 Advances in Condensed Matter Physics 凝聚态物理学进展, 2013, 2, 17-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/cmp.2013.21004 Published Online February 2013 (http://www.hanspub.org/journal/cmp.html) The Longitudinally Driven Giant Magneto-Impedance Effect of Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 Films Guang Chu, Yunzhang Fang, Xingwei He, Yun Ma, Wenzhong Li College of Mathematics, Physics and Information Engineering, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua Email: audy915@163.com Received: Jan. 14th, 2013; revised: Jan. 16th, 2013; accepted: Feb. 5th, 2013 Abstract: Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 single-layer films were prepared by magnetron sputtering. An HP4294A impedance ana- lyzer was used to measure the curves of longitudinally driven giant magneto-impedance. Films with 3.0 m thickness were annealed under different temperatures. The results showed that at a driven frequency of 190 kHz for the samples annealed at 250˚C, the maximum giant magneto-impedance effect of the samples with thickness of 3.0 μm is 157.32%. And the sensitivity of it is 1.55%/(A·m−1). Keywords: Giant Magneto-Impedance Effect; Film; Longitudinally Driven; Sensitivity Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 薄膜的纵向驱动巨磁阻抗效应 褚 光,方允樟,何兴伟,马 云,李文忠 浙江师范大学数理与信息工程学院,金华 Email: audy915@163.com 收稿日期:2013 年1月14 日;修回日期:2013年1月16日;录用日期:2013 年2月5日 摘 要:采用磁控溅射方法制备了单层 Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 薄膜,利用 HP4294A 型阻抗分析仪测量了经过不同温 度退火 3.0 μm厚的FeSiBPC 薄膜的纵向驱动巨磁阻抗效应。实验结果表明:经 250℃退火的薄膜样品在190 kHz 驱动频率下的最大巨磁阻抗比为157.32%,外场灵敏度为1.55 %/(A·m−1)。 关键词:巨磁阻抗效应;薄膜;纵向驱动;灵敏度 1. 引言 自日本学者Mohri等人[1]首次在 CoFeSiB 非晶丝 中观察到了巨磁阻抗效应(giant magneto-impedance, 简写为 GMI)即材料的交流阻抗随着外加直流磁场的 改变而发生变化的特性以来。由于其具有高灵敏度、 响应快、非接触[2]稳定性好等特点,受到了研究者的 广泛关注。近年来,对GMI 效应的研究在很多方面 都有了较大的突破。