Statistics and Application
Vol.05 No.04(2016), Article ID:19336,9
pages
10.12677/SA.2016.54041
Mean Square Consensus for Leader-Following Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems under Markov Switching Topologies
Zhichao Li
Department of Mathematics, School of Science, Beijing Technology and Business University, Beijing

Received: Nov. 28th, 2016; accepted: Dec. 13th, 2016; published: Dec. 23rd, 2016
Copyright © 2016 by author and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



ABSTRACT
In recent years, with the rapid development of science and application, cooperative control of multi-agent systems has become a hot research in the field of control. As the basis of the coordination problem for multi-agent systems, the consensus problem has attracted more and more attentions. Aimed at nonlinear multi-agent systems, control algorithm has been designed, using Riccati equation, and some criteria for achieving the mean square consensus via the properties of Markov theory. Finally, some simulation examples are provided to illustrate the effectiveness of the theoretical results.
Keywords:Multi-Agent Systems, Mean Square Consensus, Leader, Riccati Equation, Markov Switch Topologies

带有领航者的非线性Markov切换多智能体系统的均方一致性
李智超
北京工商大学理学院数学系,北京

收稿日期:2016年11月28日;录用日期:2016年12月13日;发布日期:2016年12月23日

摘 要
近年来,随着科学技术的迅速发展及应用的需要,多智能体系统的协调控制成为控制领域的一个研究热点。一致性问题作为多智能体系统协调控制的基础,受到了各个领域的研究学者越来越多的关注。本文针对非线性多智能体系统设计了相应的一致性控制算法,利用黎卡迪方程方法以及Markov的特性使非线性系统达到均方一致性,最后通过仿真验证了结果的正确性和有效性。
关键词 :多智能体系统,均方一致,领航者,黎卡迪方程,马尔科夫切换拓扑

