Pure Mathematics
Vol.05 No.05(2015), Article ID:16092,8 pages
10.12677/PM.2015.55031
Quaternion-Valued Admissible Wavelet Transform and Weyl Transform
Yin Liu, Jiman Zhao*
Key Laboratory of Mathematics and Complex Systems, Ministry of Education, School of Mathematical Sciences, Beijing Normal University, Beijing
Email: lylight@mail.bnu.edu.cn, *jzhao@bnu.edu.cn
Received: Aug. 30th, 2015; accepted: Sep. 22nd, 2015; published: Sep. 25th, 2015
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



ABSTRACT
In this paper, we study one kind of quaternion-valued admissible wavelet transform
related to a special Fourier transform. We present some properties of this kind
of the admissible wavelet transform. Then, we define the Weyl transform associated
with the quaternion-valued admissible wavelet transform, and prove that the Weyl
operators
 are bounded when
are bounded when .
.
Keywords:Quaternion, Admissible Wavelet, Weyl Transform

四元数值可允许小波变换及Weyl变换
刘茵,赵纪满*
北京师范大学数学科学学院,数学与复杂系统教育部重点实验室,北京
Email: lylight@mail.bnu.edu.cn, *jzhao@bnu.edu.cn
收稿日期:2015年8月30日;录用日期:2015年9月22日;发布日期:2015年9月25日

摘 要
本文研究了一种与特殊的Fourier变换相关的四元数值可允许小波变换,给出了此类可允许小波变换的一些性质,然后定义了与其相关的Weyl变换,证明当 时,Weyl算子
时,Weyl算子 是有界的。
是有界的。
关键词 :四元数,可允许小波,Weyl变换