在材料方面,从最初的 Co 基合 金发展到以 FeCuNbSiB[3]为代表的 Fe 基合金材料[4,5]; 在结构方面,也从单一结构的非晶丝[1]、薄带[6] 、单 层薄膜[7]发展到了复合结构的薄带[8]、玻璃包裹丝[9]、 三明治薄膜[10]等。然而对于单一结构材料 GMI 效应 的研究基本上都是集中在传统的横向驱动模式上,对 采用纵向驱动模式[11]的报道却很少见,本文选用具有 1.44 T相当高的饱和磁化场和1.2 A/m低的矫顽力的 Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 合金材料[5],利用射频磁控溅射法制 备Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 薄膜,通过不同温度的热处理, 研究了该组分薄膜的纵向驱动GMI 效应。 2. 实验 采用射频溅射法制备 FeSiBPC 非晶态薄膜。靶材 的组分为 Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9。衬底为 Si(100),在其表 面射频溅射一层1.8 μm厚的SiO2。衬底依次在丙酮、 Copyright © 2013 Hanspub 17 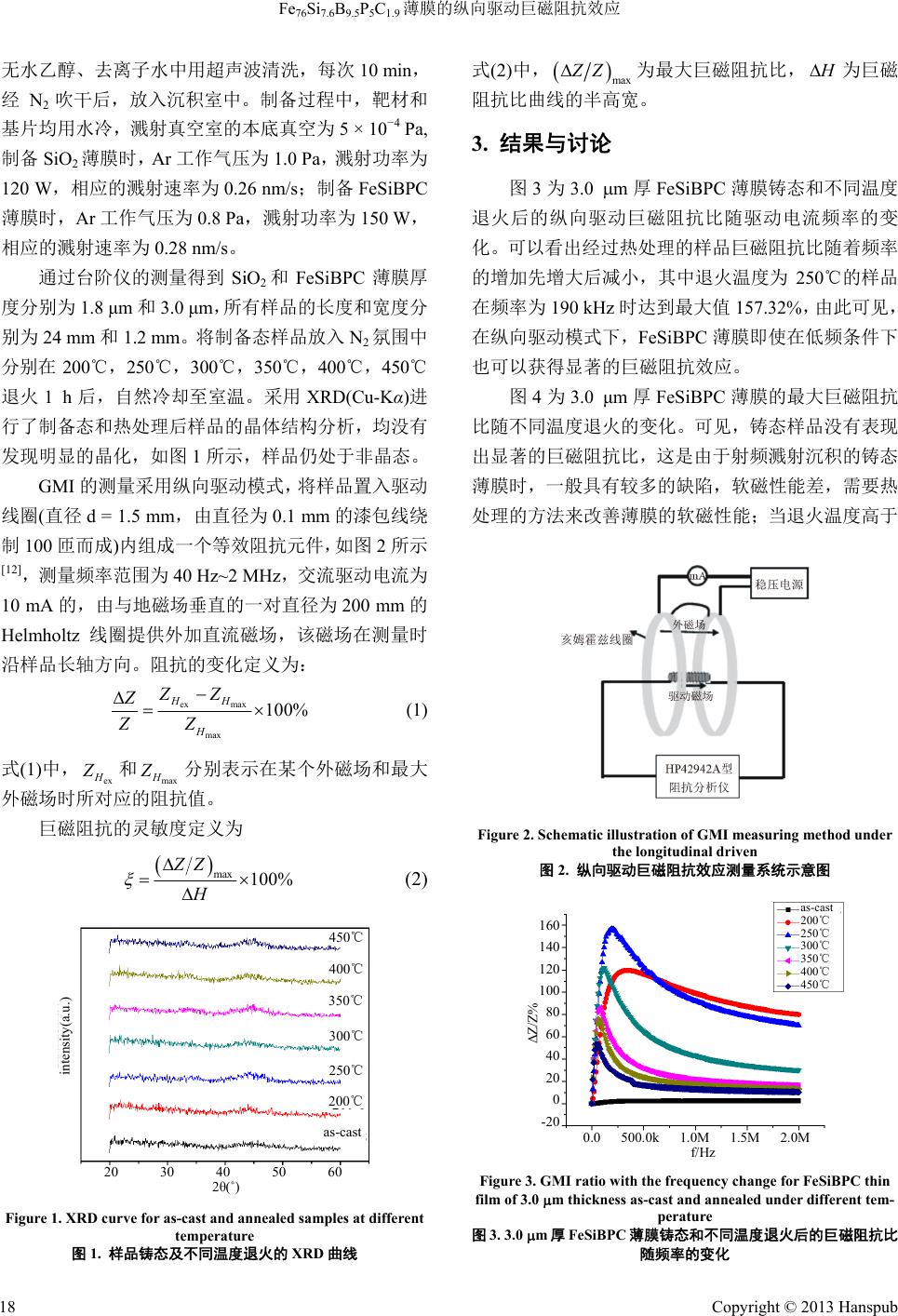 Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 薄膜的纵向驱动巨磁阻抗效应 无水乙醇、去离子水中用超声波清洗,每次10 min, 经N2吹干后,放入沉积室中。制备过程中,靶材和 基片均用水冷,溅射真空室的本底真空为5 × 10−4 Pa, 制备 SiO2薄膜时,Ar 工作气压为 1.0 Pa,溅射功率为 120 W,相应的溅射速率为 0.26 nm/s;制备 FeSiBPC 薄膜时,Ar 工作气压为 0.8 Pa,溅射功率为 150 W, 相应的溅射速率为 0.28 nm/s。 通过台阶仪的测量得到 SiO2和FeSiBPC 薄膜厚 度分别为1.8 μm和3.0 μm,所有样品的长度和宽度分 别为 24 mm 和1.2 mm。将制备态样品放入 N2氛围中 分别在 200℃,250℃,300℃,350℃,400℃,450℃ 退火 1 h后,自然冷却至室温。采用XRD(Cu-Kα)进 行了制备态和热处理后样品的晶体结构分析,均没有 发现明显的晶化,如图 1所示,样品仍处于非晶态。 GMI 的测量采用纵向驱动模式,将样品置入驱动 线圈(直径 d = 1.5 mm,由直径为 0.1 mm的漆包线绕 制100匝而成)内组成一个等效阻抗元件,如图2所示 [12],测量频率范围为 40 Hz~2 MHz,交流驱动电流为 10 mA的,由与地磁场垂直的一对直径为200 mm的 Helmholtz 线圈提供外加直流磁场,该磁场在测量时 沿样品长轴方向。阻抗的变化定义为: ex max max 100% HH H Z Z Z ZZ (1) 式(1)中, ex H Z 和分别表示在某个外磁场和最大 外磁场时所对应的阻抗值。 max H Z 巨磁阻抗的灵敏度定义为 max 100% ZZ H (2) 450℃ 20 30 40 50 60 2θ(˚) as-cast 400℃ 350℃ 300℃ 250℃ 200℃ intensity(a.u.) Figure 1. XRD curve for as-cast and annealed samples at different temperature 图1. 样品铸态及不同温度退火的 XRD 曲线 式(2)中, ZZ为最大巨磁阻抗比, max H 为巨磁 的半高宽 3. 结果与讨论 图3为3.0 m厚FeSiBPC 薄膜铸态和不同温度 退火后的纵向驱动巨磁阻抗比随驱动电流频率的变 巨磁阻抗 比随 阻抗比曲线 。 化。可以看出经过热处理的样品巨磁阻抗比随着频率 的增加先增大后减小,其中退火温度为 250℃的样品 在频率为190 kHz 时达到最大值 157.32%,由此可见, 在纵向驱动模式下,FeSiBPC 薄膜即使在低频条件下 也可以获得显著的巨磁阻抗效应。 图4为3.0 μm厚FeSiBPC薄膜的最大 不同温度退火的变化。