1. 引言
近年来,多智能体系统的协调控制发展的越来越快,应用也越来越广泛,比如无人机、编队控制、群集、同步等等,引起了专家学者的广泛关注和深入研究。在多智能体系统的协调控制问题中,多智能体一致性问题是智能体之间协调控制的基础。Vicsek,A.Jadbabaie,Olfati-Saber,Murry和Ren等人 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] 分别对一致性展开了研究,做出了理论分析。
上述的文献主要研究的是固定拓扑下的多智能体系统一致性问题,但是在实际问题中,我们经常会遇到很多随机因素的影响,许多系统的操作环境会带有不确定性,导致其通信拓扑结构可能会是随机切换的。在Olfati-Saber和Murry研究一致性问题的影响下,Costa在文献 [6] 中对带有干扰的连续时间马尔科夫切换下的多智能体系统进行了分析,并使其达到均方一致。对于离散时间下的多智能体系统,Zhang和Mo [7] [8] 也研究了马尔科夫切换拓扑下的均方一致性问题。Li等人 [9] 分别对离散和连续时间随机切换下的高阶多智能体系统的一致性问题展开了研究。Miao等人 [10] 研究了带有领航者的马尔科夫切换拓扑下的均方一致性问题。文献 [11] 基于采样控制研究了马尔科夫切换拓扑下二阶多智能体系统的均方一致性问题。
在上述文献中的多智能体系统的动力学为一阶、二阶或高阶的,但在实际生活中,一般的物理系统都是非线性的,因此对非线性系统的研究有着重大的意义。文献 [12] 研究了有向拓扑结构下的具有非线性系统模型的多智能体系统的同步问题,提出了有向拓扑有生成树可以使多智能体系统达到一致。 [13] 提出对二阶非线性多智能体系统,其系统可以达到一致。 [14] 提出了分布式非线性控制协议使多智能体系统达到一致。 [15] 讨论了有向网络下非线性多智能体系统的协调跟踪问题。
注意到已有的非线性多智能体系统一致性结果其网络拓扑图一般是固定的,往往忽略了其操作环境带来的不确定因素,使得文章的可行性不是很强。目前的文献主要是对于多智能体系统在随机切换下的一致性问题和非线性多智能体系统一致性问题分别给出的,但是同时考虑了随机切换拓扑和非线性多智能体系统下的文章并不多。本文研究了其均方一致性问题,首先假设其拓扑结构受到一个遍历的马氏链驱动,然后运用黎卡迪方程方法和随机系统理论,给出了实现均方一致的条件。
2. 问题描述
2.1. 图论基础
代数图论在多智能体系统中起着关键重要的作用,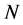 个智能体间的信息交互网络拓扑图记为
个智能体间的信息交互网络拓扑图记为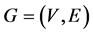 ,其中顶点的集合
,其中顶点的集合 表示有
表示有 个智能体,
个智能体, 是图的边集。
是图的边集。 的边
的边 表示智能体
表示智能体 和智能体
和智能体 之间可以发生信息的交互。图
之间可以发生信息的交互。图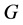 的邻接矩阵
的邻接矩阵 ,其中
,其中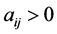 表示节点
表示节点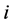 和
和 之间的连接权重,当节点
之间的连接权重,当节点 能从节点
能从节点 得到其信息时
得到其信息时 ,否则
,否则 。图
。图 的拉普拉斯矩阵定义为
的拉普拉斯矩阵定义为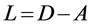 ,其中度矩阵
,其中度矩阵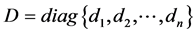 是对角元为
是对角元为 ,其它元为零的对角矩阵。即有
,其它元为零的对角矩阵。即有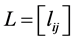 ,
,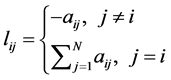 。对于无向图
。对于无向图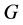 ,其的拉普拉斯矩阵
,其的拉普拉斯矩阵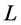 为一个对称矩阵。本文中我们用用顶点0表示领航者,信息在领航者和包含在领航者邻居集内的智能体之间交互,其拓扑图由图
为一个对称矩阵。本文中我们用用顶点0表示领航者,信息在领航者和包含在领航者邻居集内的智能体之间交互,其拓扑图由图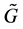 表示,并且图
表示,并且图 由图
由图 、领航者0以及领航者与其邻居之间的边组成。
、领航者0以及领航者与其邻居之间的边组成。
考虑 个图
个图 的并图:
的并图:
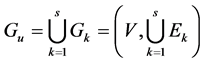
设 分别是
分别是 的邻接矩阵和拉普拉斯矩阵,若
的邻接矩阵和拉普拉斯矩阵,若 的邻接矩阵
的邻接矩阵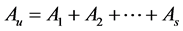 ,则
,则 是
是 的一个有效拉普拉斯矩阵。设
的一个有效拉普拉斯矩阵。设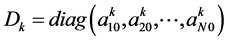 ,其中
,其中 是第
是第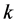 个图中第
个图中第 个智能体与领航者之间的权值,若智能体与领航者互为邻居
个智能体与领航者之间的权值,若智能体与领航者互为邻居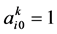 ,否则
,否则 。矩阵
。矩阵 ,若对所有
,若对所有 ,
, ,则称矩阵
,则称矩阵 是对角占优的。设
是对角占优的。设 ,由
,由 是对角占优矩阵,可知
是对角占优矩阵,可知 也是对角占优矩阵。由
也是对角占优矩阵。由

可知 也是对角占优矩阵。
也是对角占优矩阵。
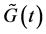 在
在 个不同的拓扑上
个不同的拓扑上 随机切换,
随机切换, 当且仅当随机变量
当且仅当随机变量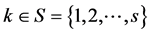 。切换过程
。切换过程 取决于时间齐次马尔科夫过程,这个马尔科夫过程的状态空间相当于所有可能的拓扑。
取决于时间齐次马尔科夫过程,这个马尔科夫过程的状态空间相当于所有可能的拓扑。
2.2. 系统模型
考虑包含N个智能体和一个领航者的多智能体系统,智能体i和领航者的系统方程如下所示:
 (2.1)
(2.1)
 (2.2)
(2.2)
其中常数矩阵 表示为状态输入矩阵,
表示为状态输入矩阵, 表示控制输入矩阵,
表示控制输入矩阵, 表示智能体
表示智能体 在
在 时刻的状态,
时刻的状态, 表示领航者的状态,
表示领航者的状态, 表示为控制输入,
表示为控制输入, ,是一个连续的向量值函数,它表示网络中各个体的固有非线性动态。
,是一个连续的向量值函数,它表示网络中各个体的固有非线性动态。
在随机切换拓扑 上,根据多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)的领航者跟随一致性问题,我们设计如下一致性协议为:
上,根据多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)的领航者跟随一致性问题,我们设计如下一致性协议为:
 (2.3)
(2.3)
其中 是控制增益。
是控制增益。
定义1:对任意的 和
和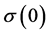 的初始分布,若存在一致增益
的初始分布,若存在一致增益 使得:
使得:
 (2.4)
(2.4)
则称多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)在协议(2.3)下达到领航者跟随一致。
若存在正数 和
和 使得:
使得:

则称以速度 达到连续时间领航者跟随一致。
达到连续时间领航者跟随一致。
引理2.1 [16] :若 连通,则
连通,则 是一个正定矩阵。
是一个正定矩阵。
假设2.1:图 连通。
连通。
在假设2.1的条件下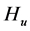 是一个正定矩阵,则
是一个正定矩阵,则 的所有特征值大于0,设
的所有特征值大于0,设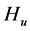 的最小特征值为
的最小特征值为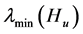 ,最大特征值为
,最大特征值为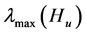 ,且存在正交矩阵
,且存在正交矩阵 ,使得
,使得 ,其中
,其中 是矩阵
是矩阵 的特征值,
的特征值, 。
。
引理2.4 [17] :非线性函数 满足如下Lipschitz条件:
满足如下Lipschitz条件:
 (2.5)
(2.5)
其中 ;
; 为正常数;
为正常数; 为Euclidean范数。
为Euclidean范数。
引理2.5 [18] :任意两个向量 和任意的正定对称矩阵
和任意的正定对称矩阵 ,有
,有
 (2.6)
(2.6)
假设2.2:连续时间马尔科夫过程具有遍历性。
在假设3.1成立的条件下,马尔科夫过程容许唯一的不变分布 ,且马尔科夫过程中的任一状态可以从状态空间中的任何其他状态达到。其中
,且马尔科夫过程中的任一状态可以从状态空间中的任何其他状态达到。其中 。不失一般性,对所有的
。不失一般性,对所有的 ,马尔科夫过程
,马尔科夫过程 的分布由
的分布由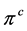 给出。
给出。
假设2.3: 镇定。
镇定。
若 可镇定,则如下黎卡迪(Riccati)方程存在正定解
可镇定,则如下黎卡迪(Riccati)方程存在正定解 使得
使得

可找到 使得
使得
 (2.7)
(2.7)
若 连通,增益矩阵设计为 [19]
连通,增益矩阵设计为 [19]

其中系数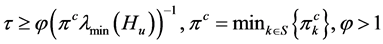 。
。
假设2.4:存在一个 使得:
使得:
 (2.8)
(2.8)
成立,其中 。
。
3. 主要结论
这部分研究多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)在协议(2.3)下的领航者跟随一致性问题。
定理3.1:考虑马尔科夫切换拓扑,假定假设2.1、假设2.2、假设2.3、假设2.4成立,设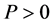 是(3.1)的解,
是(3.1)的解, 。则对任意的初始条件,在控制协议(2.3)下,多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)可以速度
。则对任意的初始条件,在控制协议(2.3)下,多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)可以速度 达到了领航者跟随一致。
达到了领航者跟随一致。
证明:智能体 和领航者之间的状态误差表示为
和领航者之间的状态误差表示为 ,
, 的动态为
的动态为

其中当 时,
时, ,当
,当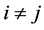 时,
时, 。设
。设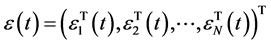


 是
是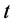 时刻的拉普拉斯矩阵,由此可得:
时刻的拉普拉斯矩阵,由此可得:
 (3.3)
(3.3)
其中 。
。
考虑如下函数 ,我们设
,我们设