1. 引言及预备知识
四元数[1] 是Clifford代数的一种,在所有的Clifford代数中,四元数最先被发现,最接近我们所熟悉的实数复数体系。
小波分析是近30年来发展起来的新兴学科,作为一种快速高效,高精度的近似方法,它是Fourier分析的一个突破性发展,给许多相关学科的研究领域带来了新的思想,为工程应用提供了一种新的分析工具。关于小波理论,有两个分支:可允许(或连续)小波变换和由多分辨率分析生成的离散小波。关于Clifford值小波,Mitrea
[2] 提出了离散Clifford值小波变换,将经典小波推广到了Clifford代数,Brackx和Sommen [3] -[6] 建立了 上此类小波的理论。Peng和Zhao [7] 刻画了与超过二维的可伸缩的欧氏群相关的Clifford代数值可允许小波,[8]
研究了与
上此类小波的理论。Peng和Zhao [7] 刻画了与超过二维的可伸缩的欧氏群相关的Clifford代数值可允许小波,[8]
研究了与 (二维可伸缩的欧氏群)相关的四元数值可允许小波,用 Fourier变换语言给出了可允许条件的准确刻画,并给出了一些可允许小波。Mawardi,Adji和Zhao
[9] 用可允许相似群来构造Clifford代数值可允许小波变换,Swanhild Bernstein [10] 以Clifford分析为工具来构造小波。本文研究一种与特殊的Fourier变换相关的四元数值可允许小波变换,Fourier变换中采用的是
(二维可伸缩的欧氏群)相关的四元数值可允许小波,用 Fourier变换语言给出了可允许条件的准确刻画,并给出了一些可允许小波。Mawardi,Adji和Zhao
[9] 用可允许相似群来构造Clifford代数值可允许小波变换,Swanhild Bernstein [10] 以Clifford分析为工具来构造小波。本文研究一种与特殊的Fourier变换相关的四元数值可允许小波变换,Fourier变换中采用的是
(其中是任意给定的单位向量,它定义了变换轴。在处理RGB (红绿蓝)图象时,常选,对应于单位RGB颜色块的照明,灰度,轴。在本文中,为简便起见,也用),
而不是经典意义下的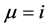 [11]
[12] ,所以用此Fourier变换语言所刻画的可允许条件是本文给出的第一个新的结果,也是本文的基础,接着举例给出一个可允许小波,然后给出此类可允许小波变换的一些性质,诸如Plancherel公式,Parseval公式,重构公式,再生核等。
[11]
[12] ,所以用此Fourier变换语言所刻画的可允许条件是本文给出的第一个新的结果,也是本文的基础,接着举例给出一个可允许小波,然后给出此类可允许小波变换的一些性质,诸如Plancherel公式,Parseval公式,重构公式,再生核等。
Weyl算子理论是数学分析和物理学都非常感兴趣的一大课题,在偏微分方程理论中,Weyl算子是被作为一类特殊的拟微分算子来研究的,并且证明它在一系列问题中都有很好的应用,诸如:椭圆理论,谱渐近性,正则问题等[13]
-[17] 。本文定义了与四元数值可允许小波变换相关的Weyl变换 ,证明了当
,证明了当 ,
, 时,
时, 是有界的。
是有界的。
现在,简单的回顾一下四元数[18] 。作为一类特殊的Clifford代数, 上的四元数代数
上的四元数代数 是可结合但不可交换的代数。它的基是:1,
是可结合但不可交换的代数。它的基是:1, ,
, ,
, ,满足
,满足
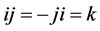 ,
, ,
, ,
, 。
。
给两个四元数 ,
, ,令
,令
 ,
, 。
。
记 ,
, ,其中
,其中 是
是 的标量部分,
的标量部分, 是
是 的向量部分,则:
的向量部分,则:
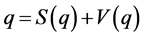
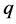 的共轭四元数记为
的共轭四元数记为 ,
,
 的范数(也叫模)记为
的范数(也叫模)记为 。
。
实部 的四元数为纯四元数,有非零实部的四元数为全四元数,单位四元数模为1。
的四元数为纯四元数,有非零实部的四元数为全四元数,单位四元数模为1。
设 为两个纯四元数,
为两个纯四元数, 可以进行如下分解:
可以进行如下分解:
 ,
, ,
, ,
, ;
(1.1)
;
(1.1)
有 [19]
。
[19]
。
同理得到一个全四元数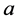 关于一个向量
关于一个向量 可以分解为:
可以分解为: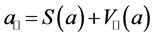 ,
,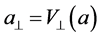 。
。
一般来说,四元数乘法不可交换,但对于平行四元数来说,乘法可以交换。
令 是一个单位纯四元数,欧拉公式仍然成立:
是一个单位纯四元数,欧拉公式仍然成立: 。任意一个四元数都可以表示成极形式:
。任意一个四元数都可以表示成极形式: ,其中
,其中 指的是坐标轴,
指的是坐标轴,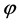 是角度,
是角度,
 ,
,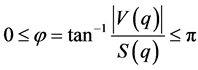
如果 ,角度无定义[18]
。
,角度无定义[18]
。
关于四元数的更多内容,参看[19] [20] 以及其中的参考文献。
定义1.1 [8] :四元数模 定义为
定义为
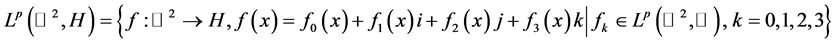 上的内积和范数定义为:
上的内积和范数定义为:
 ,
, ,
,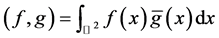
 ,
,
 ,
,
类似的,可以定义 ,
,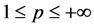 上的内积和范数。
上的内积和范数。
 上的内积定义为:
上的内积定义为:
 ,
,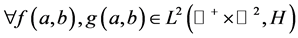 (1.2)
(1.2)
本文所采用Fourier变换定义如下:
定义1.2 [18] : ,四元数Fourier变换对定义为:
,四元数Fourier变换对定义为:
 ,
,
对于 ,由计算可得:
,由计算可得:
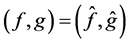 (1.3)
(1.3)
本文中出现的速降函数均采用四元数值的,类似经典情况,速降函数定义如下:
对于 :
:

其中 ,
, ,
,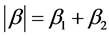 ,
,

 :表示无穷次可微的函数全体。这样的
:表示无穷次可微的函数全体。这样的 称为速降函数空间。
称为速降函数空间。
2. 主要结果
本节首先推导得出可允许条件,接着举例给出一个可允许小波,然后给出此类可允许小波变换的一些性质。
下面先刻画可允许条件。
令 ,定义
,定义
 (2.1)
(2.1)
则 的Fourier变换是
的Fourier变换是 。
。
现在定义 上的算子
上的算子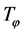 :
:

 (2.2)
(2.2)
由直接计算可得:
 (2.3)
(2.3)
令 ,
, ,
, ,为了像经典情况一样得到重构公式,计算
,为了像经典情况一样得到重构公式,计算 。
。
由(2.2),(2.3),(1.2),可得:

假设:
 (2.4)
(2.4)
且对几乎处处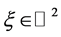 ,
, 是常数,
是常数,
则可得:

因为 在
在 中稠密,故
中稠密,故 在
在 中成立。
中成立。
记:

则有:

如果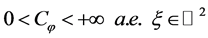 ,则重构公式在弱意义下成立:
,则重构公式在弱意义下成立:
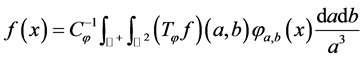
下面给出满足(2.4)的函数 。
。
假设 ,则由(2.4)可得:
,则由(2.4)可得:

从而得到 ,
,
所以应有 ,故得到
,故得到 ,
,
由于 ,
,
且由四元数的性质可知 ,故可得
,故可得 ,
,
从而由(1.1)可得 ,因此有
,因此有 ,
,
因此,可得 应为如下形式
应为如下形式

总结如下:
定义2.1:令 ,当
,当 ,并且:
,并且:
 时,称
时,称 为可允许小波,
为可允许小波,
称 为可允许条件,
为可允许条件,
称相应的变换 为可允许小波变换。
为可允许小波变换。
记:

 上的范数记作:
上的范数记作:

下面给出一个可允许小波的例子。
令 ,则:
,则:

另一方面,

所以 ,
,
又由于:

所以综上可知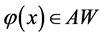 。
。
由上述推理过程可得可允许小波变换的性质。
定理2.2:(Plancherel公式)令 ,
,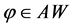 ,则:
,则:

定理2.3:(Parseval公式)令 ,
, ,
, ,则:
,则:

由Parseval公式可得下面的重构公式:
定理2.4:(Reconstruction公式)令 ,
, ,则:
,则:
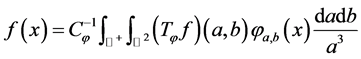
现在定义 ,
,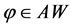 ,则
,则 是带再生核的Hilbert空间。
是带再生核的Hilbert空间。
定理2.5:(再生核) 的再生核是:
的再生核是: 。
。
证明:由重构公式可得:
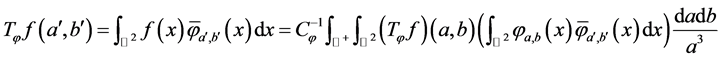
所以,再生核: 。证毕。
。证毕。
定理2.6:令 ,
, ,则
,则 ,
,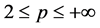 ,即
,即 是
是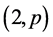 型。
型。
证明:当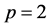 时,由Plancherel公式,
时,由Plancherel公式, 。
。
当 时,由Hölder不等式可得
时,由Hölder不等式可得

因此 。
。
所以由Riesz-Thorin定理可知 是
是 型,
型, 。证毕。
。证毕。
3. 与四元数值可允许小波变换相关的Weyl变换
本节将在上一节的基础上研究与四元数值可允许小波变换相关的Weyl变换。
定义3.1:令 ,则Weyl算子
,则Weyl算子 定义为:
定义为:

其中 ,
, 。
。
由定义可得
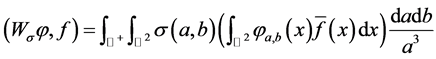
因此:

其中 是关于第二个变量的伸缩平移变换,
是关于第二个变量的伸缩平移变换,
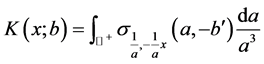
定理3.2:令 ,则Weyl算子定义了一个有界映射
,则Weyl算子定义了一个有界映射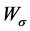 :
: ,并且:
,并且:
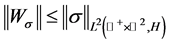
所以对于符号 ,算子
,算子 有定义,并且也有
有定义,并且也有 。
。
证明:首先证明如果 ,则
,则 。
。
事实上,对于 ,
,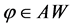 ,由定义,Hölder不等式和plancherel公式可得:
,由定义,Hölder不等式和plancherel公式可得:

所以, 。
。
另一方面,由于 在
在 中稠密,所以可以将算子
中稠密,所以可以将算子 延拓到
延拓到 上,并且
上,并且 也成立。证毕。
也成立。证毕。
定理3.3:假设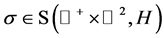 ,则算子
,则算子 也满足:
也满足:

因此Weyl算子可以延拓到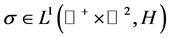 上,并且
上,并且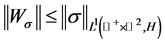 。
。
证明:因为 ,
, ,可得:
,可得:

故对于

所以 。
。
因为 在
在 中稠密,所以可以将算子
中稠密,所以可以将算子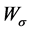 延拓到
延拓到 上。证毕。
上。证毕。
由Riesz-Thorin定理及定理3.2,定理3.3可得下面的定理。
定理3.4:对于 ,存在唯一的从
,存在唯一的从 到
到 的算子
的算子 ,使得对所有的
,使得对所有的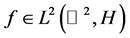 ,
,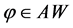 ,有:
,有:

并且 。
。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(No. 11471040),中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(No. 2014kJJCA10)资助。
文章引用
刘 茵,赵纪满. 四元数值可允许小波变换及Weyl变换
Quaternion-Valued Admissible Wavelet Transform and Weyl Transform[J]. 理论数学, 2015,
05(05): 219-226. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/PM.2015.55031
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Hamilton, W.R. (1866) Elements of Quaternions. Longmans, Green, London.
- 2. Mitrea, M. (1994) Clifford Wavelets, Singular Integrals and Hardy Spaces. Lectures Notes in Mathematics, 1575.
- 3. Brackx, F. and Sommen, F. (2000) Clifford-Hermite Wavelets in Euclidean Space. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 6, 209-310. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf02511157
- 4. Brackx, F. and Sommen, F. (2001) The Continuous Wavelet Transform in Clifford Analysis. Clifford Analysis and Its Applications, 9-26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0862-4_2
- 5. Brackx, F. and Sommen, F. (2001) The Generalized Clif-ford-Hermite Continuous Wavelet Transform. Advances in Applied Clifford Algebras, 11, 219-231. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03042219
- 6. Brackx, F. and Sommen, F. (2002) Benchmarking of Three-Dimensional Clifford Wavelet Functions. Complex Variables: Theory and Application, 47, 577-588. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02781070290016269
- 7. Zhao, J.M. and Peng, L.Z. (2006) Clifford Algebra-Valued Admissible Wavelets Associated with More than 2-Di- mensional Euclidean Group with Dilations, Wavelets, Multiscale Systems and Hypercomplex Analysis. Operator Theory: Advances and Applications, 167, 183-190.
- 8. Zhao, J.M. and Peng, L.Z. (2007) Quaternion-Valued Admissible Wavelets and Orthogonal Decomposition of . Frontiers of Mathematics in China, 2, 491-499. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11464-007-0030-5
- 9. Bahri, M., Adji, S. and Zhao, J.M. (2011) Clifford Algebra-Valued Wavelet Transform on Multivector Fields. Advances in Applied Clifford Algebras, 21, 13-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00006-010-0239-3
- 10. Bernstein, S. (2014) Wavelets in Clifford Analysis. Operator Theory, 1-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-0692-3_17-1
- 11. Bateman, H. (1954) Tables of Integral Transforms. Staff of the Bateman Manuscript Project, 1, 313.
- 12. Ding, Y. (2008) The Basis of Modern Analysis. Beijing Normal University Press, Beijing.
- 13. Boggiatto, P. and Rodino, L. (2003) Quantization and Pseudo-Differential Operators. Cubo Matemática Educacional, 5, 237-272.
- 14. Dachraoui, A. (2001) Weyl-Bessel Transforms. Journal of Computa-tional and Applied Mathematics, 133, 263-276. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0427(00)00649-X
- 15. Peng, L.Z. and Ma, R.Q. (2005) Wavelets Associated with Hankel Transform and Their Weyl Transform. Science in China Series A-Mathematics, 5, 497-503.
- 16. Rachdi, L.T. and Trimèche, K. (2003) Weyl Transforms Associated with the Spherical Mean Operator. Analysis and Applications, 2, 141-164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S0219530503000156
- 17. Zhao, J.M. and Peng, L.Z. (2004) Wavelet and Weyl Transforms Associated with the Spherical Mean Operator. Integral Equations and Operator Theory, 50, 279-290.http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00020-003-1222-3
- 18. Moxey, C.E., Stephen, J.S. and Todd, A.E. (2003) Hypercomplex Correlation Techniques for Vector Images. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51, 1941-1953. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2003.812734
- 19. Coxeter, H.S.M. (1946) Quaternions and Reflections. The American Mathematical Monthly, 53, 136-146. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2304897
- 20. Gürlebeck, K. and Spröbig, W. (1990) Quaternionic Analysis and Elliptic Boundary Value Problems. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-7295-9
NOTES
*通讯作者。