可见,铸态样品没有表现 出显著的巨磁阻抗比,这是由于射频溅射沉积的铸态 薄膜时,一般具有较多的缺陷,软磁性能差,需要热 处理的方法来改善薄膜的软磁性能;当退火温度高于 Figure 2. Schematic illustration of GMI measuring method under 图2. 纵向 统示意图 the longitudinal driven 驱动巨磁阻抗效应测量系 intensity(a.u.) 0.0 500.0k 1.0M 1.5M 2.0M f/Hz as-cast 200℃ 250℃ 300℃ 350℃ 400℃ 450℃ 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 -20 ΔZ/Z% Figure 3. GMI ratio with the frequency change for FeSiBthin 图3. 3.0 m厚FeSiBPC 薄膜 同温度退火后的巨磁阻抗比 PC film of 3.0 m thickness as-cast and annealed under different tem- perature 铸态和不 随频率的变化 Copyright © 2013 Hanspub 18 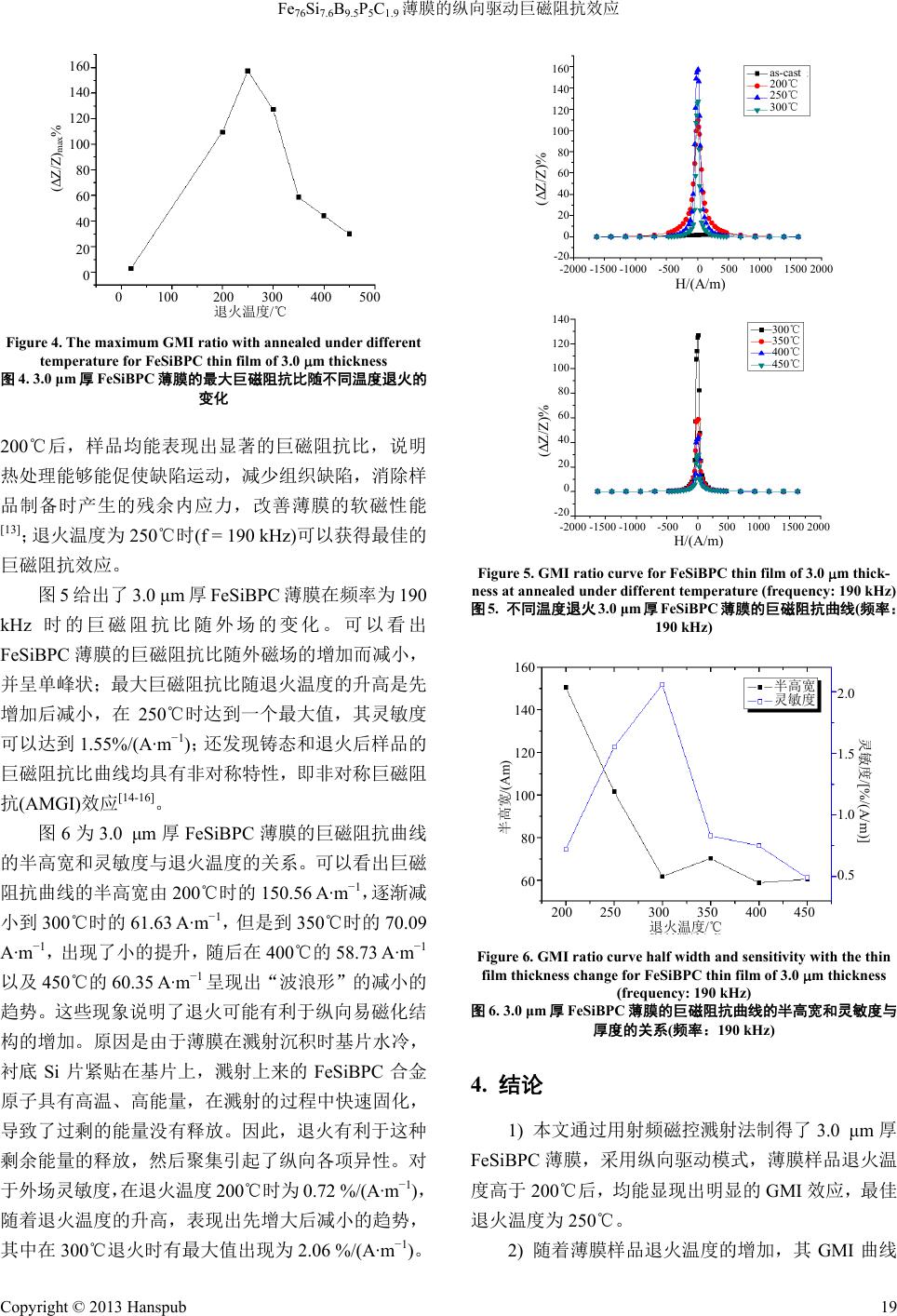 Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 薄膜的纵向驱动巨磁阻抗效应 (ΔZ/Z) max % 0 100 200 300 400 500 退火温度/℃ 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Figure 4. The maximum GMI ratio with annealed under dient 图4. 火的 00℃后,样品均能表现出显著的巨磁阻抗比,说明 巨磁阻抗 .0 μm厚FeSiBPC 薄膜在频率为190 kHz B μmFeSiBPC薄膜的巨磁阻抗曲线 的半 45 火 ffer temperature for FeSiBPC thin film of 3.0 m thickness 3.0 μm厚FeSiBPC 薄膜的最大巨磁阻抗比随不同温度退 变化 2 热处理能够能促使缺陷运动,减少组织缺陷,消除样 品制备时产生的残余内应力,改善薄膜的软磁性能 [13];退火温度为 250℃时(f = 190 kHz)可以获得最佳的 效应。 图5给出了 3 时的巨磁阻抗比随外场的变化。可以看出 FeSiPC 薄膜的巨磁阻抗比随外磁场的增加而减小, 并呈单峰状;最大巨磁阻抗比随退火温度的升高是先 增加后减小,在250℃时达到一个最大值,其灵敏度 可以达到1.55%/(A·m−1);还发现铸态和退火后样品的 巨磁阻抗比曲线均具有非对称特性,即非对称巨磁阻 抗(AMGI)效应[14-16]。 图6为3.0 厚 高宽和灵敏度与退火温度的关系。可以看出巨磁 阻抗曲线的半高宽由 200℃时的 150.56 A·m−1,逐渐减 小到 300℃时的61.63 A·m−1,但 是 到350℃时的 70.09 A·m−1,出现了小的提升,随后在 400℃的 58.73 A·m−1 以及 0℃的 60.35 A·m−1呈现出“波浪形”的减小的 趋势。这些现象说明了退 可能有利于纵向易磁化结 构的增加。原因是由于薄膜在溅射沉积时基片水冷, 衬底 Si 片紧贴在基片上,溅射上来的 FeSiBPC 合金 原子具有高温、高能量,在溅射的过程中快速固化, 导致了过剩的能量没有释放。因此,退火有利于这种 剩余能量的释放,然后聚集引起了纵向各项异性。对 于外场灵敏度,在退火温度200℃时为0.72 %/(A·m−1), 随着退火温度的升高,表现出先增大后减小的趋势, 其中在 300℃退火时有最大值出现为2.06 %/(A·m−1)。 