其中 。
。
通过 [20] 中的引理4.2得

可知

又由引理1.4和引理1.5可知

可知
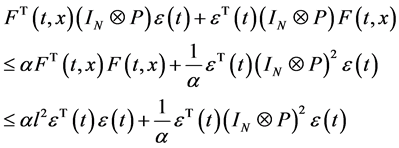
设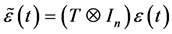 ,
, 的分布由
的分布由 给出,可得
给出,可得

又由假设3.2、假设3.3可知
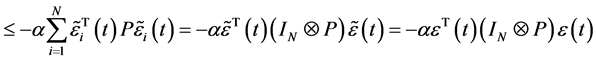
可得 ,即
,即 ,
, 以速度
以速度 收敛到0,则在控制协议(2.3)下多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)可以以速度
收敛到0,则在控制协议(2.3)下多智能体系统(2.1)~(2.2)可以以速度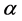 达到领航者跟随一致。
达到领航者跟随一致。
注3.1:文章 [9] 证明了在连续系统切换拓扑是联合连通的情况下,系统会实现均方一致性。本文在该基础上,以黎卡迪方程方法和随机系统理论方法,构造V函数,给出了实现均方一致的数值条件,具有很大的实际意义,而且考虑的系统模型是非线性的,得到的结果也具有工程意义。
4. 数值仿真
这部分给出例子来证明上述理论的有效性。考虑如图1所示的网络拓扑图,通信拓扑在 ,
, ,
, 之间随机切换,图里
之间随机切换,图里 ,
, ,
, 所有边的权值都为1,并图
所有边的权值都为1,并图 边的权值是
边的权值是 ,
, ,
, 对应边的权值之和。
对应边的权值之和。
考虑包含一个领航者和四个智能体的多智能体系统,如图1,通信拓扑在 ,
, ,
,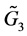 之间随机切换,假定系数矩阵
之间随机切换,假定系数矩阵
 ,
,
容易验证出 是可镇定的。由图1可知
是可镇定的。由图1可知 ,
, ,
, 是不连通的,
是不连通的, 是连通的。
是连通的。
我们可以得出
 ,
,  ,
, 
继而

可得 。设连续马尔科夫过程的初始分布
。设连续马尔科夫过程的初始分布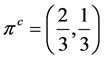 ,假定我们以速度
,假定我们以速度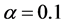 达到领航者跟随一致。当
达到领航者跟随一致。当 ,
, 时,由(3.1)可得
时,由(3.1)可得
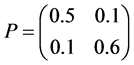
由 ,取
,取 ,可得
,可得

令 ,在控制协议(1.3)下,状态误差轨迹如图2和图3所示,可知4个智能体全部与
,在控制协议(1.3)下,状态误差轨迹如图2和图3所示,可知4个智能体全部与
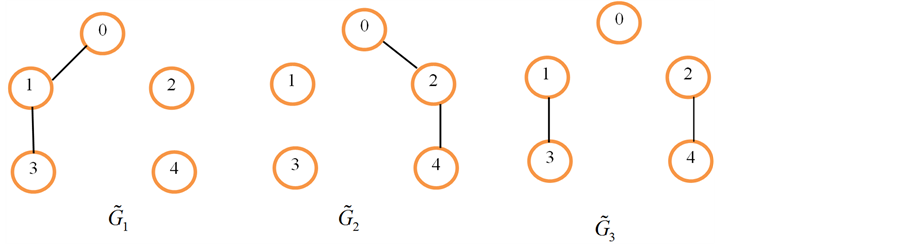
Figure 1. The network topology ,
,  ,
, 
图1. 网络拓扑图: ,
, ,
,

