Advances in Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.03(2017), Article ID:20674,8
pages
10.12677/AAM.2017.63031
Stability for Discrete Complex Networks with Switching and Delayed Coupling
Yaru Zhao, Honghua Bin
School of Science, Jimei University, Xiamen Fujian

Received: May 4th, 2017; accepted: May 19th, 2017; published: May 25th, 2017

ABSTRACT
This paper studies the stability for discrete complex networks with switching and delayed coupling. Based on Lyapunov stability theory, the sufficient conditions are derived by using LMI method for the asymptotic stability under arbitrary switching strategy. Moreover, this paper develops the convex combination conditions for asymptotic stability of the networks and gives the way to choose switching strategy. That is to say, for the arbitrary switching rule, the system (1) can achieve the asymptotic stability when it satisfies the linear matrix inequality (3). The simulation result proves the validity of the designed switching strategy.
Keywords:Switching Systems, Delayed Coupling, LMI, Stability
具有耦合时滞和切换的离散复杂网络稳定性
赵亚茹,宾红华
集美大学理学院,福建 厦门
收稿日期:2017年5月4日;录用日期:2017年5月19日;发布日期:2017年5月25日

摘 要
文章研究具有耦合时滞和切换的离散复杂网络稳定性。在任意切换信号作用下,利用Lyapunov稳定性理论,推导出以线性矩阵不等式表示的网络渐近稳定的充分性条件,给出了网络渐近稳定的凸组合条件。即当系统(1)满足线性矩阵不等式(3)时,对于任意的切换,网络可达到渐近稳定。仿真实例证明了所设计方案的有效性。
关键词 :切换系统,耦合时滞,线性矩阵不等式,稳定性

Copyright © 2017 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


1. 引言
复杂网络常常用来描述复杂系统,其中节点表示个体,链接用来表示个体之间的相互作用。例如,社交网络、生物网络、互联网、食物链网等等。稳定性是复杂网络动力学行为中最重要的性质之一,也是一个网络能够良好运行的基础.通过对复杂网络的稳定性研究,一方面,我们可以将复杂网络稳定性研究的成果应用到实际中去,可设计出更好性质的网络或使网络处于更有利的状态。
时滞现象时常存在与现实网络中,例如长距离的传送以及网络障碍都会导致网络延迟现象的发生,这些扰动是不能忽略的。因此具有时滞的复杂网络模型则精确的描述了现实网络中出现时滞的现象。文献 [1] 研究了时滞复杂网络的全局渐近稳定性。文献 [2] 研究了含有分布时滞的随机Cohen-Grossberg网络的稳定性。文献 [3] 研究了含有时变延迟的随机的复杂网络的指数型稳定。文献 [4] [5] [6] 研究了几类典型的含有时滞项的复杂网络的稳定性。
在以上的参考文献当中,显然具有时滞的复杂网络的稳定性问题已经受到了学者的广泛关注,而且也有很多显著的成果。另一方面,为了更好的描述大规模的现实网络系统,文献 [7] [8] [9] [10] 分别研究了具有时滞和无时滞的离散复杂网络模型。文献 [10] 研究了具有时滞耦合和非时滞耦合的复杂动态网络的稳定性。
切换系统的应用背景十分广泛,因为现实中很多系统往往会表现出各种各样的模态特性,这些特性通常会发生切换,尤其是在大型的供电系统、现代高速交通系统、飞行器以及空中交通系统等。但是,目前很少有文献去考虑同时具有耦合时滞和切换的离散复杂网络的稳定性问题。在研究此类复杂网络的稳定性问题时,通常会将网络的稳定性问题转换为切换系统的稳定性问题。研究这类问题获得的结果不仅可以包含不含切换的复杂网络(即只有一个子系统的情况),而且也可以看作是在具有耦合时滞的复杂网络上的一个推广。在研究具有切换的复杂网络中,通常会找到一个切换信号,使得原本不稳定的系统在切换信号的作用下趋于稳定。在此方面,也有了一些成果。文献 [11] 利用平均驻留时间的方法研究了切换复杂网络的稳定性。文献 [12] 研究了异步切换下不确定耦合切换复杂网络的同步。文献 [13] [14] [15] 研究了离散切换复杂网络的稳定性。
但在以上文献中,并没有将所有情况都考虑进去,尚未完善。例如在文献 [10] 中,模型仅仅考虑了具有时滞耦合和非时滞耦合的离散复杂网路,并没有将经常出现的切换现象考虑进去,而本文则主要受到文献 [10] 的启发,将切换现象考虑进去,主要研究了具有耦合时滞和切换的离散复杂网络的稳定性,利用李雅普诺夫稳定性理论,得到了网络渐近稳定的充分条件。
2. 模型描述和相关知识
考虑如下具有耦合时滞和切换的离散复杂网络模型:
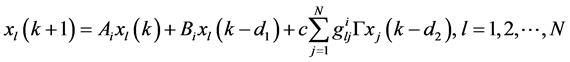
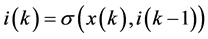 (1)
(1)
其中 表示
表示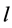 在
在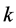 时刻的状态,常数
时刻的状态,常数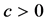 是网络的耦合强度,
是网络的耦合强度,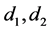 是正整数,表示网络的时滞项;
是正整数,表示网络的时滞项;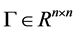 为内部耦合矩阵,
为内部耦合矩阵, 为外部耦合矩阵。
为外部耦合矩阵。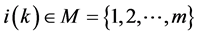 ,表示系统的第
,表示系统的第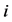 个子系统,
个子系统,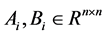 为第
为第 个子系统对应的常数矩阵;
个子系统对应的常数矩阵; 表示切换方案。当
表示切换方案。当 时,表示
时,表示 时刻第
时刻第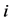 个子系统正在运行。
个子系统正在运行。
定义1 [16] Kronecker算法描述如下:
设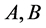 为两个矩阵,且
为两个矩阵,且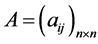 ,则有
,则有
 .
.
3. 主要结果
令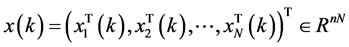 ,运用Kronecker算法,模型(1)可以写成如下形式:
,运用Kronecker算法,模型(1)可以写成如下形式:
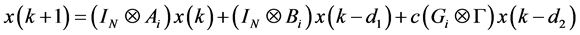 (2)
(2)
这里 为单位矩阵。
为单位矩阵。
为简化表述,首先对后文用到的一些符号进行简要说明。
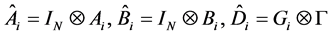
定理1 对于系统(2),若存在正定对称矩阵 满足下述不等式:
满足下述不等式:
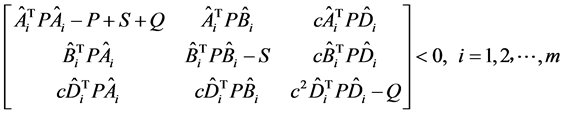 (3)
(3)
则对于任意的切换策略,都可确保系统渐近稳定。
证明若存在对称正定矩阵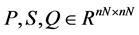 满足矩阵不等式(3),构造一个Lyapunov函数
满足矩阵不等式(3),构造一个Lyapunov函数 :
:

根据已知条件,显然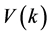 是正定的,且其前向差分为:
是正定的,且其前向差分为:

整理得
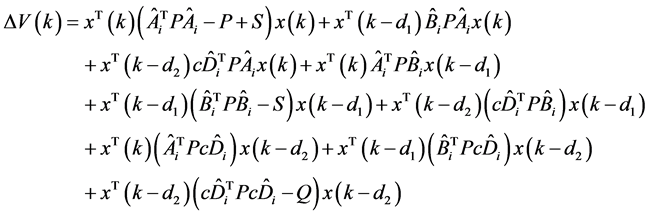
将其化成向量的形式有
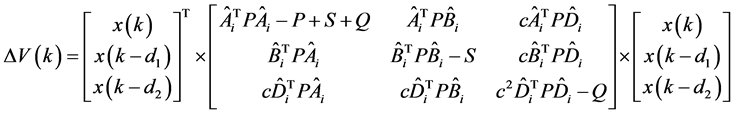
所以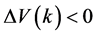 的一个充分条件是:
的一个充分条件是:

由于矩阵不等式(3)对所有 都成立,因此无论切换方案如何选取,都有
都成立,因此无论切换方案如何选取,都有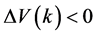 。由Lyapunov稳定性理论,系统(2)是渐近稳定的。
。由Lyapunov稳定性理论,系统(2)是渐近稳定的。
定理2 对于系统(2),若存在 ,对称正定矩阵
,对称正定矩阵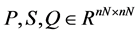 满足下述条件:
满足下述条件:
1) 
2) 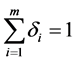
3) 
则存在切换方案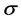 可保证系统渐近稳定。
可保证系统渐近稳定。
证明 取