160 as-cast 200℃ 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 -20 (ΔZ/Z)% -2000 -1500 -1000 -500 0 500 1000 1500 2000 H/ ( A/m ) 250℃ 300℃ 300℃ 350℃ 400℃ 450℃ 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 -20 (ΔZ/Z)% -2000 -1500 -1000 -500 0 500 1000 1500 2000 H/ ( A/m ) Figure 5. GMI ratio curve for FeSiBPC thin film of 3.0 thick- n m ess at annealed under different temperature (frequency: 190 kHz) 图5. 不同温度退火 3.0 μm厚FeSiBPC 薄膜的巨磁阻抗曲线(频率: 190 kHz) 200 250 300 350 400 450 退火温度/℃ 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 160 140 120 100 80 60 半高宽/(Am) 灵敏度/[%/(A/m)] 半高宽 灵敏度 Figure 6. GMI ratio curve half width and sensitivity with the thin 图 4. 结论 1) 本文通过用射频磁控溅射法制得了3.0 μm厚 FeSi 退火温度的增加,其GMI 曲线 film thickness change for FeSiBPC thin film of 3.0 m thickness (frequency: 190 kHz) 6. 3.0 μm厚FeSiBPC薄膜的巨磁阻抗曲线的半高宽和灵敏度与 关系(频率:190 kH厚度的 z) BPC 薄膜,采用纵向驱动模式,薄膜样品退火温 度高于 200℃后,均能显现出明显的 GMI 效应,最佳 退火温度为 250℃。 2) 随着薄膜样品 Copyright © 2013 Hanspub 19  Fe76Si7.6B9.5P5C1.9 薄膜的纵向驱动巨磁阻抗效应 Copyright © 2013 Hanspub 20 的半 感谢国家自然科学基金项目(11079029)的资助。 参考文献 (References) shima, et al. Magneto-inductive . Gijs. Giant magnetoimpedance in trilayer ct in ultra-thin glass- Mohri and T. Uchiyama. Giant magneto-im- 向驱动巨磁阻抗效 带巨磁阻抗效应 - trical magneto- Kim, J. Jang, D. Y. Kim and S. S. Yoon. Analysis of da Silva, A. D. C. Viegas, et al. High frequency mag- 高宽逐渐减小,灵敏度曲线则是先增加后减小, 在样品退火温度为 300℃时,达到最大为 2.06%/ (A·m−1)。 5. 致谢 [1] K. Mohri, T. Kohzawa, K. Kawa 的新型磁 effect in amorphous wires. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1992, 28(5): 3150-3152. [2] Z. C. Wang, F. F. Gong, X. L. Yang, et al. Longitudinally driven giant magnetoimpedance effect in stress-annealed Fe-based nano- crystalline ribbons. Journal of Applied Physics, 2000, 87(9): 4819- 4821. [3] Y. Yoshizawa, S. Oguma and K. Yamauchi. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. Journal of Applied Physics, 1998, 64(10): 6044-6046. [4] Z. H. Gan, H. Y. Yi, et al. Preparation of bulk amorphous Fe- Ni-P-B-Ga alloys from industrial raw materials. Scripta Ma- terialia, 2003, 48(11): 1543-1547. [5] C. Chang, T. Kubota, et al. Synthesis of ferromagnetic Fe-based bulk glassy alloys in the Fe-Si-B-P-C system. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 473(1-2): 368-372. [6] M. L. Sartorelli, M. Knobel and J. Schoenmaker. Giant mag- neto-impedance and its relaxation in Co-Fe-Si-B amorphous rib- bons. Applied Physics Letters, 1997, 75(15): 2208-2210. [7] S. Q. Xiao, Y. H. Liu, L. Zhang, et al. Magneto-impedance in amorphous FeCuNbSiB films. Chinese Physics Letters, 1998, 15(10): 748-749. [8] F. Amalou, M. A structures of patterned magnetic amorphous ribbons. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 81(9): 1654-1656. [9] V. Zhukova, M. Ipatov, et al. GMI effe coated co-rich amorphous wires. Sensors and Actuators B, 2007, 126(1): 232-234. [10] L. V. Panina, K. pedance (GMI) in amorphous wire, single layer and sandwich film. Physica A, 1997, 241(1-2): 429-438. [11] 杨介信, 杨燮龙, 陈国等. 一种新型的纵 应[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(10): 1051-1053. [12] 何理, 郑金菊, 金林枫等. 基于 Fe基合金薄 敏传感器[J]. 磁性材料与器件, 2009, 40(6): 40-43. [13] R. L. Sommer, C. L. Chien. Longitudinal and transverse mag neto-impedance in amorphous Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 films. Ap- plied Physics Letters, 1995, 67(22): 3346-3348. [14] T. Kitoh, K. Mohri and T. Uchiyama. Asymme impedance effect in twisted amorphous wires for sensitive mag- netic sensors. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1995, 31(6): 3137- 3139. [15] C. G. asymmetric giant magneto impedance in field-annealed co-based amorphous ribbon. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 75(2114): 2114- 2116. [16] R. B. netoimpedance in Ni81Fe19/Fe50Mn50 exchange biased multilayer. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(4): Article ID: 042501. |