乘以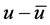 ,在
,在 上积分,得
上积分,得
 (3.6)
(3.6)
由中值定理知, 介于
介于 之间,使得
之间,使得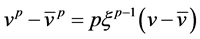 ,因为
,因为 ,所以
,所以 。又因为
。又因为 ,
, ,
, ,所以由(3.6)得
,所以由(3.6)得
 (3.7)
(3.7)
取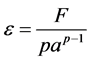 ,于是由(3.7)可化为
,于是由(3.7)可化为

由于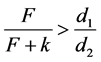 再结合(3.7)和(3.5),则
再结合(3.7)和(3.5),则 。
。
于是,得
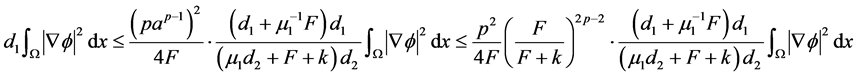
所以,当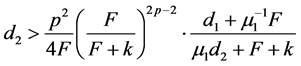 时,
时, 。
。
类似地可得到第二个结论。这样,定理1.2得证。
基金项目
辽宁省大学生创新创业项目(编号:S201512026049)。
文章引用
杨 玲,李 莹. 广义Gray-Scott模型非常值正稳态解的不存在性
Nonexistence of Positive Nonconstant Stationary Solutions for Generalized Gray-Scott Model[J]. 理论数学, 2016, 06(06): 480-485. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/PM.2016.66066
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Hale, J., Peletier, L.A. and Troy, W.C. (2000) Exact Homoclinic and Heteroclinic Solutions of the Gray-Scott Model for Autocalysis. SIAM Journalon Applied Mathematics, 61,102-130. https:/doi.org/10.1137/S0036139998334913
- 2. Gray, P. and Scott, S.K. (1983) Autocatalytic Reactions in the Isothermal Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor: Isolas and Other Forms of Multistability. Chemical Engineering Science, 38, 29-43. https:/doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(83)80132-8
- 3. Gray, P. and Scott, S.K. (1984) Autocatalytic Reaction in the CSTR: Oscillations and Instabilities in the System . Chemical Engineering Science, 39, 1087-1097. https:/doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(84)87017-7
- 4. Ai, S.B. (2004) Homoclinic Solutions to the Gray-Scott Model. Applied Mathematics Letters, 17, 1357-1361. https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.am1.2004.02.004
- 5. Kolokolnikova, T., Warda, M.J. and Wei, J.C. (2005) The Existence and Stability of Spike Equilibria in the One-Di- mensional Gray-Scott Model on a Finite Domain. Applied Mathematics Letters, 18, 951-956. https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2004.06.024
- 6. Muratov, C.B. and Osipov, V.V.(2000)Static Spike Autosolutions in the Gray-Scott Model. Journal of Physics A-Mathematical and General, 33, 8893-8916. https:/doi.org/10.1088/0305-4470/33/48/321
- 7. Mcgough, J.S. and Kiley, K. (2004) Pattern Formation in the Gray-Scott Model. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 5, 105-121. https:/doi.org/10.1016/S1468-1218(03)00020-8
- 8. Peng, R. and Wang, M.X. (2007) On Pattern Formation in the Gray-Scott Model. Science in China Series A: Mathematics, 50, 377-386. https:/doi.org/10.1007/s11425-007-0001-z
- 9. Peng, R. and Wang, M.X. (2009) Some Nonexistence Results for Nonconstant Stationary Solutions to the Gray-Scott Model in a Bounded Domain. Applied Mathematics Letters, 22,569-573. https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2008.06.032
- 10. Wang, M.X. (2003) Non-Constant Positive Steady States of the Sel’kov Model. Journal of Differential Equations, 190, 600-620. https:/doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0396(02)00100-6
- 11. Peng, R. (2007) Qualitative Analysis of Steady States to the Sel’kov Model. Journal of Differential Equations, 241, 386-398. https:/doi.org/10.1016/j.jde.2007.06.005
- 12. Ghergu, M. (2008) Non-Constant Steady-State Solutions for Brusselator Type Systems. Nonlinearity, 21, 2331-2345. https:/doi.org/10.1088/0951-7715/21/10/007
- 13. Schnakenberg, J. (1979) Simple Chemical Reaction Systems with Limit Cycle Behavior. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 81, 389-400. https:/doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(79)90042-0
- 14. Lou, Y. and Ni, W.M. (1996) Diffusion, Self-Diffusion and Cross-Diffusion. Journal of Differential Equations, 131, 79-131. https:/doi.org/10.1006/jdeq.1996.0157