则 的前向差分为:
的前向差分为:
 .
.
采用反证法,假设存在某个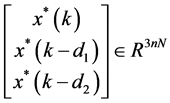 满足
满足
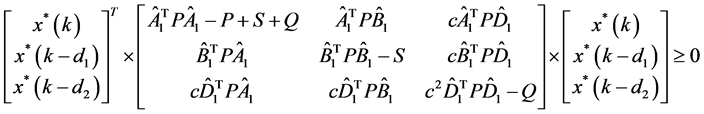

以上所有不等式,则以 为加权系数对各不等式求得加权和,
为加权系数对各不等式求得加权和,
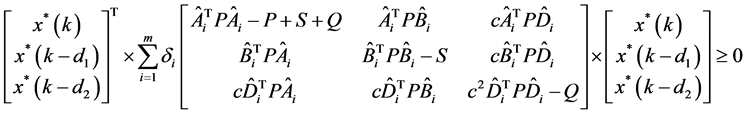
显然与已知条件矛盾,即不存在一个 满足以上所有不等式,也就是对于任意的
满足以上所有不等式,也就是对于任意的 ,总存在一个
,总存在一个 使得
使得

因此(2)渐近稳定。
切换方案 可以如下选取:
可以如下选取:

本文与文献 [10] 相比较,都是运用LMI和李雅普诺夫的稳定性理论,得到文章所需要的充分条件,但文献 [10] 研究了具有时滞耦合和非时滞耦合的离散动态网络同步条件,而本文则在文献 [10] 的基础上研究含有切换拓扑的离散复杂网络稳定性问题,因此文章所研究的模型当中,模型将现实网络中所出现的时滞现象和切换现象都考虑了进去,并且给出了具体的切换规则,与此文献相比本文模型更具一般性和实际意义。
4. 数值模拟
对模型(2)进行仿真。令 为2阶单位矩阵,
为2阶单位矩阵,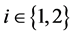 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,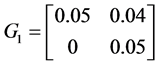 ,
, ,
,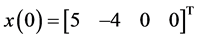 。根据定理(2),由MATLAB65中的LMI工具箱可求得P,S。仿真结果如下图所示:
。根据定理(2),由MATLAB65中的LMI工具箱可求得P,S。仿真结果如下图所示:
图1,图2分别为两个不稳定子系统的状态曲线,图3为两个不稳定子系统在切换信号下的状态曲线,图4为系统的切换规则.可以看出,由两个不稳定的子系统组成的切换系统在切换规则的作用下逐渐趋于稳定。
5. 结论
针对具有耦合时滞和切换的离散复杂网络的稳定问题,本文利用Lyapunov稳定性理论,给出了网络渐近稳定的充分性条件,以及如何选取切换规则的方法。由数值模拟可知,当子系统都不稳定的时候,在满足一定的条件下,对于任意的切换可使系统达到稳定。