Figure 2. xi (1) agent state trajectory
图2. xi (1)智能体的状态轨迹

Figure 3. xi (2) agent state trajectory
图3. xi (2)智能体的状态轨迹
领航者达到一致。
5. 结论
本文主要研究了连续时间随机切换拓扑情况下的领航者跟随一致性问题,在拓扑图的并图连通的情况下,设计了基于多智能体之间信息的控制协议,利用黎卡迪(Riccati)方程、马尔科夫理论分析得到了领航者跟随的均方一致性,最后通过Matlab仿真验证了结果的正确性。
文章引用
李智超. 带有领航者的非线性Markov切换多智能体系统的均方一致性
Mean Square Consensus for Leader-Following Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems under Markov Switching Topologies[J]. 统计学与应用, 2016, 05(04): 380-388. http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/SA.2016.54041
参考文献 (References)
- 1. Vicsek, T., et al. (2006) Novel Type of Phase Transition in a System of Self-Driven Particles. Physical Review Letters, 75, 1226-1229. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.1226
- 2. Jadbabaie, A., Lin, J. and Morse, A.S. (2003) Coordination of Groups of Mobile Autonomous Agents Using Nearest Neighbor. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 48, 988-1001. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2003.812781
- 3. Olfatisaber, R. and Murray, R.M. (2004) Consensus Problems in Networks of Agents with Switching Topology and Time-Delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 49, 1520-1533. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2004.834113
- 4. Ren, W. and Beard, R.W. (2005) Consensus Seeking in Multiagent Systems under Dynamically Changing Interaction Topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 50, 655-661. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2005.846556
- 5. Yu, W., Chen, G., Ren, W., Kurths, J. and Zheng, W.X. (2011) Distributed Higher Order Consensus Protocols in Multiagent Dynamical Systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 58, 1924-1932. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2011.2106032
- 6. Fragoso, M.D. and Costa, O.L.V. (2005) A United Approach for Stochastic and Mean Square Stability of Continuous-Time Linear Systems with Markovian Jumping Parameters and Additive Disturbances. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 44, 1165-1191.
- 7. Zhang, Y. and Tian, Y.P. (2009) Consent Ability and Protocol Design of Multi-Agent Systems with Stochastic Switching Topology. Automatica, 45, 1195-1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2008.11.005
- 8. Pan, T., Mo, L. and Cao, X. (2015) Consensus of Discrete-time Mul-ti-Agent Systems with White Noise Disturbance. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 48, 202-205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.12.125
- 9. You, K., Li, Z. and Xie, L. (2013) Consensus Condition for Linear Multi-Agent Systems over Randomly Switching Topologies. Automatica, 49, 3125-3132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2013.07.024
- 10. Miao, G. and Li, T. (2015) Mean Square Containment Control Problems of Multi-Agent Systems under Markov Switching Topologies. Advances in Difference Equations, 2015, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-015-0437-3
- 11. Zhao, H.Y., Xu, S.Y. and Yuan, D.M. (2012) Consensus of Data-Sampled Multi-Agent Systems with Markovian Switching Topology. Asian Journal of Control, 14, 1366-1373. https://doi.org/10.1002/asjc.444
- 12. Wu, C.W. (2005) Synchronization in Networks of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Coupled via a Directed Graph. Nonlinearity, 18, 1057-1064. https://doi.org/10.1088/0951-7715/18/3/007
- 13. Yu, W.W., Chen, G., Cao, M., et al. (2010) Second-Order Consensus for Multi-Agent Systems with Directed Topologies and Non Linear Dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, 40, 881- 891. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2009.2031624
- 14. Liu, X.W., Chen, T.P. and Lu, W.L. (2010) Consensus Problem in Directed Networks of Multi-Agents via Nonlinear Protocols. Physics Letters A, 373, 3122-3127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2009.06.054
- 15. Ma, G.-F. and Mei, J. (2011) Coordinated Tracking for Nonlinear Mul-ti-Agent Systems under Directed Networks. Control and Decision, 26, 1001-0920.
- 16. Hong, Y., Gao, L., Cheng, D. and Hu, J. (2007) Lyapunov-Based Approach to Multiagent Systems with Switching Jointly Connected Interconnection. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 52, 943-948,
- 17. Khalil, H.K. (2002) Nonlinear Systems. 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle Riv-er.
- 18. Horn, R. and Johnson, C. (1985) Matrix Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- 19. Li, Z., Duan, Z. and Chen, G. (2011) Dynamic Consensus of Linear Multi-Agent Systems. IET Control Theory and Applications, 5, 19-28. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cta.2009.0466
- 20. Costa, O. and Fragoso, M. (2005) A Unified Approach for Stochastic and Mean Square Stability of Continuous-Time Linear Systems with Markovian Jumping Parameters and Additive Disturbances. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 44, 1165-1191. https://doi.org/10.1137/S0363012903434753