Figure 1. The state curves of the subsystem (1)
图1. 子系统(1)的仿真

Figure 2. The state curves of the subsystem (2)
图2. 子系统(2)的仿真
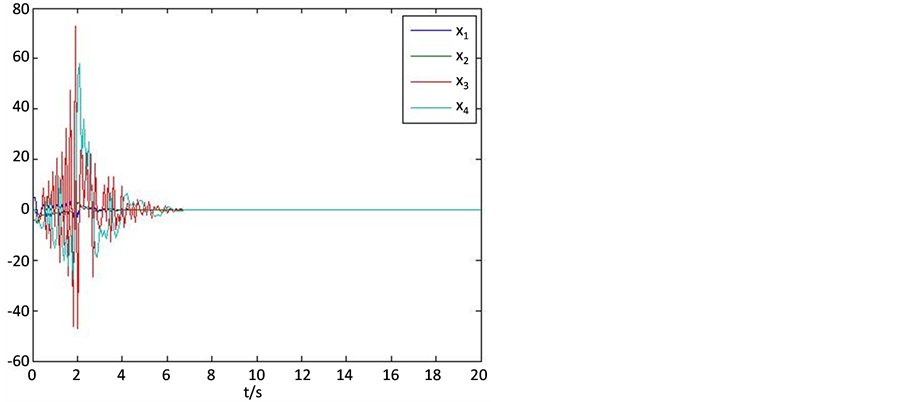
Figure 3. The state curves of switched systems
图3. 切换系统的状态曲线
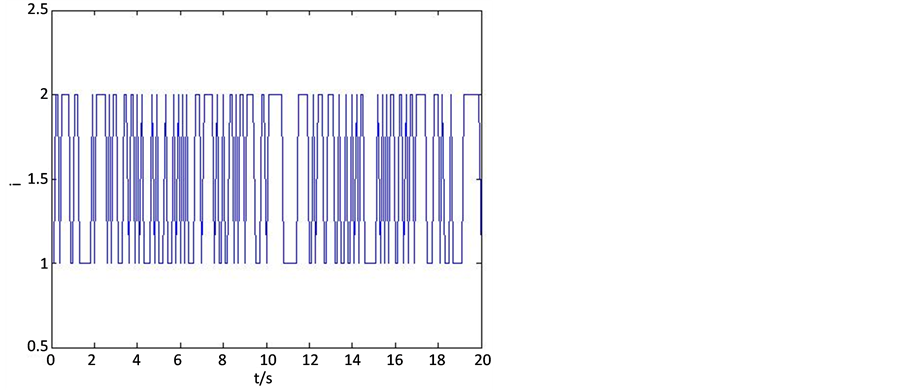
Figure 4. The switching signal of the system
图4. 系统的切换规则
致 谢
首先,我向我的导师宾红华表达我最真挚的谢意,感谢我的老师对我的论文细致又严谨的指导。
其次,我向我的同门表示感谢,感谢他们跟我一起讨论,帮助我解决了很多疑问。
基金项目
福建省自然科学基金会(2012J06001);国家自然科学基金(11361010)。
文章引用
赵亚茹,宾红华. 具有耦合时滞和切换的离散复杂网络稳定性
Stability for Discrete Complex Networks with Switching and Delayed Coupling[J]. 应用数学进展, 2017, 06(03): 259-266. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/AAM.2017.63031
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Arik, S. and Tavsanoglu, V. (2001) On the Global Asymptotic Stability of Delay Cellular Neural Network. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Application, 47, 571-574. https://doi.org/10.1109/81.841859
- 2. Huang, C. and Cao, J. (2011) Convergence Dynamics of Stochastic Cohen-Grossberg Neural Networks with Unbounded Distributed Delays. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 22, 561-572. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2011.2109012
- 3. Huang, C., He, Y. and Wang, H. (2008) Mean Square Exponential Stability of Stochastic Recurrent Neural Networks with Time-Varing Delays. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 56, 1773-1778.
- 4. Huang, L., Huang, C. and Liu, B. (2005) Dynamics of a Class of Celluar Neural Networks with Time-Varying Delays. Physics Letters A, 345, 330-334.
- 5. Liu, B., Lu, W. and Chen, T. (2015) New Criterion of Asymptotic Stability for Delay Systems with Time-Varying Structures and Delays. Neural Networks, 54, 103-111.
- 6. Hu, J. and Wang, J. (2015) Global Exponential Periodicity and Stability of Discrete-Time Complex-Valued Recurrent Neural Networks with Time Delays. Neural Networks, 66, 119-130.
- 7. Park, M.J. and Kwon, O.M. (2014) Synchronization of Discrete-Time Complex Dynamical Networks with Interval Time-Varying Delays via Non-Fragile Controller with Randomly Occurring Perturbation. Journal of The Franklin Institute, 351, 4850-4871.
- 8. Guo, W. and Faustain, S. (2010) Global Synchronization of Nonlinearly Coupled Complex Networks with Non-Delayed and Delayed Coupling. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 15, 1631- 1639.
- 9. Park, M.J. and Kwon, O.M. (2013) On Synchronization Criterion for Coupled Discrete-Time Neural Networks with Interval Time-Varying Delays. Neurocomputing, 99, 188-196.
- 10. Wu, Z. (2015) Synchronization of Discrete Dynamical Networks with Non-Delayed And Delayed Coupling. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 260, 57-62.
- 11. Huang, C., Cao, J. and Cao, J. (2016) Stability Analysis of Switched Cellular Neural Networks: A Mode-Dependent Average Dwell Time Approach. Neural Networks, 82, 84-99.
- 12. Wu, Y., Cao, J. and Li, Q. (2017) Finite-Time Synchronization of Uncertain Coupled Switched Neural Networks under Asynchronous Switching. Neural Networks, 85, 128-139.
- 13. Yang, X., Feng, Z. and Cao, J. (2016) Synchronization of Discrete-Time Neural Networks with Delays and Markov Jump Topologies Based on Tracker Information. Neural Networks, 85, 157-164. .
- 14. Li, Z., Fang, J. and Miao, Q. (2015) Exponential Synchronization of Impulsive Discrete-Time Complex Networks with Time-Varying Delay. Neurocomputing, 157, 335-343.
- 15. 卢建宁, 赵光宙. 离散时滞切换系统稳定性分析[J]. 信息与控制, 2005, 34(3): 381-384.
- 16. Langville, A.N. and Stewart, W.J. (2004) The Kronecker Product and Stochastic Automata Networks. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 167, 429-447.